大纲
1.NodeSelectorSlot构建资源调用树
2.LogSlot和StatisticSlot采集资源的数据
3.Sentinel监听器模式的规则对象与规则管理
4.AuthoritySlot控制黑白名单权限
5.SystemSlot根据系统保护规则进行流控
1.NodeSelectorSlot构建资源调用树
(1)Entry的处理链的执行入口
(2)NodeSelectorSlot的源码
(3)Context对象中存储的资源调用树总结
(1)Entry的处理链的执行入口
每当一个线程处理包含某些资源的接口请求时,会调用SphU的entry()方法去创建并管控该接口中涉及的Entry资源访问对象。
在创建Entry资源访问对象的期间,会创建一个ResourceWrapper对象、一个Context对象、以及根据ResourceWrapper对象创建或获取一个ProcessorSlotChain对象,也就是把ProcessorSlotChain对象、Context对象与ResourceWrapper对象绑定到Entry对象中。- public class SphU {
- private static final Object[] OBJECTS0 = new Object[0];
- ...
- public static Entry entry(String name) throws BlockException {
- //调用CtSph.entry()方法创建一个Entry资源访问对象,默认的请求类型为OUT
- return Env.sph.entry(name, EntryType.OUT, 1, OBJECTS0);
- }
- }
- public class Env {
- //创建一个CtSph对象
- public static final Sph sph = new CtSph();
- static {
- InitExecutor.doInit();
- }
- }
- public class CtSph implements Sph {
- //Same resource will share the same ProcessorSlotChain}, no matter in which Context.
- //Same resource is that ResourceWrapper#equals(Object).
- private static volatile Map<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain> chainMap = new HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain>();
- ...
- @Override
- public Entry entry(String name, EntryType type, int count, Object... args) throws BlockException {
- //StringResourceWrapper是ResourceWrapper的子类,且StringResourceWrapper的构造方法默认了资源类型为COMMON
- StringResourceWrapper resource = new StringResourceWrapper(name, type);
- return entry(resource, count, args);
- }
-
- //Do all {@link Rule}s checking about the resource.
- public Entry entry(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) throws BlockException {
- //调用CtSph.entryWithPriority()方法,执行如下处理:
- //初始化Context -> 将Context与线程绑定 -> 初始化Entry -> 将Context和ResourceWrapper放入Entry中
- return entryWithPriority(resourceWrapper, count, false, args);
- }
-
- private Entry entryWithPriority(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws BlockException {
- //从当前线程中获取Context
- Context context = ContextUtil.getContext();
- if (context instanceof NullContext) {
- return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);
- }
- //如果没获取到Context
- if (context == null) {
- //Using default context.
- //创建一个名为sentinel_default_context的Context,并且与当前线程绑定
- context = InternalContextUtil.internalEnter(Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME);
- }
- //Global switch is close, no rule checking will do.
- if (!Constants.ON) {
- return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);
- }
- //调用CtSph.lookProcessChain()方法初始化处理链(处理器插槽链条)
- ProcessorSlot<Object> chain = lookProcessChain(resourceWrapper);
- if (chain == null) {
- return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);
- }
- //创建出一个Entry对象,将处理链(处理器插槽链条)、Context与Entry绑定
- //其中会将Entry的三个基础属性(封装在resourceWrapper里)以及当前Entry所属的Context作为参数传入CtEntry的构造方法
- Entry e = new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, chain, context);
- try {
- //处理链(处理器插槽链条)入口,负责采集数据,规则验证
- //调用DefaultProcessorSlotChain.entry()方法执行处理链每个节点的逻辑(数据采集+规则验证)
- chain.entry(context, resourceWrapper, null, count, prioritized, args);
- } catch (BlockException e1) {
- //规则验证失败,比如:被流控、被熔断降级、触发黑白名单等
- e.exit(count, args);
- throw e1;
- } catch (Throwable e1) {
- RecordLog.info("Sentinel unexpected exception", e1);
- }
- return e;
- }
- ...
-
- private final static class InternalContextUtil extends ContextUtil {
- static Context internalEnter(String name) {
- //调用ContextUtil.trueEnter()方法创建一个Context对象
- return trueEnter(name, "");
- }
-
- static Context internalEnter(String name, String origin) {
- return trueEnter(name, origin);
- }
- }
-
- //Get ProcessorSlotChain of the resource.
- //new ProcessorSlotChain will be created if the resource doesn't relate one.
- //Same resource will share the same ProcessorSlotChain globally, no matter in which Context.
- //Same resource is that ResourceWrapper#equals(Object).
- ProcessorSlot<Object> lookProcessChain(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) {
- ProcessorSlotChain chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper);
- if (chain == null) {
- synchronized (LOCK) {
- chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper);
- if (chain == null) {
- //Entry size limit.
- if (chainMap.size() >= Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE) {
- return null;
- }
- //调用SlotChainProvider.newSlotChain()方法初始化处理链(处理器插槽链条)
- chain = SlotChainProvider.newSlotChain();
- //写时复制
- Map<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain> newMap = new HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain>(chainMap.size() + 1);
- newMap.putAll(chainMap);
- newMap.put(resourceWrapper, chain);
- chainMap = newMap;
- }
- }
- }
- return chain;
- }
- }
- public class StringResourceWrapper extends ResourceWrapper {
- public StringResourceWrapper(String name, EntryType e) {
- //调用父类构造方法,且默认资源类型为COMMON
- super(name, e, ResourceTypeConstants.COMMON);
- }
- ...
- }
- //Utility class to get or create Context in current thread.
- //Each SphU.entry() should be in a Context.
- //If we don't invoke ContextUtil.enter() explicitly, DEFAULT context will be used.
- public class ContextUtil {
- //Store the context in ThreadLocal for easy access.
- //存放线程与Context的绑定关系
- //每个请求对应一个线程,每个线程绑定一个Context,所以每个请求对应一个Context
- private static ThreadLocal<Context> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
- //Holds all EntranceNode. Each EntranceNode is associated with a distinct context name.
- //以Context的name作为key,EntranceNode作为value缓存到HashMap中
- private static volatile Map<String, DefaultNode> contextNameNodeMap = new HashMap<>();
- private static final ReentrantLock LOCK = new ReentrantLock();
- private static final Context NULL_CONTEXT = new NullContext();
- ...
-
- //ContextUtil.trueEnter()方法会尝试从ThreadLocal获取一个Context对象
- //如果获取不到,再创建一个Context对象然后放入ThreadLocal中
- //入参name其实一般就是默认的Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME=sentinel_default_context
- //由于当前线程可能会涉及创建多个Entry资源访问对象,所以trueEnter()方法需要注意并发问题
- protected static Context trueEnter(String name, String origin) {
- //从ThreadLocal中获取当前线程绑定的Context对象
- Context context = contextHolder.get();
- //如果当前线程还没绑定Context对象,则初始化Context对象并且与当前线程进行绑定
- if (context == null) {
- //首先要获取或创建Context对象所需要的EntranceNode对象,EntranceNode会负责统计名字相同的Context下的指标数据
- //将全局缓存contextNameNodeMap赋值给一个临时变量localCacheNameMap
- //因为后续会对contextNameNodeMap的内容进行修改,所以这里需要将原来的contextNameNodeMap复制一份出来
- //从而避免后续对contextNameNodeMap的内容进行修改时,可能造成对接下来读取contextNameNodeMap内容的影响
- Map<String, DefaultNode> localCacheNameMap = contextNameNodeMap;
- //从缓存副本localCacheNameMap中获取EntranceNode
- //这个name其实一般就是默认的sentinel_default_context
- DefaultNode node = localCacheNameMap.get(name);
- //如果获取的EntranceNode为空
- if (node == null) {
- //为了防止缓存无限制地增长,导致内存占用过高,需要设置一个上限,只要超过上限,就直接返回NULL_CONTEXT
- if (localCacheNameMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {
- setNullContext();
- return NULL_CONTEXT;
- } else {
- //如果Context还没创建,缓存里也没有当前Context名称对应的EntranceNode,并且缓存数量尚未达到2000
- //那么就创建一个EntranceNode,创建EntranceNode时需要加锁,否则会有线程不安全问题
- //毕竟需要修改HashMap类型的contextNameNodeMap
- //通过加锁 + 缓存 + 写时复制更新缓存,避免并发情况下创建出多个EntranceNode对象
- //一个线程对应一个Context对象,多个线程对应多个Context对象
- //这些Context对象会使用ThreadLocal进行隔离,但它们的name默认都是sentinel_default_context
- //根据下面的代码逻辑:
- //多个线程(对应多个Context的name默认都是sentinel_default_context)会共用同一个EntranceNode
- //于是可知,多个Context对象会共用一个EntranceNode对象
- LOCK.lock();
- try {
- //从缓存中获取EntranceNode
- node = contextNameNodeMap.get(name);
- //对node进行Double Check
- //如果没获取到EntranceNode
- if (node == null) {
- if (contextNameNodeMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {
- setNullContext();
- return NULL_CONTEXT;
- } else {
- //创建EntranceNode,缓存到contextNameNodeMap当中
- node = new EntranceNode(new StringResourceWrapper(name, EntryType.IN), null);
- //Add entrance node.
- //将新创建的EntranceNode添加到ROOT中,ROOT就是每个Node的根结点
- Constants.ROOT.addChild(node);
- //写时复制,将新创建的EntranceNode添加到缓存中
- Map<String, DefaultNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(contextNameNodeMap.size() + 1);
- newMap.putAll(contextNameNodeMap);
- newMap.put(name, node);
- contextNameNodeMap = newMap;
- }
- }
- } finally {
- //解锁
- LOCK.unlock();
- }
- }
- }
- //此处可能会有多个线程同时执行到此处,并发创建多个Context对象
- //但这是允许的,因为一个请求对应一个Context,一个请求对应一个线程,所以一个线程本来就需要创建一个Context对象
- //初始化Context,将刚获取到或刚创建的EntranceNode放到Context的entranceNode属性中
- context = new Context(node, name);
- context.setOrigin(origin);
- //将创建出来的Context对象放入ThreadLocal变量contextHolder中,实现Context对象与当前线程的绑定
- contextHolder.set(context);
- }
- return context;
- }
- ...
- }
- public final class SlotChainProvider {
- private static volatile SlotChainBuilder slotChainBuilder = null;
- //The load and pick process is not thread-safe,
- //but it's okay since the method should be only invoked via CtSph.lookProcessChain() under lock.
