背景
如标题所说,我手里维护了一个重要的老项目,使用jdk1.7,里面对接了很多个第三方服务,协议多种多样,其中涉及http/https的,调用方式也是五花八门,比如:commons-httpclient、apache httpclient、原生的url.openConnection()等。- <dependency>
- <groupId>commons-httpclient</groupId>
- commons-httpclient</artifactId>
- <version>3.0</version>
- </dependency>
-
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
- httpclient</artifactId>
- <version>4.5.3</version>
- </dependency>
这边服务方也比较猛,直接就升级了,升级后没一会,他观察影响到我们这边的调用了,又回退了。
目前就是希望我们这边,作为客户端,先升级到tls1.2,即:调用他们服务的时候,使用tls1.2去调用。
本来我也不想动,你个服务端,安安心心地兼容下tls1.0、tls1.1,不是简单的很吗,最终拉扯了一顿,行吧,那就我们先研究下,看看好不好升级到tls1.2。如果实在不好弄,到时候直接改成http调用得了,搞啥https?
研究下来的方案,感觉还凑合,然后就改了,已经提交测试了,今天就先记录一下。
报错现象
我在网上找了个工具,可以测试目标https网站,支持哪几个版本的tls,如下所示,-p指定端口,后面的www.baidu.com就是目标ip或者域名。
https://nmap.org/- nmap --script ssl-enum-ciphers -p 443 www.baidu.com
比如上图的百度,就还在兼容老版本。
我在网上又试了几个域名,找到了一个只支持tls1.2的。
下面,我们就拿blog.csdn.net举例,看看用tls1.0发送请求,会报什么错:
可以看到,当我们三次握手完成,发送了第一个ssl握手消息(client hello,版本为tlsv1)后,对方(blog.csdn.net)直接来了个Alert,然后服务端就主动断开socket了。这,连接都建不起来,还怎么消息交互呢,自然是所有调用全部失败。
报错代码debug
sslcontext获取
给大家看下我们这边调用发起的代码,这个代码就是用的上面说的那个commons-httpclient包,这个包算是apache早期维护的http调用工具,后来慢慢就重心不在这里了,转到了apache httpclient。
https://hc.apache.org/httpclient-legacy/
- HttpClient httpClient = new HttpClient();