- public static ProcessorSlotChain newSlotChain() {
- //如果存在,则直接返回
- if (slotChainBuilder != null) {
- return slotChainBuilder.build();
- }
- //Resolve the slot chain builder SPI.
- //通过SPI机制初始化SlotChainBuilder
- slotChainBuilder = SpiLoader.of(SlotChainBuilder.class).loadFirstInstanceOrDefault();
- if (slotChainBuilder == null) {
- //Should not go through here.
- RecordLog.warn("[SlotChainProvider] Wrong state when resolving slot chain builder, using default");
- slotChainBuilder = new DefaultSlotChainBuilder();
- } else {
- RecordLog.info("[SlotChainProvider] Global slot chain builder resolved: {}", slotChainBuilder.getClass().getCanonicalName());
- }
- return slotChainBuilder.build();
- }
-
- private SlotChainProvider() {
-
- }
- }
- @Spi(isDefault = true)
- public class DefaultSlotChainBuilder implements SlotChainBuilder {
- @Override
- public ProcessorSlotChain build() {
- //创建一个DefaultProcessorSlotChain对象实例
- ProcessorSlotChain chain = new DefaultProcessorSlotChain();
- //通过SPI机制加载责任链的节点ProcessorSlot实现类
- //然后按照@Spi注解的order属性进行排序并进行实例化
- //最后将ProcessorSlot实例放到sortedSlotList中
- List<ProcessorSlot> sortedSlotList = SpiLoader.of(ProcessorSlot.class).loadInstanceListSorted();
- //遍历已排好序的ProcessorSlot集合
- for (ProcessorSlot slot : sortedSlotList) {
- //安全检查,防止业务系统也写了一个SPI文件,但没按规定继承AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot
- if (!(slot instanceof AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot)) {
- RecordLog.warn("The ProcessorSlot(" + slot.getClass().getCanonicalName() + ") is not an instance of AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot, can't be added into ProcessorSlotChain");
- continue;
- }
- //调用DefaultProcessorSlotChain.addLast()方法构建单向链表
- //将责任链的节点ProcessorSlot实例放入DefaultProcessorSlotChain中
- chain.addLast((AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?>) slot);
- }
- //返回单向链表
- return chain;
- }
- }
当一个线程调用SphU的entry()方法创建完与接口相关的Entry对象后,就会调用DefaultProcessorSlotChain的entry()方法执行处理链节点的逻辑。因为NodeSelectorSlot是Entry的处理链ProcessorSlotChain的第一个节点,所以接着会调用NodeSelectorSlot的entry()方法。由于处理链中紧接着NodeSelectorSlot的下一个节点是ClusterBuilderSlot,所以执行完NodeSelectorSlot的entry()方法后,会接着执行ClusterBuilderSlot的entry()方法。- public class DefaultProcessorSlotChain extends ProcessorSlotChain {
- ...
- @Override
- public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object t, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
- //默认情况下会调用处理链的第一个节点NodeSelectorSlot的transformEntry()方法
- first.transformEntry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<T> implements ProcessorSlot<T> {
- ...
- void transformEntry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object o, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
- T t = (T)o;
- entry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
- }
- ...
- }
NodeSelectorSlot和ClusterBuilderSlot会一起构建Context的资源调用树,资源调用树的作用其实就是用来统计资源的调用数据。
在一个Context对象实例的资源调用树上主要会有如下三类节点:DefaultNode、EntranceNode、ClusterNode,分别对应于:单机里的资源维度、接口维度、集群中的资源维度。
其中DefaultNode会统计名字相同的Context下的某个资源的调用数据,EntranceNode会统计名字相同的Context下的全部资源的调用数据,ClusterNode会统计某个资源在全部Context下的调用数据。
在执行NodeSelectorSlot的entry()方法时,首先会从缓存(NodeSelectorSlot.map属性)中获取一个DefaultNode对象。如果获取不到,再通过DCL机制创建一个DefaultNode对象并更新缓存。其中缓存的key是Context的name,value是DefaultNode对象。由于默认情况下多个线程对应的Context的name都相同,所以多个线程访问同一资源时使用的DefaultNode对象也一样。
在执行ClusterBuilderSlot的entry()方法时,首先会判断缓存是否为null,若是则创建一个ClusterNode对象,然后再将ClusterNode对象设置到DefaultNode对象的clusterNode属性中。
由DefaultNode、EntranceNode、ClusterNode构成的资源调用树:因为DefaultNode是和资源ResourceWrapper以及Context挂钩的,所以DefaultNode应该添加到EntranceNode中。因为ClusterNode和资源挂钩,而不和Context挂钩,所以ClusterNode应该添加到DefaultNode中。
具体的资源调用树构建源码如下:- //This class will try to build the calling traces via:
- //adding a new DefaultNode if needed as the last child in the context.
- //the context's last node is the current node or the parent node of the context.
- //setting itself to the context current node.
- //It works as follow:
- // ContextUtil.enter("entrance1", "appA");
- // Entry nodeA = SphU.entry("nodeA");
- // if (nodeA != null) {
- // nodeA.exit();
- // }
- // ContextUtil.exit();
- //Above code will generate the following invocation structure in memory:
- // machine-root
- // /
- // /
- // EntranceNode1
- // /
- // /
- // DefaultNode(nodeA)- - - - - -> ClusterNode(nodeA);
- //Here the EntranceNode represents "entrance1" given by ContextUtil.enter("entrance1", "appA").
- //Both DefaultNode(nodeA) and ClusterNode(nodeA) holds statistics of "nodeA", which is given by SphU.entry("nodeA").
- //The ClusterNode is uniquely identified by the ResourceId;
- //The DefaultNode is identified by both the resource id and {@link Context}.
- //In other words, one resource id will generate multiple DefaultNode for each distinct context,
- //but only one ClusterNode.
- //the following code shows one resource id in two different context:
- // ContextUtil.enter("entrance1", "appA");
- // Entry nodeA = SphU.entry("nodeA");
- // if (nodeA != null) {
- // nodeA.exit();
- // }
- // ContextUtil.exit();
- // ContextUtil.enter("entrance2", "appA");
- // nodeA = SphU.entry("nodeA");
- // if (nodeA != null) {
- // nodeA.exit();
- // }
- // ContextUtil.exit();
- //Above code will generate the following invocation structure in memory:
- // machine-root
- // / \
- // / \
- // EntranceNode1 EntranceNode2
- // / \
- // / \
- // DefaultNode(nodeA) DefaultNode(nodeA)
- // | |
- // +- - - - - - - - - - +- - - - - - -> ClusterNode(nodeA);
- //As we can see, two DefaultNode are created for "nodeA" in two context,
- //but only one ClusterNode is created.
- //We can also check this structure by calling: http://localhost:8719/tree?type=root
- @Spi(isSingleton = false, order = Constants.ORDER_NODE_SELECTOR_SLOT)
- public class NodeSelectorSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<Object> {
- //DefaultNodes of the same resource in different context.
- //缓存map以Context的name为key,DefaultNode为value
- //由于默认情况下多个线程对应的Context的name都相同,所以多个线程访问资源时使用的DefaultNode也一样
- private volatile Map<String, DefaultNode> map = new HashMap<String, DefaultNode>(10);
-
- @Override
- public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
- //It's interesting that we use context name rather resource name as the map key.
- //Remember that same resource will share the same ProcessorSlotChain globally, no matter in which context.
- //Same resource is that ResourceWrapper#equals(Object).
- //So if code goes into entry(Context, ResourceWrapper, DefaultNode, int, Object...),
- //the resource name must be same but context name may not.
-
- //If we use SphU.entry(String resource)} to enter same resource in different context,
- //using context name as map key can distinguish the same resource.
- //In this case, multiple DefaultNodes will be created of the same resource name,
- //for every distinct context (different context name) each.
-
- //Consider another question. One resource may have multiple DefaultNode,
- //so what is the fastest way to get total statistics of the same resource?
- //The answer is all DefaultNodes with same resource name share one ClusterNode.
- //See ClusterBuilderSlot for detail.
- //先从缓存中获取
- DefaultNode node = map.get(context.getName());
- if (node == null) {
- //使用DCL机制,即Double Check + Lock机制
- synchronized (this) {
- node = map.get(context.getName());
- if (node == null) {
- //每个线程访问Entry时,都会调用CtSph.entry()方法创建一个ResourceWrapper对象
- //下面根据ResourceWrapper创建一个DefaultNode对象
- node = new DefaultNode(resourceWrapper, null);
- //写时复制更新缓存map
- HashMap<String, DefaultNode> cacheMap = new HashMap<String, DefaultNode>(map.size());
- cacheMap.putAll(map);
- cacheMap.put(context.getName(), node);
- map = cacheMap;
- //Build invocation tree
- //首先会调用context.getLastNode()方法,获取到的是Context.entranceNode属性即一个EntranceNode对象
- //EntranceNode对象是在执行ContextUtil.trueEnter()方法创建Context对象实例时添加到Context对象中的
- //然后会将刚创建的DefaultNode对象添加到EntranceNode对象的childList列表中
- ((DefaultNode) context.getLastNode()).addChild(node);
- }
- }
- }
- //设置Context的curNode属性为当前获取到或新创建的DefaultNode对象
- context.setCurNode(node);
- //触发执行下一个ProcessorSlot,即ClusterBuilderSlot
- fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) {
- fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);
- }
- }
- //This slot maintains resource running statistics (response time, qps, thread count, exception),
- //and a list of callers as well which is marked by ContextUtil.enter(String origin).
- //One resource has only one cluster node, while one resource can have multiple default nodes.
- @Spi(isSingleton = false, order = Constants.ORDER_CLUSTER_BUILDER_SLOT)
- public class ClusterBuilderSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<DefaultNode> {
- //Remember that same resource will share the same ProcessorSlotChain globally, no matter in which context.
- //Same resource is that ResourceWrapper#equals(Object).
- //So if code goes into entry(Context, ResourceWrapper, DefaultNode, int, boolean, Object...),
- //the resource name must be same but context name may not.
-
- //To get total statistics of the same resource in different context,
- //same resource shares the same ClusterNode} globally.
- //All ClusterNodes are cached in this map.
- //The longer the application runs, the more stable this mapping will become.
- //so we don't concurrent map but a lock.
- //as this lock only happens at the very beginning while concurrent map will hold the lock all the time.