- httpClient.getParams().setContentCharset(charset);
- httpClient.getParams().setParameter(HttpMethodParams.RETRY_HANDLER, new DefaultHttpMethodRetryHandler(0,false));
- // 1 根据url,生成要调用的http method
- PostMethod httpMethod = new PostMethod(urlPath);
- try
- {
- long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
- // 2 实际发起调用
- int statusCode = httpClient.executeMethod(httpMethod);
- long spendTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - t1;
- ...
- }
- System.setProperty("https.protocols", "TLSv1.2");
- 或者
- 虚拟机参数设置 -Dhttps.protocols=TLSv1.2
从如下地方开始debug代码,因为实际执行连接是在这里:- int statusCode = httpClient.executeMethod(httpMethod);
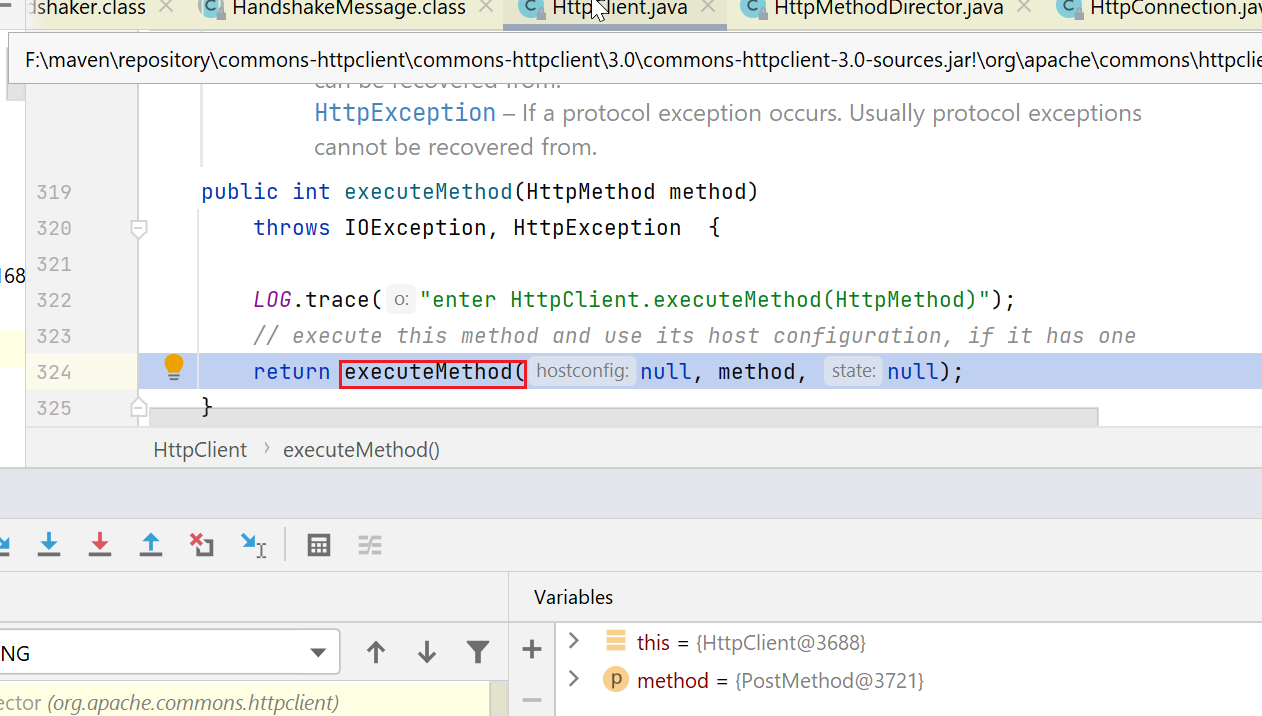
然后进入下图,交给一个叫HttpMethodDirector的类执行,这个类的注释是说:负责执行,及一些认证、重定向、报错重试等相关事情
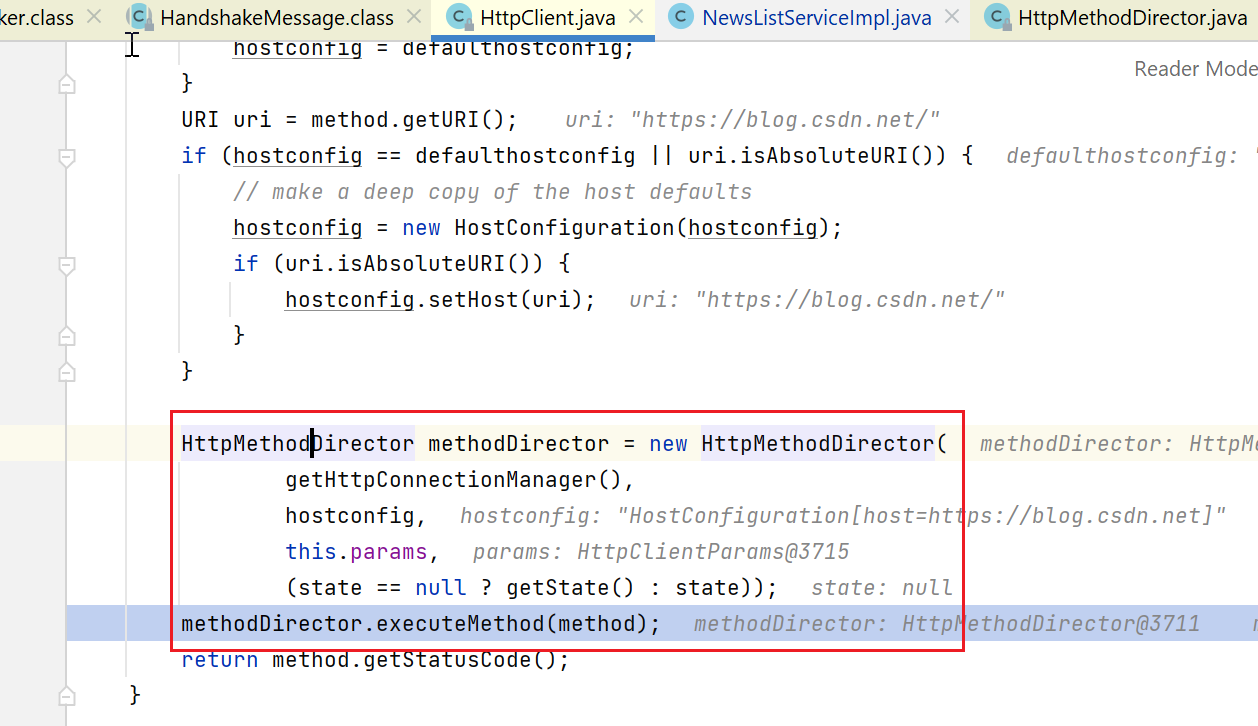
后续会进入到:org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpMethodDirector#executeWithRetry
这里要先打开socket连接:
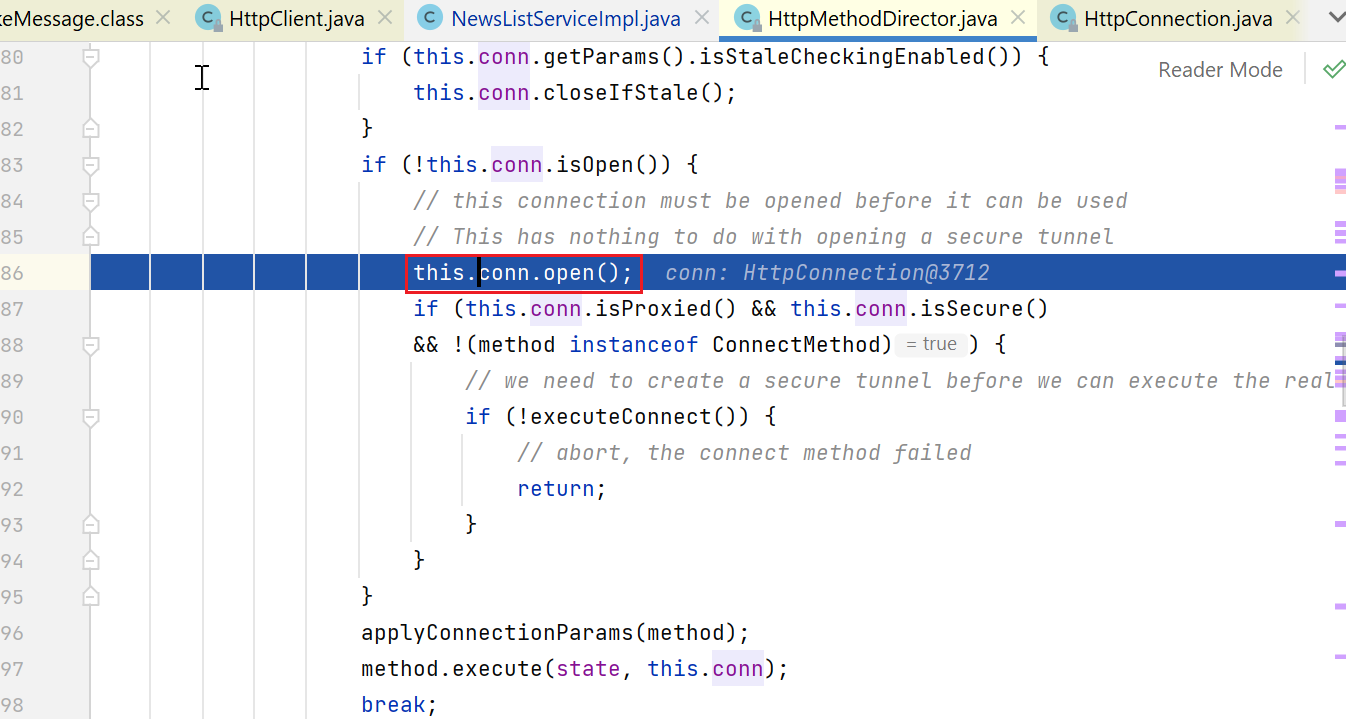
这个conn.open比较重要:
下面1处,判断是否是https调用,且未使用代理,如果是的话,最终就是要走ssl握手那一套,构造的socket也不一样,如javax.net.ssl.SSLSocket
2处,如果是https调用但使用了代理,这里就用普通http(不知道为啥),但反正我们没使用代理,不涉及。
3处,就是我们会进入的分支,获取对应的ProtocolSocketFactory(org.apache.commons.httpclient.protocol.ProtocolSocketFactory,该框架中的一个接口,反正是负责创建socket的)