- private static volatile Map<ResourceWrapper, ClusterNode> clusterNodeMap = new HashMap<>();
- private static final Object lock = new Object();
- private volatile ClusterNode clusterNode = null;
- @Override
- public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
- if (clusterNode == null) {
- //使用DCL机制,即Double Check + Lock机制
- synchronized (lock) {
- if (clusterNode == null) {
- //Create the cluster node.
- //创建ClusterNode对象
- clusterNode = new ClusterNode(resourceWrapper.getName(), resourceWrapper.getResourceType());
- HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ClusterNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(Math.max(clusterNodeMap.size(), 16));
- newMap.putAll(clusterNodeMap);
- newMap.put(node.getId(), clusterNode);
- clusterNodeMap = newMap;
- }
- }
- }
-
- //设置DefaultNode的clusterNode属性为获取到的ClusterNode对象
- node.setClusterNode(clusterNode);
- //if context origin is set, we should get or create a new {@link Node} of the specific origin.
- if (!"".equals(context.getOrigin())) {
- Node originNode = node.getClusterNode().getOrCreateOriginNode(context.getOrigin());
- context.getCurEntry().setOriginNode(originNode);
- }
- //执行下一个ProcessorSlot
- fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
- }
- @Override
- public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) {
- fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);
- }
- ...
- }
其实Context对象的属性entranceNode就代表了一棵资源调用树。
首先,在调用ContextUtil的trueEnter()方法创建Context对象实例时,便会创建一个EntranceNode对象并赋值给Context的entranceNode属性,以及调用Constants.ROOT的addChild()方法,将这个EntranceNode对象放入Constants.ROOT的childList列表中。
然后,执行NodeSelectorSlot的entry()方法时,便会创建一个DefaultNode对象。该DefaultNode对象会被添加到Context.entranceNode的childList列表中,也就是前面创建的EntranceNode对象的childList列表中。
接着,执行ClusterBuilderSlot的entry()方法时,便会创建一个ClusterNode对象,该ClusterNode对象会赋值给前面DefaultNode对象中的clusterNode属性。
至此,便构建完Context下的资源调用树了。Constants.ROOT的childList里会存放多个EntranceNode对象,每个EntranceNode对象的childList里会存放多个DefaultNode对象,而每个DefaultNode对象会指向一个ClusterNode对象。- //This class holds metadata of current invocation:
- //the EntranceNode: the root of the current invocation tree.
- //the current Entry: the current invocation point.
- //the current Node: the statistics related to the Entry.
- //the origin: The origin is useful when we want to control different invoker/consumer separately.
- //Usually the origin could be the Service Consumer's app name or origin IP.
- //Each SphU.entry() or SphO.entry() should be in a Context,
- //if we don't invoke ContextUtil.enter() explicitly, DEFAULT context will be used.
- //A invocation tree will be created if we invoke SphU.entry() multi times in the same context.
- //Same resource in different context will count separately, see NodeSelectorSlot.
- public class Context {
- //Context name.
- private final String name;
- //The entrance node of current invocation tree.
- private DefaultNode entranceNode;
- //Current processing entry.
- private Entry curEntry;
- //The origin of this context (usually indicate different invokers, e.g. service consumer name or origin IP).
- private String origin = "";
- ...
- public Context(DefaultNode entranceNode, String name) {
- this(name, entranceNode, false);
- }
-
- public Context(String name, DefaultNode entranceNode, boolean async) {
- this.name = name;
- this.entranceNode = entranceNode;
- this.async = async;
- }
-
- //Get the parent Node of the current.
- public Node getLastNode() {
- if (curEntry != null && curEntry.getLastNode() != null) {
- return curEntry.getLastNode();
- } else {
- return entranceNode;
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class ContextUtil {
- //以Context的name作为key,EntranceNode作为value缓存所有的EntranceNode到HashMap中
- private static volatile Map<String, DefaultNode> contextNameNodeMap = new HashMap<>();
- ...
- protected static Context trueEnter(String name, String origin) {
- ...
- //从缓存中获取EntranceNode
- DefaultNode node = contextNameNodeMap.get(name);
- ...
- //创建EntranceNode,缓存到contextNameNodeMap当中
- node = new EntranceNode(new StringResourceWrapper(name, EntryType.IN), null);
- //将新创建的EntranceNode添加到ROOT中,ROOT就是每个Node的根结点
- Constants.ROOT.addChild(node);
- ...
- //初始化Context,将刚获取到或刚创建的EntranceNode放到Context的entranceNode属性中
- context = new Context(node, name);
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
- public final class Constants {
- ...
- //Global ROOT statistic node that represents the universal parent node.
- public final static DefaultNode ROOT = new EntranceNode(
- new StringResourceWrapper(ROOT_ID, EntryType.IN),
- new ClusterNode(ROOT_ID, ResourceTypeConstants.COMMON)
- );
- ...
- }
- //A Node used to hold statistics for specific resource name in the specific context.
- //Each distinct resource in each distinct Context will corresponding to a DefaultNode.
- //This class may have a list of sub DefaultNodes.
- //Child nodes will be created when calling SphU.entry() or SphO.entry() multiple times in the same Context.
- public class DefaultNode extends StatisticNode {
- //The resource associated with the node.
- private ResourceWrapper id;
- //The list of all child nodes.
- private volatile Set<Node> childList = new HashSet<>();
- //Associated cluster node.
- private ClusterNode clusterNode;
- ...
-
- //Add child node to current node.
- public void addChild(Node node) {
- if (node == null) {
- RecordLog.warn("Trying to add null child to node <{}>, ignored", id.getName());
- return;
- }
- if (!childList.contains(node)) {
- synchronized (this) {
- if (!childList.contains(node)) {
- Set<Node> newSet = new HashSet<>(childList.size() + 1);
- newSet.addAll(childList);
- newSet.add(node);
- childList = newSet;
- }
- }
- RecordLog.info("Add child <{}> to node <{}>", ((DefaultNode)node).id.getName(), id.getName());
- }
- }
-
- //Reset the child node list.
- public void removeChildList() {
- this.childList = new HashSet<>();
- }
- ...
- }
- @Spi(isSingleton = false, order = Constants.ORDER_NODE_SELECTOR_SLOT)
- public class NodeSelectorSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<Object> {
- //DefaultNodes of the same resource in different context.
- //缓存map以Context的name为key,DefaultNode为value
- //由于默认情况下多个线程对应的Context的name都相同,所以多个线程访问资源时使用的DefaultNode也一样
- private volatile Map<String, DefaultNode> map = new HashMap<String, DefaultNode>(10);
- ...
-
- @Override
- public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
- ...
- //先从缓存中获取
- DefaultNode node = map.get(context.getName());
- ...
- //下面根据ResourceWrapper创建一个DefaultNode对象
- node = new DefaultNode(resourceWrapper, null);
- ...
- //Build invocation tree
- //首先会调用context.getLastNode()方法,获取到的是Context.entranceNode属性即一个EntranceNode对象
- //EntranceNode对象是在执行ContextUtil.trueEnter()方法创建Context对象实例时添加到Context对象中的
- //然后会将刚创建的DefaultNode对象添加到EntranceNode对象的childList列表中
- ((DefaultNode) context.getLastNode()).addChild(node);
- ...
- //执行下一个ProcessorSlot
- fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
- }
- ...
- }
- @Spi(isSingleton = false, order = Constants.ORDER_CLUSTER_BUILDER_SLOT)
- public class ClusterBuilderSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<DefaultNode> {
- ...
- private volatile ClusterNode clusterNode = null;
-
- @Override
- public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
- ...
- //创建ClusterNode对象
- clusterNode = new ClusterNode(resourceWrapper.getName(), resourceWrapper.getResourceType());
- ...
- //设置DefaultNode的clusterNode属性为获取到的ClusterNode对象
- node.setClusterNode(clusterNode);
- ...
- //执行下一个ProcessorSlot
- fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
- }
- ...
- }
- //资源调用树的示例如下所示:
- // machine-root
- // / \
- // / \
- // EntranceNode1 EntranceNode2
- // / \
- // / \
- // DefaultNode(nodeA) DefaultNode(nodeA)
- // | |
- // +- - - - - - - - - - +- - - - - - -> ClusterNode(nodeA);
- //其中,machine-root中的childList里会有很多个EntranceNode对象
- //EntranceNode对象中的childList里又会有很多个DefaultNode对象
- //每个DefaultNode对象下都会指向一个ClusterNode对象
一个线程对应一个ResourceWrapper对象实例,一个线程对应一个Context对象实例。如果ResourceWrapper对象相同,则会共用一个ProcessorSlotChain实例。如果ResourceWrapper对象相同,则也会共用一个ClusterNode实例。如果Context对象的名字相同,则会共用一个EntranceNode对象实例。如果Context对象的名字相同,则也会共用一个DefaultNode对象实例。- //每个请求对应一个线程,每个线程绑定一个Context,所以每个请求对应一个Context
- private static ThreadLocal<Context> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
- //以Context的name作为key,EntranceNode作为value缓存所有的EntranceNode到HashMap中
- private static volatile Map<String, EntranceNode> contextNameNodeMap = new HashMap<>();
- //Same resource will share the same ProcessorSlotChain}, no matter in which Context.
- //Same resource is that ResourceWrapper#equals(Object).
- private static volatile Map<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain> chainMap = new HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain>();
- //DefaultNodes of the same resource in different context.
- //以Context的name作为key,DefaultNode作为value
- //由于默认情况下多个线程对应的Context的name都相同,所以多个线程访问资源时使用的DefaultNode也一样
- private volatile Map<String, DefaultNode> map = new HashMap<String, DefaultNode>(10);
-
- //To get total statistics of the same resource in different context,
- //same resource shares the same ClusterNode globally.
- //All ClusterNodes are cached in this map.
- private static volatile Map<ResourceWrapper, ClusterNode> clusterNodeMap = new HashMap<>();
2.LogSlot和StatisticSlot采集资源的数据
(1)LogSlot的源码
(2)StatisticSlot的源码
(3)记录资源在不同维度下的调用数据
(1)LogSlot的源码
LogSlot用于记录异常请求日志,以便于故障排查。也就是当出现BlockException异常时,调用EagleEyeLogUtil的log()方法将日志写到sentinel-block.log文件中。- //A ProcessorSlot that is response for logging block exceptions to provide concrete logs for troubleshooting.
- @Spi(order = Constants.ORDER_LOG_SLOT)
- public class LogSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<DefaultNode> {
- @Override
- public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
- try {
- //调用下一个ProcessorSlot
- fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, obj, count, prioritized, args);
- } catch (BlockException e) {
- //被流控或者熔断降级后打印log日志
- EagleEyeLogUtil.log(resourceWrapper.getName(), e.getClass().getSimpleName(), e.getRuleLimitApp(), context.getOrigin(), e.getRule().getId(), count);
- throw e;
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- RecordLog.warn("Unexpected entry exception", e);
- }
- }
- @Override
- public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) {
- try {
- //调用下一个ProcessorSlot
- fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- RecordLog.warn("Unexpected entry exit exception", e);
- }
- }
- }
- public class EagleEyeLogUtil {
- public static final String FILE_NAME = "sentinel-block.log";
- private static StatLogger statLogger;
- static {
- String path = LogBase.getLogBaseDir() + FILE_NAME;
- statLogger = EagleEye.statLoggerBuilder("sentinel-block-log")
- .intervalSeconds(1)
- .entryDelimiter('|')
- .keyDelimiter(',')
- .valueDelimiter(',')
- .maxEntryCount(6000)
- .configLogFilePath(path)
- .maxFileSizeMB(300)
- .maxBackupIndex(3)
- .buildSingleton();
- }
-
- public static void log(String resource, String exceptionName, String ruleLimitApp, String origin, Long ruleId, int count) {
- String ruleIdString = StringUtil.EMPTY;
- if (ruleId != null) {
- ruleIdString = String.valueOf(ruleId);
- }
- statLogger.stat(resource, exceptionName, ruleLimitApp, origin, ruleIdString).count(count);
- }
- }
StatisticSlot用于统计资源的调用数据,如请求成功数、请求失败数、响应时间等。
注意:开始对请求进行规则验证时,需要调用SphU的entry()方法。完成对请求的规则验证后,也需要调用Entry的exit()方法。- //A processor slot that dedicates to real time statistics.
- //When entering this slot, we need to separately count the following information:
- //ClusterNode: total statistics of a cluster node of the resource ID.
- //Origin node: statistics of a cluster node from different callers/origins.
- //DefaultNode: statistics for specific resource name in the specific context.
- //Finally, the sum statistics of all entrances.
- @Spi(order = Constants.ORDER_STATISTIC_SLOT)
- public class StatisticSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<DefaultNode> {
- @Override
- public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
- try {
- //Do some checking.
- //执行下一个ProcessorSlot,先进行规则验证等
- fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
- //Request passed, add thread count and pass count.
- //如果通过了后面ProcessorSlot的验证
- //则将处理当前资源resourceWrapper的线程数 + 1 以及 将对当前资源resourceWrapper的成功请求数 + 1
- node.increaseThreadNum();
- node.addPassRequest(count);
- if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
- //Add count for origin node.
- context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();
- context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().addPassRequest(count);
- }
- if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
- //Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
- Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();
- Constants.ENTRY_NODE.addPassRequest(count);
- }
- //Handle pass event with registered entry callback handlers.
- for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
- handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
- }
- } catch (PriorityWaitException ex) {
- node.increaseThreadNum();
- if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
- //Add count for origin node.
- context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();
- }
- if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
- //Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
- Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();
- }
-
- //Handle pass event with registered entry callback handlers.
- for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
- handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
- }
- } catch (BlockException e) {//捕获BlockException
- //Blocked, set block exception to current entry.
- context.getCurEntry().setBlockError(e);
- //Add block count.
- //如果规则验证失败,则将BlockQps+1
- node.increaseBlockQps(count);
- if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
- context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseBlockQps(count);
- }
- if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
- //Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
- Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseBlockQps(count);
- }
- //Handle block event with registered entry callback handlers.
- for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
- handler.onBlocked(e, context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
- }
- throw e;
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- //Unexpected internal error, set error to current entry.
- context.getCurEntry().setError(e);
- throw e;
- }
- }
-
- //开始对请求进行规则验证时,需要调用SphU.entry()方法
- //完成对请求的规则验证后,也需要调用Entry.exit()方法
- @Override
- public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) {
- Node node = context.getCurNode();
- if (context.getCurEntry().getBlockError() == null) {
- //Calculate response time (use completeStatTime as the time of completion).
- //获取系统当前时间
- long completeStatTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
- context.getCurEntry().setCompleteTimestamp(completeStatTime);
- //计算响应时间 = 系统当前事件 - 根据资源resourceWrapper创建Entry资源访问对象时的时间
- long rt = completeStatTime - context.getCurEntry().getCreateTimestamp();
- Throwable error = context.getCurEntry().getError();
- //Record response time and success count.
- //记录响应时间等信息
- recordCompleteFor(node, count, rt, error);
- recordCompleteFor(context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode(), count, rt, error);
- if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
- recordCompleteFor(Constants.ENTRY_NODE, count, rt, error);
- }
- }
- //Handle exit event with registered exit callback handlers.
- Collection<ProcessorSlotExitCallback> exitCallbacks = StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getExitCallbacks();
- for (ProcessorSlotExitCallback handler : exitCallbacks) {
- handler.onExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);
- }
-
- fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);
- }
- private void recordCompleteFor(Node node, int batchCount, long rt, Throwable error) {
- if (node == null) {
- return;
- }
- node.addRtAndSuccess(rt, batchCount);
- node.decreaseThreadNum();
- if (error != null && !(error instanceof BlockException)) {
- node.increaseExceptionQps(batchCount);
- }
- }
- }
一.如何统计单机里某个资源的调用数据
二.如何统计所有资源的调用数据即接口调用数据
三.如何统计集群中某个资源的调用数据
一.如何统计单机里某个资源的调用数据
由于DefaultNode会统计名字相同的Context下的某个资源的调用数据,它是按照单机里的资源维度进行调用数据统计的,所以在StatisticSlot的entry()方法中,会调用DefaultNode的方法来进行统计。- //A Node used to hold statistics for specific resource name in the specific context.
- //Each distinct resource in each distinct Context will corresponding to a DefaultNode.
- //This class may have a list of sub DefaultNodes.
- //Child nodes will be created when calling SphU.entry() or SphO.entry() multiple times in the same Context.
- public class DefaultNode extends StatisticNode {
- //The resource associated with the node.
- private ResourceWrapper id;
- //Associated cluster node.
- private ClusterNode clusterNode;
- ...
-
- @Override
- public void increaseThreadNum() {
- super.increaseThreadNum();
- this.clusterNode.increaseThreadNum();
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addPassRequest(int count) {
- super.addPassRequest(count);
- this.clusterNode.addPassRequest(count);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void increaseBlockQps(int count) {
- super.increaseBlockQps(count);
- this.clusterNode.increaseBlockQps(count);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addRtAndSuccess(long rt, int successCount) {
- super.addRtAndSuccess(rt, successCount);
- this.clusterNode.addRtAndSuccess(rt, successCount);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void decreaseThreadNum() {
- super.decreaseThreadNum();
- this.clusterNode.decreaseThreadNum();
- }
- ...
- }
- public class StatisticNode implements Node {
- //The counter for thread count.
- private LongAdder curThreadNum = new LongAdder();
- //Holds statistics of the recent INTERVAL milliseconds.
- //The INTERVAL is divided into time spans by given sampleCount.
- private transient volatile Metric rollingCounterInSecond = new ArrayMetric(SampleCountProperty.SAMPLE_COUNT, IntervalProperty.INTERVAL);
- //Holds statistics of the recent 60 seconds.
- //The windowLengthInMs is deliberately set to 1000 milliseconds,
- //meaning each bucket per second, in this way we can get accurate statistics of each second.
- private transient Metric rollingCounterInMinute = new ArrayMetric(60, 60 * 1000, false);
- ...
-
- @Override
- public void increaseThreadNum() {
- curThreadNum.increment();
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addPassRequest(int count) {
- rollingCounterInSecond.addPass(count);
- rollingCounterInMinute.addPass(count);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void increaseBlockQps(int count) {
- rollingCounterInSecond.addBlock(count);
- rollingCounterInMinute.addBlock(count);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addRtAndSuccess(long rt, int successCount) {
- rollingCounterInSecond.addSuccess(successCount);
- rollingCounterInSecond.addRT(rt);
- rollingCounterInMinute.addSuccess(successCount);
- rollingCounterInMinute.addRT(rt);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void decreaseThreadNum() {
- curThreadNum.decrement();
- }
- ...
- }
由于EntranceNode会统计名字相同的Context下的全部资源的调用数据,它是按接口维度来统计调用数据的,即统计接口下所有资源的调用情况,所以可以通过遍历EntranceNode的childList来统计接口的调用数据。- //A Node represents the entrance of the invocation tree.
- //One Context will related to a EntranceNode,
- //which represents the entrance of the invocation tree.
- //New EntranceNode will be created if current context does't have one.
- //Note that same context name will share same EntranceNode globally.
- public class EntranceNode extends DefaultNode {
- public EntranceNode(ResourceWrapper id, ClusterNode clusterNode) {
- super(id, clusterNode);
- }
-
- @Override
- public double avgRt() {
- double total = 0;
- double totalQps = 0;
- for (Node node : getChildList()) {
- total += node.avgRt() * node.passQps();
- totalQps += node.passQps();
- }
- return total / (totalQps == 0 ? 1 : totalQps);
- }
-
- @Override
- public double blockQps() {
- double blockQps = 0;
- for (Node node : getChildList()) {
- blockQps += node.blockQps();
- }
- return blockQps;
- }
-
- @Override
- public long blockRequest() {
- long r = 0;
- for (Node node : getChildList()) {
- r += node.blockRequest();
- }
- return r;
- }
-
- @Override
- public int curThreadNum() {
- int r = 0;
- for (Node node : getChildList()) {
- r += node.curThreadNum();
- }
- return r;
- }
-
- @Override
- public double totalQps() {
- double r = 0;
- for (Node node : getChildList()) {
- r += node.totalQps();
- }
- return r;
- }
-
- @Override
- public double successQps() {
- double r = 0;
- for (Node node : getChildList()) {
- r += node.successQps();
- }
- return r;
- }
-
- @Override
- public double passQps() {
- double r = 0;
- for (Node node : getChildList()) {
- r += node.passQps();
- }
- return r;
- }
-
- @Override
- public long totalRequest() {
- long r = 0;
- for (Node node : getChildList()) {
- r += node.totalRequest();
- }
- return r;
- }
-
- @Override
- public long totalPass() {
- long r = 0;
- for (Node node : getChildList()) {
- r += node.totalPass();
- }
- return r;
- }
- }
由于ClusterNode会统计某个资源在全部Context下的调用数据,它是按照集群中的资源维度进行调用数据统计的,而StatisticSlot的entry()调用DefaultNode的方法统计单机下的资源时,会顺便调用ClusterNode的方法来统计集群下的资源调用,所以通过ClusterNode就可以获取集群中某个资源的调用数据。- //A Node used to hold statistics for specific resource name in the specific context.