4处,创建socket- org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpConnection#open
-
- public void open() throws IOException {
- LOG.trace("enter HttpConnection.open()");
- final String host = (proxyHostName == null) ? hostName : proxyHostName;
- final int port = (proxyHostName == null) ? portNumber : proxyPortNumber;
-
- try {
- if (this.socket == null) {
- // 1
- usingSecureSocket = isSecure() && !isProxied();
- ProtocolSocketFactory socketFactory = null;
- // 2
- if (isSecure() && isProxied()) {
- Protocol defaultprotocol = Protocol.getProtocol("http");
- socketFactory = defaultprotocol.getSocketFactory();
- } else {
- // 3
- socketFactory = this.protocolInUse.getSocketFactory();
- }
- // 4
- this.socket = socketFactory.createSocket(
- host, port,
- localAddress, 0,
- this.params);
- }
- socket.setTcpNoDelay(this.params.getTcpNoDelay());
- socket.setSoTimeout(this.params.getSoTimeout());
-
- inputStream = new BufferedInputStream(socket.getInputStream(), inbuffersize);
- outputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream(), outbuffersize);
- isOpen = true;
- } catch (IOException e) {
- throw e;
- }
- }
其中,我们来看看是如何createSocket的:
这里会调用javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory#getDefault,可以从包名看到,已经开始和jdk中ssl部分的类交互了:
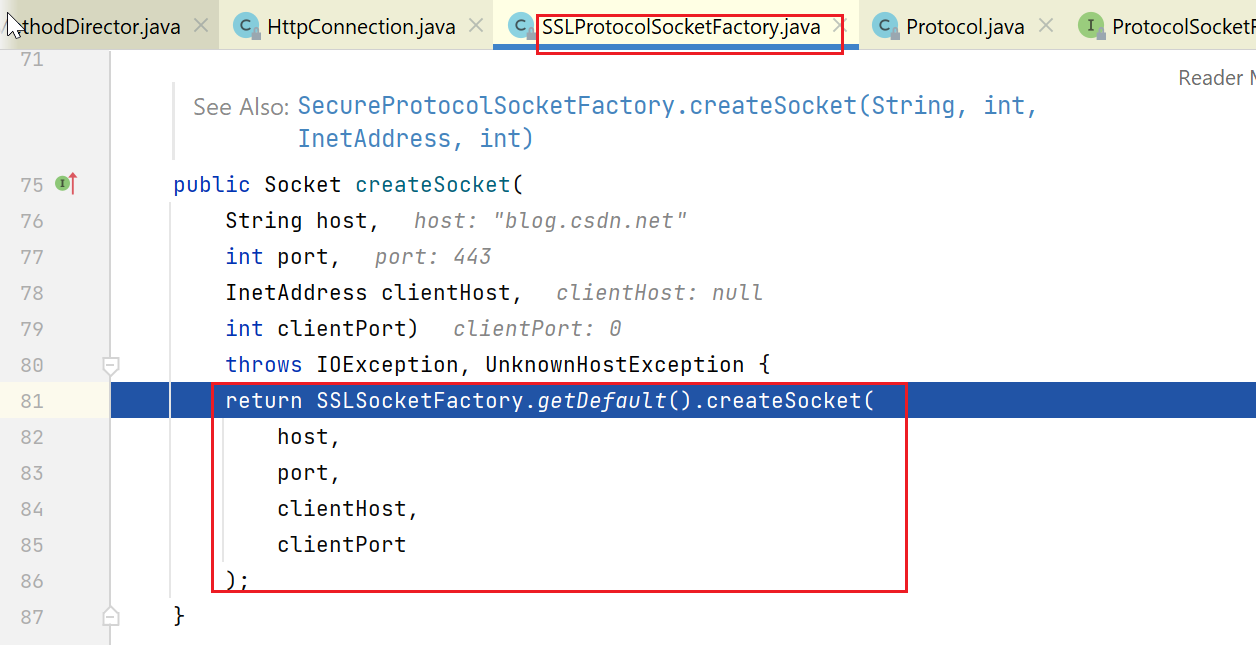
在jdk 1.7的javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory中,有一个static的全局变量,theFactory。
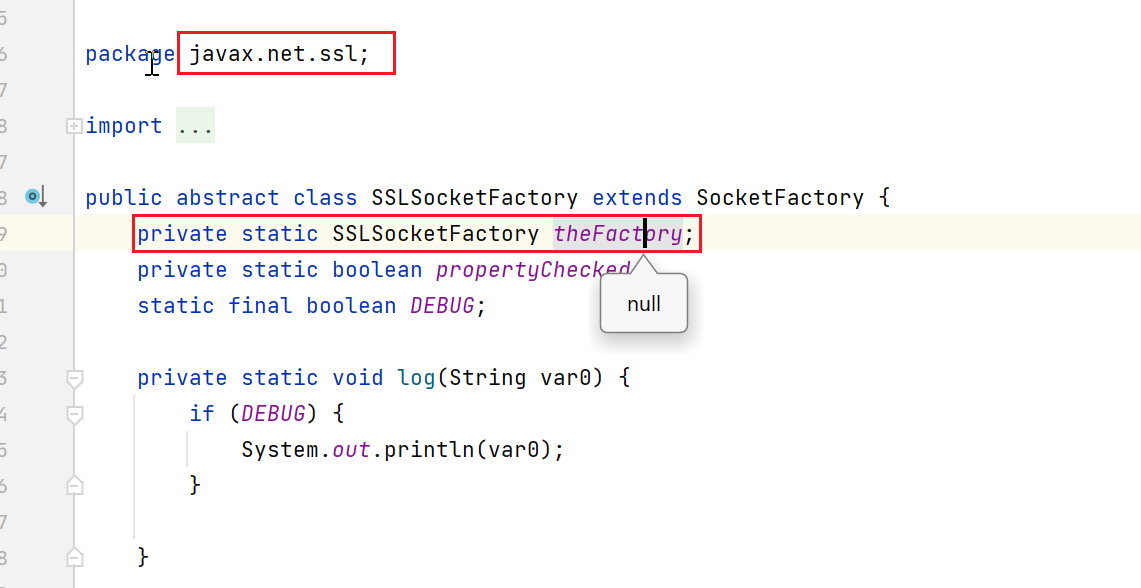
我们看看这个getdefault的逻辑:
1处,如果static field不为空,直接返回这个field。
2处,如果自己指定了ssl.SocketFactory.provider,也可以用我们自定义的,我没用这种方法,跳过
3处,SSLContext.getDefault()获取到一个SSLContext,然后调用javax.net.ssl.SSLContext#getSocketFactory来获取一个factory。- public static synchronized SocketFactory getDefault() {
- if (theFactory != null) {
- // 1
- return theFactory;
- } else {
- if (!propertyChecked) {
- propertyChecked = true;
- // 2
- String var0 = getSecurityProperty("ssl.SocketFactory.provider");
- if (var0 != null) {
- ...
- Class var1 = = Class.forName(var0);
- SSLSocketFactory var2 = (SSLSocketFactory)var1.newInstance();
- // 2.1 设置theFactory
- theFactory = var2;
- return var2;
- }
- }
- try {
- // 3
- return SSLContext.getDefault().getSocketFactory();
- } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException var4) {
- return new DefaultSSLSocketFactory(var4);
- }
- }
- }
这里会获取静态字段SSLContext defaultContext,如果为null就先初始化:- private static SSLContext defaultContext;