- //Each distinct resource in each distinct Context will corresponding to a DefaultNode.
- //This class may have a list of sub DefaultNodes.
- //Child nodes will be created when calling SphU.entry() or SphO.entry() multiple times in the same Context.
- public class DefaultNode extends StatisticNode {
- //The resource associated with the node.
- private ResourceWrapper id;
- //Associated cluster node.
- private ClusterNode clusterNode;
- ...
-
- @Override
- public void increaseThreadNum() {
- super.increaseThreadNum();
- this.clusterNode.increaseThreadNum();
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addPassRequest(int count) {
- super.addPassRequest(count);
- this.clusterNode.addPassRequest(count);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void increaseBlockQps(int count) {
- super.increaseBlockQps(count);
- this.clusterNode.increaseBlockQps(count);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addRtAndSuccess(long rt, int successCount) {
- super.addRtAndSuccess(rt, successCount);
- this.clusterNode.addRtAndSuccess(rt, successCount);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void decreaseThreadNum() {
- super.decreaseThreadNum();
- this.clusterNode.decreaseThreadNum();
- }
- ...
- }
3.Sentinel监听器模式的规则对象与规则管理
(1)Sentinel的规则对象
(2)Sentinel的规则管理
(1)Sentinel的规则对象
一.Sentinel中的规则其实就是配置
二.规则接口Rule和抽象父类AbstractRule及其具体实现类
一.Sentinel中的规则其实就是配置
黑白名单控制规则:例如需要设置一份配置,确定哪些请求属于黑名单、哪些请求属于白名单,那么这份配置就是黑白名单控制规则。
系统负载自适应规则:例如需要设置当CPU使用率达到90%时,系统就不再接受新请求以防止系统崩溃,那么这个90%的CPU使用率阈值就是系统负载自适应规则。
流量控制规则:例如需要设置单机QPS最高为100,那么这个单机限流100QPS便是流量控制规则。
熔断降级规则:例如需要设置当错误比例在1秒内超过10次时,系统自动触发熔断降级,那么这个1秒内超过10次的错误比例就是熔断降级规则。
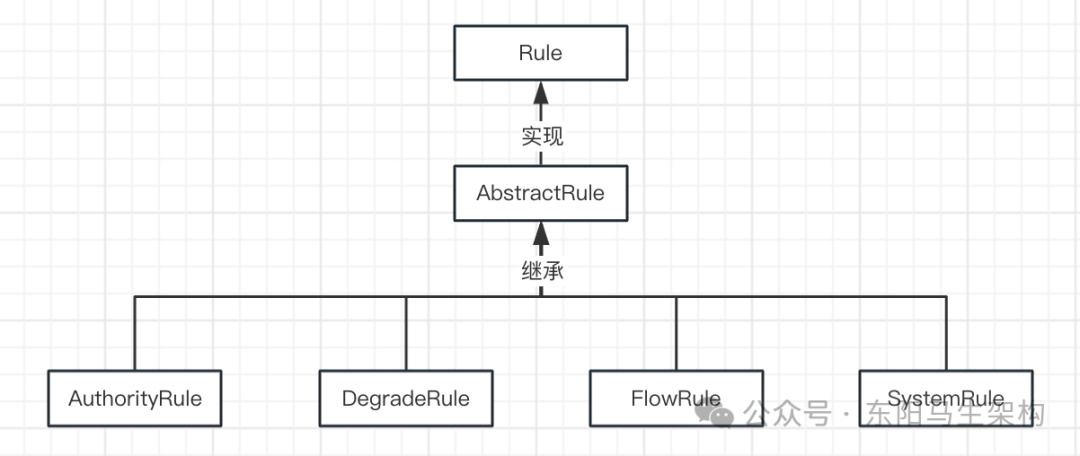
二.规则接口Rule和抽象父类AbstractRule及其具体实现类
首先规则与资源是紧密关联的,规则会对资源起作用,因此规则接口Rule需要一个获取资源的方法getResource()。
然后每一条具体的规则都应继承抽象父类AbstractRule并具备三个字段:规则id、资源name以及针对来源limitApp。其中针对来源指的是诸如黑名单值、白名单值等,默认是default。- //Base interface of all rules.
- public interface Rule {
- //Get target resource of this rule.
- //获取当前规则起作用的目标资源
- String getResource();
- }
- //Abstract rule entity. AbstractRule是实现了规则接口Rule的抽象规则类
- public abstract class AbstractRule implements Rule {
- //rule id. 规则id
- private Long id;
- //Resource name. 资源名称
- private String resource;
- //针对来源,默认是default
- //多个来源使用逗号隔开,比如黑名单规则,限制userId是1和3的访问,那么就设置limitApp为"1,3"
- //Application name that will be limited by origin.
- //The default limitApp is default, which means allowing all origin apps.
- //For authority rules, multiple origin name can be separated with comma (',').
- private String limitApp;
-
- public Long getId() {
- return id;
- }
-
- public AbstractRule setId(Long id) {
- this.id = id;
- return this;
- }
-
- @Override
- public String getResource() {
- return resource;
- }
-
- public AbstractRule setResource(String resource) {
- this.resource = resource;
- return this;
- }
-
- public String getLimitApp() {
- return limitApp;
- }
-
- public AbstractRule setLimitApp(String limitApp) {
- this.limitApp = limitApp;
- return this;
- }
- ...
- }
- //Authority rule is designed for limiting by request origins.
- public class AuthorityRule extends AbstractRule {
- ...
- }
- public class SystemRule extends AbstractRule {
- ...
- }
- public class FlowRule extends AbstractRule {
- ...
- }
- public class DegradeRule extends AbstractRule {
- ...
- }
(2)Sentinel的规则管理
一.PropertyListener监听器接口及其实现类
二.SentinelProperty监听器接口管理所有PropertyListener子类
三.DynamicSentinelProperty会触发监听器PropertyListener的回调
一.PropertyListener监听器接口及其实现类
为了感知规则Rule的变化,需要一个负责监听规则变化的类,也就是需要一个监听器来监听规则Rule的变化,这个监听器就是PropertyListener。
PropertyListener是一个接口,它定义了两个方法:方法一是首次加载规则时触发的回调方法configLoad(),方法二是规则变更时触发的回调方法configUpdate()。
PropertyListener接口使用了泛型T而不是规则接口Rule来定义,是因为除了规则的变化需要监听器监听外,还有其他场景也需要监听。
PropertyListener接口的具体实现类有:- AuthorityRuleManager.RulePropertyListener
- FlowRuleManager.FlowPropertyListener
- DegradeRuleManager.RulePropertyListener
- SystemRuleManager.SystemPropertyListener
- //This class holds callback method when SentinelProperty.updateValue(Object) need inform the listener.
- public interface PropertyListener<T> {
- //Callback method when {@link SentinelProperty#updateValue(Object)} need inform the listener.
- //规则变更时触发的回调方法
- void configUpdate(T value);
- //The first time of the {@code value}'s load.
- //首次加载规则时触发的回调方法
- void configLoad(T value);
- }
- //Manager for authority rules.
- public final class AuthorityRuleManager {
- //key是资源名称,value是资源对应的规则
- private static volatile Map<String, Set> authorityRules = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
- //饿汉式单例模式实例化黑白名单权限控制规则的监听器对象
- private static final RulePropertyListener LISTENER = new RulePropertyListener();
- //监听器对象的管理器
- private static SentinelProperty<List> currentProperty = new DynamicSentinelProperty<>();
-
- static {
- //将黑白名单权限控制规则的监听器对象添加到DynamicSentinelProperty中
- currentProperty.addListener(LISTENER);
- }
- ...
-
- private static class RulePropertyListener implements PropertyListener<List> {
- @Override
- public synchronized void configLoad(List value) {
- authorityRules = loadAuthorityConf(value);
- RecordLog.info("[AuthorityRuleManager] Authority rules loaded: {}", authorityRules);
- }
-
- @Override
- public synchronized void configUpdate(List conf) {
- authorityRules = loadAuthorityConf(conf);
- RecordLog.info("[AuthorityRuleManager] Authority rules received: {}", authorityRules);
- }
-
- private Map<String, Set> loadAuthorityConf(List list) {
- Map<String, Set> newRuleMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
- if (list == null || list.isEmpty()) {
- return newRuleMap;
- }
- for (AuthorityRule rule : list) {
- if (!isValidRule(rule)) {
- RecordLog.warn("[AuthorityRuleManager] Ignoring invalid authority rule when loading new rules: {}", rule);
- continue;
- }
- if (StringUtil.isBlank(rule.getLimitApp())) {
- rule.setLimitApp(RuleConstant.LIMIT_APP_DEFAULT);
- }
- String identity = rule.getResource();
- Set ruleSet = newRuleMap.get(identity);
- //putIfAbsent
- if (ruleSet == null) {
- ruleSet = new HashSet<>();
- ruleSet.add(rule);
- newRuleMap.put(identity, ruleSet);
- } else {
- //One resource should only have at most one authority rule, so just ignore redundant rules.
- RecordLog.warn("[AuthorityRuleManager] Ignoring redundant rule: {}", rule.toString());
- }
- }
- return newRuleMap;
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class FlowRuleManager {
- private static volatile Map<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRules = new HashMap<>();
- private static final FlowPropertyListener LISTENER = new FlowPropertyListener();
- private static SentinelProperty<List<FlowRule>> currentProperty = new DynamicSentinelProperty<List<FlowRule>>();
-
- static {
- currentProperty.addListener(LISTENER);
- startMetricTimerListener();
- }
- ...
-
- private static final class FlowPropertyListener implements PropertyListener<List<FlowRule>> {
- @Override
- public synchronized void configUpdate(List<FlowRule> value) {
- Map<String, List<FlowRule>> rules = FlowRuleUtil.buildFlowRuleMap(value);
- if (rules != null) {
- flowRules = rules;
- }
- RecordLog.info("[FlowRuleManager] Flow rules received: {}", rules);
- }
-
- @Override
- public synchronized void configLoad(List<FlowRule> conf) {
- Map<String, List<FlowRule>> rules = FlowRuleUtil.buildFlowRuleMap(conf);
- if (rules != null) {
- flowRules = rules;
- }
- RecordLog.info("[FlowRuleManager] Flow rules loaded: {}", rules);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public final class DegradeRuleManager {
- private static final RulePropertyListener LISTENER = new RulePropertyListener();
- private static SentinelProperty<List<DegradeRule>> currentProperty = new DynamicSentinelProperty<>();
-
- static {
- currentProperty.addListener(LISTENER);
- }
- ...
-
- private static class RulePropertyListener implements PropertyListener<List<DegradeRule>> {
- ...
- @Override
- public void configUpdate(List<DegradeRule> conf) {
- reloadFrom(conf);
- RecordLog.info("[DegradeRuleManager] Degrade rules has been updated to: {}", ruleMap);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void configLoad(List<DegradeRule> conf) {
- reloadFrom(conf);
- RecordLog.info("[DegradeRuleManager] Degrade rules loaded: {}", ruleMap);
- }
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
为了在创建规则时回调configLoad()方法初始化规则配置,以及在规则变更时回调configUpdate()方法通知到所有监听者,需要一个类来管理所有监听器,比如将所有监听器添加到集合中。当配置发生变化时,就可以遍历监听器集合然后调用回调方法进行处理。
其实就是使用监听器模式或观察者模式,创建一个实现了SentinelProperty接口的类,专门负责管理所有实现了PropertyListener接口的监听器。
其中SentinelProperty接口如下所示:- //This class holds current value of the config,
- //and is responsible for informing all PropertyListeners added on this when the config is updated.
- //Note that not every updateValue(Object newValue) invocation should inform the listeners,
- //only when newValue is not Equals to the old value, informing is needed.
- public interface SentinelProperty<T> {
- //添加监听者
- //Add a PropertyListener to this SentinelProperty.
- //After the listener is added, updateValue(Object) will inform the listener if needed.
- //This method can invoke multi times to add more than one listeners.
- void addListener(PropertyListener<T> listener);
- //移除监听者
- //Remove the PropertyListener on this.
- //After removing, updateValue(Object) will not inform the listener.
- void removeListener(PropertyListener<T> listener);
- //当监听值有变化时,调用此方法进行通知
- //Update the newValue as the current value of this property and inform all
- //PropertyListeners added on this only when new value is not Equals to the old value.
- boolean updateValue(T newValue);
- }
DynamicSentinelProperty会使用写时复制集合CopyOnWriteArraySet来存储监听器,当DynamicSentinelProperty添加监听器或者更新新值时,便会触发执行PropertyListener接口的两个回调方法。
具体就是:当执行DynamicSentinelProperty的addListener()方法添加监听器时,会将监听器保存到DynamicSentinelProperty的写时复制集合CopyOnWriteArraySet中,并且回调监听器的configLoad()方法来初始化规则配置。由于监听器监听的是规则,而规则又是和资源绑定的,所以初始化就是将资源和规则绑定到一个Map中:即形如Map这样的Map。
当执行DynamicSentinelProperty的updateValue()方法更新规则配置时,则会遍历所有监听器并调用每个监听器的configUpdate()方法进行更新,也就是更新Map这种Map里的value。- public class DynamicSentinelProperty<T> implements SentinelProperty<T> {
- protected Set<PropertyListener<T>> listeners = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();
- private T value = null;
-
- public DynamicSentinelProperty() {
-
- }
-
- public DynamicSentinelProperty(T value) {
- super();
- this.value = value;
- }
-
- //添加监听器到集合
- @Override
- public void addListener(PropertyListener<T> listener) {
- listeners.add(listener);
- //回调监听器的configLoad()方法初始化规则配置
- listener.configLoad(value);
- }
-
- //移除监听器
- @Override
- public void removeListener(PropertyListener<T> listener) {
- listeners.remove(listener);
- }
-
- //更新值
- @Override
- public boolean updateValue(T newValue) {
- //如果值没变化,直接返回
- if (isEqual(value, newValue)) {
- return false;
- }
- RecordLog.info("[DynamicSentinelProperty] Config will be updated to: {}", newValue);
- value = newValue;
- //如果值发生了变化,则遍历监听器,回调监听器的configUpdate()方法更新对应的值
- for (PropertyListener<T> listener : listeners) {
- listener.configUpdate(newValue);
- }
- return true;
- }
- ...
- }
一.PropertyListener
PropertyListener是一个泛型接口,用于监听配置变更。它包含两个方法:configUpdate()方法和configLoad()方法。
PropertyListener的configUpdate()方法在配置发生变化时触发,PropertyListener的configLoad()方法在首次加载配置时触发。通过实现PropertyListener接口,可以实现不同类型的监听器,例如FlowPropertyListener等。
二.SentinelProperty
SentinelProperty是一个用于管理PropertyListener监听器的接口,它提供了添加、移除和更新监听器的方法。
添加监听器可调用SentinelProperty实现类的addListener()方法实现添加,配置变更可调用SentinelProperty实现类的updateValue()方法通知监听器。Sentinel提供了默认的SentinelProperty实现:DynamicSentinelProperty。
4.AuthoritySlot控制黑白名单权限
(1)黑白名单权限控制规则的配置Demo
(2)AuthoritySlot验证黑白名单权限控制规则
(1)黑白名单权限控制规则的配置Demo
一.配置黑白名单权限控制规则的过程
二.AuthorityRuleManager初始化和加载黑白名单权限控制规则详情
一.配置黑白名单权限控制规则的过程
首先创建一个AuthorityRule规则对象,然后设置三个关键要素:通过setStrategy()方法设置规则是黑名单还是白名单、通过setResource()方法设置规则绑定到哪个资源、通过setLimitApp()方法设置限制哪些来源,最后调用AuthorityRuleManager的loadRules()方法加载此规则。所以黑白名单权限规则是通过AuthorityRuleManager类来进行管理的。- //Authority rule is designed for limiting by request origins.
- //In blacklist mode, requests will be blocked when blacklist contains current origin, otherwise will pass.
- //In whitelist mode, only requests from whitelist origin can pass.
- public class AuthorityDemo {
- private static final String RESOURCE_NAME = "testABC";
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println("========Testing for black list========");
- initBlackRules();
- testFor(RESOURCE_NAME, "appA");
- testFor(RESOURCE_NAME, "appB");
- testFor(RESOURCE_NAME, "appC");
- testFor(RESOURCE_NAME, "appE");
- System.out.println("========Testing for white list========");
- initWhiteRules();
- testFor(RESOURCE_NAME, "appA");
- testFor(RESOURCE_NAME, "appB");
- testFor(RESOURCE_NAME, "appC");
- testFor(RESOURCE_NAME, "appE");
- }
-
- private static void testFor(String resource, String origin) {
- ContextUtil.enter(resource, origin);
- Entry entry = null;
- try {
- entry = SphU.entry(resource);
- System.out.println(String.format("Passed for resource %s, origin is %s", resource, origin));
- } catch (BlockException ex) {
- System.err.println(String.format("Blocked for resource %s, origin is %s", resource, origin));
- } finally {
- if (entry != null) {
- entry.exit();
- }
- ContextUtil.exit();
- }
- }
-
- private static void initWhiteRules() {
- AuthorityRule rule = new AuthorityRule();
- rule.setResource(RESOURCE_NAME);
- rule.setStrategy(RuleConstant.AUTHORITY_WHITE);
- rule.setLimitApp("appA,appE");
- AuthorityRuleManager.loadRules(Collections.singletonList(rule));
- }
-
- private static void initBlackRules() {
- AuthorityRule rule = new AuthorityRule();
- rule.setResource(RESOURCE_NAME);
- rule.setStrategy(RuleConstant.AUTHORITY_BLACK);
- rule.setLimitApp("appA,appB");
- AuthorityRuleManager.loadRules(Collections.singletonList(rule));
- }
- }
AuthorityRuleManager类中有一个静态变量LISTENER,该变量指向由饿汉式单例模式实例化的黑白名单权限控制规则监听器对象。
AuthorityRuleManager类有一个静态代码块,在该代码块中,会调用DynamicSentinelProperty的addListener(LISTENER)方法,将黑白名单权限控制规则的监听器对象添加到DynamicSentinelProperty。
在DynamicSentinelProperty的addListener()方法中,又会回调LISTENER的configLoad()方法初始化黑白名单权限规则。
当AuthorityDemo调用AuthorityRuleManager的loadRules()方法加载规则时,便会执行DynamicSentinelProperty的updateValue()方法,也就是会触发执行LISTENER的configUpdate()方法加载权限规则到一个map中,即执行RulePropertyListener的loadAuthorityConf()方法加载规则,从而完成黑白名单权限控制规则的加载和初始化。其中map是AuthorityRuleManager的Map。- //Manager for authority rules.
- public final class AuthorityRuleManager {
- //key是资源名称,value是资源对应的规则
- private static volatile Map<String, Set> authorityRules = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
- //饿汉式单例模式实例化黑白名单权限控制规则的监听器对象
- private static final RulePropertyListener LISTENER = new RulePropertyListener();
- //监听器对象的管理器
- private static SentinelProperty<List> currentProperty = new DynamicSentinelProperty<>();
-
- static {
- //将黑白名单权限控制规则的监听器对象添加到DynamicSentinelProperty中
- currentProperty.addListener(LISTENER);
- }
-
- //Load the authority rules to memory.
- public static void loadRules(List rules) {
- currentProperty.updateValue(rules);
- }
- ...
-
- //静态内部类的方式实现黑白名单权限控制规则监听器
- private static class RulePropertyListener implements PropertyListener<List> {
- //黑名单权限控制规则初始化
- @Override
- public synchronized void configLoad(List value) {
- authorityRules = loadAuthorityConf(value);
- RecordLog.info("[AuthorityRuleManager] Authority rules loaded: {}", authorityRules);
- }
-
- //黑名单权限控制规则变更
- @Override
- public synchronized void configUpdate(List conf) {
- authorityRules = loadAuthorityConf(conf);
- RecordLog.info("[AuthorityRuleManager] Authority rules received: {}", authorityRules);
- }
-
- //加载黑白名单权限控制规则
- private Map<String, Set> loadAuthorityConf(List list) {
- Map<String, Set> newRuleMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
- if (list == null || list.isEmpty()) {
- return newRuleMap;
- }
- //遍历每个黑白名单权限控制规则
- for (AuthorityRule rule : list) {
- if (!isValidRule(rule)) {
- RecordLog.warn("[AuthorityRuleManager] Ignoring invalid authority rule when loading new rules: {}", rule);
- continue;
- }
- if (StringUtil.isBlank(rule.getLimitApp())) {
- rule.setLimitApp(RuleConstant.LIMIT_APP_DEFAULT);
- }
- //获取黑白名单权限控制规则对应的资源名称
- String identity = rule.getResource();
- Set ruleSet = newRuleMap.get(identity);
- //putIfAbsent
- //将黑白名单权限控制规则放到newRuleMap中
- if (ruleSet == null) {
- ruleSet = new HashSet<>();
- ruleSet.add(rule);
- newRuleMap.put(identity, ruleSet);
- } else {
- //One resource should only have at most one authority rule, so just ignore redundant rules.
- RecordLog.warn("[AuthorityRuleManager] Ignoring redundant rule: {}", rule.toString());
- }
- }
- return newRuleMap;
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class DynamicSentinelProperty<T> implements SentinelProperty<T> {
- protected Set<PropertyListener<T>> listeners = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();
- private T value = null;
-
- public DynamicSentinelProperty() {
-
- }
-
- public DynamicSentinelProperty(T value) {
- super();
- this.value = value;
- }
-
- //添加监听器到集合
- @Override
- public void addListener(PropertyListener<T> listener) {
- listeners.add(listener);
- //回调监听器的configLoad()方法初始化规则配置
- listener.configLoad(value);
- }
-
- //移除监听器
- @Override
- public void removeListener(PropertyListener<T> listener) {
- listeners.remove(listener);
- }
-
- //更新值
- @Override
- public boolean updateValue(T newValue) {
- //如果值没变化,直接返回
- if (isEqual(value, newValue)) {
- return false;
- }
- RecordLog.info("[DynamicSentinelProperty] Config will be updated to: {}", newValue);
- //如果值发生了变化,则遍历监听器,回调监听器的configUpdate()方法更新对应的值
- value = newValue;
- for (PropertyListener<T> listener : listeners) {
- listener.configUpdate(newValue);
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- private boolean isEqual(T oldValue, T newValue) {
- if (oldValue == null && newValue == null) {
- return true;
- }
- if (oldValue == null) {
- return false;
- }
- return oldValue.equals(newValue);
- }
-
- public void close() {
- listeners.clear();
- }
- }
在AuthoritySlot的checkBlackWhiteAuthority()方法中,首先会调用AuthorityRuleManager的getAuthorityRules()方法,从AuthorityRuleManager中获取全部黑白名单权限控制规则,然后再调用AuthorityRuleChecker的passCheck()方法根据规则验证权限。
在AuthorityRuleChecker的passCheck()方法中,首先会从当前上下文Context中获取调用源的名称,然后判断调用源不空且配置了黑白名单规则,才执行黑白名单验证逻辑。接着先通过indexOf()方法进行一次黑白名单的简单匹配,再通过split()方法分割黑白名单数组以实现精确匹配。如果调用源在名单中,再根据黑白名单策略来决定是否拒绝请求。
注意,实现黑白名单权限控制的前提条件是:每个客户端在发起请求时已将自己服务的唯一标志放到Context的origin属性里。- @Spi(order = Constants.ORDER_AUTHORITY_SLOT)
- public class AuthoritySlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<DefaultNode> {
- @Override
- public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
- //验证黑白名单权限控制规则
- checkBlackWhiteAuthority(resourceWrapper, context);
- fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) {
- fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);
- }
-
- void checkBlackWhiteAuthority(ResourceWrapper resource, Context context) throws AuthorityException {
- //先从AuthorityRuleManager中获取存放全部的黑白名单权限控制规则的Map
- Map<String, Set> authorityRules = AuthorityRuleManager.getAuthorityRules();
- if (authorityRules == null) {
- return;
- }
- //获取当前资源对应的黑白名单权限控制规则集合
- Set rules = authorityRules.get(resource.getName());
- if (rules == null) {
- return;
- }
- for (AuthorityRule rule : rules) {
- //验证规则
- if (!AuthorityRuleChecker.passCheck(rule, context)) {
- throw new AuthorityException(context.getOrigin(), rule);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- //Rule checker for white/black list authority.
- final class AuthorityRuleChecker {
- static boolean passCheck(AuthorityRule rule, Context context) {
- String requester = context.getOrigin();
- //Empty origin or empty limitApp will pass.
- //如果没设置来源,或者没限制app,那么就直接放行,不进行规则限制
- if (StringUtil.isEmpty(requester) || StringUtil.isEmpty(rule.getLimitApp())) {
- return true;
- }
- //Do exact match with origin name.
- //判断此次请求的来源是不是在limitApp里,注意这里用的是近似精确匹配,但不是绝对精确
- //比如limitApp写的是a,b,而资源名称是",b",那么就匹配不到,因为limitApp是按逗号隔开的,但资源却包含了逗号
- int pos = rule.getLimitApp().indexOf(requester);
- boolean contain = pos > -1;
- //如果近似精确匹配成功,则再进行精确匹配
- if (contain) {
- boolean exactlyMatch = false;
- String[] appArray = rule.getLimitApp().split(",");
- for (String app : appArray) {
- if (requester.equals(app)) {
- exactlyMatch = true;
- break;
- }
- }
- contain = exactlyMatch;
- }
- //获取策略
- int strategy = rule.getStrategy();
- //如果是黑名单,并且此次请求的来源在limitApp里,则需返回false,禁止请求
- if (strategy == RuleConstant.AUTHORITY_BLACK && contain) {
- return false;
- }
- //如果是白名单,并且此次请求的来源不在limitApp里,则也需返回false,禁止请求
- if (strategy == RuleConstant.AUTHORITY_WHITE && !contain) {
- return false;
- }
- return true;
- }
-
- private AuthorityRuleChecker() {
-
- }
- }
一.黑白名单权限验证规则涉及的核心类
二.黑白名单权限验证的处理逻辑
三.Sentinel监听器模式的处理逻辑
一.黑白名单权限验证规则涉及的核心类
首先是黑白名单管理器AuthorityRuleManager,调用方直接调用该类的loadRules()方法来通知监听器规则的变更。
然后是黑白名单监听器RulePropertyListener,它实现了PropertyListener接口,负责监听和管理黑白名单的规则变化。
二.黑白名单权限验证的处理逻辑
首先通过AuthorityRuleManager获取全部黑白名单权限控制规则,然后循环遍历这些权限控制规则逐一验证是否匹配。
这里需要注意:来源是从Context里获取的,也就是Context的getOrigin()方法。因此在进行黑白名单权限规则控制时,需要先定义好一个origin。这个origin可以是userId,也可以是IP地址,还可以是项目名称等。
此外,规则里的limitApp字段是字符串,多个时需要使用逗号隔开,然后在验证环节先通过indexOf()方法近似匹配,匹配上之后再通过split()方法转成数组进行精确匹配。
三.Sentinel监听器模式的处理逻辑
Sentinel监听器模式会包含三大角色:
角色一:监听器PropertyListener
角色二:监听器管理器SentinelProperty
角色三:规则管理器RuleManager
首先,规则管理器RuleManager在初始化时:会调用监听器管理器SentinelProperty的addListener()方法将监听器PropertyListener注册到监听器管理器SentinelProperty中。
然后,使用方使用具体的规则时:可以通过调用规则管理器RuleManager的loadRules()方法加载规则。加载规则时会调用监听器管理器SentinelProperty的的updateValue()方法通知每一个监听器,即通过监听器PropertyListener的configUpdate()方法把规则加载到规则管理器RuleManager的本地中。
5.SystemSlot根据系统保护规则进行流控
(1)系统保护规则SystemRule的配置Demo
(2)SystemRuleManager加载规则和获取系统信息
(3)SystemSlot根据系统保护规则进行流控
(1)系统保护规则SystemRule的配置Demo
系统规则类SystemRule包含了以下几个指标:highestSystemLoad、highestCpuUsage、QPS、avgRt、maxThread。
当需要限制系统的这些指标时,可以创建一个SystemRule对象并设置对应的阈值,然后通过调用SystemRuleManager的loadRules()方法,加载系统保护规则设置的阈值到SystemRuleManager。- //Sentinel System Rule makes the inbound traffic and capacity meet.
- //It takes average RT, QPS and thread count of requests into account.
- //And it also provides a measurement of system's load, but only available on Linux.
- //We recommend to coordinate highestSystemLoad, qps, avgRt and maxThread to make sure your system run in safety level.
- //To set the threshold appropriately, performance test may be needed.
- public class SystemRule extends AbstractRule {
- //对应Dashboard上阈值类型为LOAD的值,代表系统最高负载值,默认为-1,只有大于等于0才生效
- private double highestSystemLoad = -1;
- //对应Dashboard上阈值类型为CPU使用率的值,代表系统最高CPU使用率,取值是[0,1]之间,默认为-1,只有大于等于0才生效
- private double highestCpuUsage = -1;
- //对应Dashboard上阈值类型为为入口QPS的值,代表限流的阈值,默认为-1,只有大于0才生效
- private double qps = -1;
- //对应Dashboard上阈值类型为为RT的值,代表系统的平均响应时间,默认为-1,只有大于0才生效
- private long avgRt = -1;
- //对应Dashboard上阈值类型为线程数的值,代表系统允许的最大线程数,默认为-1,只有大于0才生效
- private long maxThread = -1;
- ...
- }
- public class SystemGuardDemo {
- private static AtomicInteger pass = new AtomicInteger();
- private static AtomicInteger block = new AtomicInteger();
- private static AtomicInteger total = new AtomicInteger();
- private static volatile boolean stop = false;
- private static final int threadCount = 100;
- private static int seconds = 60 + 40;
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- //启动线程定时输出信息
- tick();
- //初始化系统保护规则
- initSystemRule();
- //模拟有100个线程在访问系统
- for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
- Thread entryThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
- @Override
- public void run() {
- while (true) {
- Entry entry = null;
- try {
- entry = SphU.entry("methodA", EntryType.IN);
- pass.incrementAndGet();
- try {
- TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- // ignore
- }
- } catch (BlockException e1) {
- block.incrementAndGet();
- try {
- TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- // ignore
- }
- } catch (Exception e2) {
- // biz exception
- } finally {
- total.incrementAndGet();
- if (entry != null) {
- entry.exit();
- }
- }
- }
- }
- });
- entryThread.setName("working-thread");
- entryThread.start();
- }
- }
-
- private static void initSystemRule() {
- List<SystemRule> rules = new ArrayList<SystemRule>();
- SystemRule rule = new SystemRule();
- //最大负载是3
- rule.setHighestSystemLoad(3.0);
- //最大CPU使用率是60%
- rule.setHighestCpuUsage(0.6);
- //请求的平均响应时间最大是10ms
- rule.setAvgRt(10);
- //最大的QPS是20
- rule.setQps(20);
- //最大的工作线程数是10
- rule.setMaxThread(10);
- rules.add(rule);
- //加载系统保护规则设置的阈值到SystemRuleManager中
- SystemRuleManager.loadRules(Collections.singletonList(rule));
- }
-
- private static void tick() {
- Thread timer = new Thread(new TimerTask());
- timer.setName("sentinel-timer-task");
- timer.start();
- }
-
- static class TimerTask implements Runnable {
- @Override
- public void run() {
- System.out.println("begin to statistic!!!");
- long oldTotal = 0;
- long oldPass = 0;
- long oldBlock = 0;
-
- while (!stop) {
- try {
- TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
- }
- long globalTotal = total.get();
- long oneSecondTotal = globalTotal - oldTotal;
- oldTotal = globalTotal;
- long globalPass = pass.get();
- long oneSecondPass = globalPass - oldPass;
- oldPass = globalPass;
- long globalBlock = block.get();
- long oneSecondBlock = globalBlock - oldBlock;
- oldBlock = globalBlock;
- System.out.println(seconds + ", " + TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis() + ", total:"
- + oneSecondTotal + ", pass:"
- + oneSecondPass + ", block:" + oneSecondBlock);
- if (seconds-- <= 0) {
- stop = true;
- }
- }
- System.exit(0);
- }
- }
- }
SystemSlot会根据当前系统的实际情况,判断是否需要对请求进行限流,也就是通过调用SystemRuleManager的checkSystem()方法来进行检查。
在SystemRuleManager的checkSystem()方法中:
一.首先通过checkSystemStatus.get()判断系统保护功能是否开启
开启的入口就是:- public final class SystemRuleManager {
- //系统保护规则中的5个阈值:Load、CPU使用率、QPS、最大RT、最大线程数
- private static volatile double highestSystemLoad = Double.MAX_VALUE;
- private static volatile double highestCpuUsage = Double.MAX_VALUE;
- private static volatile double qps = Double.MAX_VALUE;
- private static volatile long maxRt = Long.MAX_VALUE;
- private static volatile long maxThread = Long.MAX_VALUE;
- ...
- //标记系统流控功能是否开启
- private static AtomicBoolean checkSystemStatus = new AtomicBoolean(false);
- //定时获取系统状态信息(负载和CPU使用率)的线程
- private static SystemStatusListener statusListener = null;
- //饿汉式单例模式实例化系统保护规则的监听器对象
- private final static SystemPropertyListener listener = new SystemPropertyListener();
- //监听器对象的管理器
- private static SentinelProperty<List<SystemRule>> currentProperty = new DynamicSentinelProperty<List<SystemRule>>();
- private final static ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1, new NamedThreadFactory("sentinel-system-status-record-task", true));
-
- static {
- checkSystemStatus.set(false);
- //启动定时任务获取系统的Load、CPU负载等信息
- statusListener = new SystemStatusListener();
- scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(statusListener, 0, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
- //添加监听器
- currentProperty.addListener(listener);
- }
-
- //Load SystemRules, former rules will be replaced.
- public static void loadRules(List<SystemRule> rules) {
- currentProperty.updateValue(rules);
- }
-
- static class SystemPropertyListener extends SimplePropertyListener<List<SystemRule>> {
- @Override
- public synchronized void configUpdate(List<SystemRule> rules) {
- restoreSetting();
- if (rules != null && rules.size() >= 1) {
- for (SystemRule rule : rules) {
- //加载系统保护规则的阈值到本地
- loadSystemConf(rule);
- }
- } else {
- checkSystemStatus.set(false);
- }
- ...
- }
- }
-
- //加载系统保护规则的阈值到本地
- public static void loadSystemConf(SystemRule rule) {
- boolean checkStatus = false;
- if (rule.getHighestSystemLoad() >= 0) {
- highestSystemLoad = Math.min(highestSystemLoad, rule.getHighestSystemLoad());
- highestSystemLoadIsSet = true;
- checkStatus = true;
- }
- if (rule.getHighestCpuUsage() >= 0) {
- if (rule.getHighestCpuUsage() > 1) {
- RecordLog.warn(String.format("[SystemRuleManager] Ignoring invalid SystemRule: " + "highestCpuUsage %.3f > 1", rule.getHighestCpuUsage()));
- } else {
- highestCpuUsage = Math.min(highestCpuUsage, rule.getHighestCpuUsage());
- highestCpuUsageIsSet = true;
- checkStatus = true;
- }
- }
- if (rule.getAvgRt() >= 0) {
- maxRt = Math.min(maxRt, rule.getAvgRt());
- maxRtIsSet = true;
- checkStatus = true;
- }
- if (rule.getMaxThread() >= 0) {
- maxThread = Math.min(maxThread, rule.getMaxThread());
- maxThreadIsSet = true;
- checkStatus = true;
- }
- if (rule.getQps() >= 0) {
- qps = Math.min(qps, rule.getQps());
- qpsIsSet = true;
- checkStatus = true;
- }
- checkSystemStatus.set(checkStatus);
- }
- ...
- }
- public class DynamicSentinelProperty<T> implements SentinelProperty<T> {
- protected Set<PropertyListener<T>> listeners = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<>();
- private T value = null;
- ...
- //添加监听器到集合
- @Override
- public void addListener(PropertyListener<T> listener) {
- listeners.add(listener);
- //回调监听器的configLoad()方法初始化规则配置
- listener.configLoad(value);
- }
-
- //更新值
- @Override
- public boolean updateValue(T newValue) {
- //如果值没变化,直接返回
- if (isEqual(value, newValue)) {
- return false;
- }
- RecordLog.info("[DynamicSentinelProperty] Config will be updated to: {}", newValue);
- //如果值发生了变化,则遍历监听器,回调监听器的configUpdate()方法更新对应的值
- value = newValue;
- for (PropertyListener<T> listener : listeners) {
- listener.configUpdate(newValue);
- }
- return true;
- }
- ...
- }
- public class SystemStatusListener implements Runnable {
- volatile double currentLoad = -1;
- volatile double currentCpuUsage = -1;
- volatile long processCpuTime = 0;
- volatile long processUpTime = 0;
- ...
- @Override
- public void run() {
- try {
- OperatingSystemMXBean osBean = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMXBean(OperatingSystemMXBean.class);
- currentLoad = osBean.getSystemLoadAverage();
- double systemCpuUsage = osBean.getSystemCpuLoad();
- //calculate process cpu usage to support application running in container environment
- RuntimeMXBean runtimeBean = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMXBean(RuntimeMXBean.class);
- long newProcessCpuTime = osBean.getProcessCpuTime();
- long newProcessUpTime = runtimeBean.getUptime();
- int cpuCores = osBean.getAvailableProcessors();
- long processCpuTimeDiffInMs = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(newProcessCpuTime - processCpuTime);
- long processUpTimeDiffInMs = newProcessUpTime - processUpTime;
- double processCpuUsage = (double) processCpuTimeDiffInMs / processUpTimeDiffInMs / cpuCores;
- processCpuTime = newProcessCpuTime;
- processUpTime = newProcessUpTime;
- currentCpuUsage = Math.max(processCpuUsage, systemCpuUsage);
- if (currentLoad > SystemRuleManager.getSystemLoadThreshold()) {
- writeSystemStatusLog();
- }
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- RecordLog.warn("[SystemStatusListener] Failed to get system metrics from JMX", e);
- }
- }
-
- public double getSystemAverageLoad() {
- return currentLoad;
- }
-
- public double getCpuUsage() {
- return currentCpuUsage;
- }
- ...
- }
Constants.ENTRY_NODE其实就是ClusterNode。在StatisticSlot的entry()方法中,会对Constants.ENTRY_NODE进行统计,所以可以通过Constants.ENTRY_NODE获取QPS、threadNum等数据。
三.然后采取BBR算法来检查系统负载是否超过系统保护规则的阈值
BBR是Google开发的一种拥塞控制算法,主要用来解决网络拥塞问题。SystemRuleManager的checkBbr()方法的目的是在系统负载较高的情况下,通过限制并行线程数来防止系统过载。
简单来说就是:检查当前线程数是否大于(每秒最大成功请求数 * 最小响应时间 / 1000)。如果大于这个值,说明系统可能出现拥塞,要返回false,否则返回true。
四.最后判断CPU使用率是否超系统保护规则的阈值
系统负载和CPU使用率是通过SystemStatusListener获取的。- ->SystemRuleManager.loadRules()方法
- ->DynamicSentinelProperty.updateValue()方法
- ->SystemPropertyListener.configUpdate()方法
- ->SystemRuleManager.loadSystemConf()方法
一.SystemSlot的使用和处理流程
二.Sentinel监听器模式的处理逻辑
一.SystemSlot的使用和处理流程
在使用SystemSlot前,需要先定义系统保护规则,设置相应的阈值,然后通过SystemRuleManager加载系统保护规则SystemRule。当请求进入SystemSlot时,会检查系统性能数据是否满足规则中的阈值。如果满足,则请求可以继续执行。如果不满足,则请求将被限流,也就是抛出SystemBlockException异常。
二.Sentinel监听器模式的处理逻辑
Sentinel监听器模式会包含三大角色:
角色一:监听器PropertyListener
角色二:监听器管理器SentinelProperty
角色三:规则管理器RuleManager
首先,规则管理器RuleManager在初始化时:会调用监听器管理器SentinelProperty的addListener()方法将监听器PropertyListener注册到监听器管理器SentinelProperty中。
然后,使用方使用具体的规则时:可以通过调用规则管理器RuleManager的loadRules()方法加载规则。加载规则时会调用监听器管理器SentinelProperty的的updateValue()方法通知每一个监听器,即通过监听器PropertyListener的configUpdate()方法把规则加载到规则管理器RuleManager的本地中。
来源:程序园用户自行投稿发布,如果侵权,请联系站长删除
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作! |