下面这个地方可以简述一下,大家看到SSLContextSpi.class了,Spi什么意思,ServiceProviderInterface,反正就是java官方负责定接口,厂商负责提供实现类,然后通过在某个配置文件中指定要使用的实现类来实现动态切换实现的效果。- public static SSLContext getInstance(String var0) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
- Instance var1 = GetInstance.getInstance("SSLContext", SSLContextSpi.class, var0);
- return new SSLContext((SSLContextSpi)var1.impl, var1.provider, var0);
- }
那,这里前面传了个“Default”进来,会获取到哪一种SSLContext呢,我们看到实现类有这么多:
结果,取到的就是:sun.security.ssl.SSLContextImpl.DefaultSSLContext#DefaultSSLContext
这里只说是默认,默认是什么意思,咱们也不知道,但是,有经验的,对这块代码熟悉的,可能知道,大概问题就在这附近了,如果这里能拿到sun.security.ssl.SSLContextImpl.TLS12Context,说不定,问题就解决了。
DefaultSSLContext
这个DefaultSSLContext继承了ConservativeSSLContext:- public static final class DefaultSSLContext extends SSLContextImpl.ConservativeSSLContext
- private static class ConservativeSSLContext extends SSLContextImpl {
- private static final SSLParameters defaultServerSSLParams;
- // 重要
- private static final SSLParameters defaultClientSSLParams;
- private static final SSLParameters supportedSSLParams = new SSLParameters();
如果我们此时看看tlsv2对应的sun.security.ssl.SSLContextImpl.TLS12Context:
人家这里就支持的多了去了:sslv3 tls1.0 tls1.1 tls1.2
SSLContext#getSocketFactory
我们此时完成了SSLContext的构建,然后看看怎么构造socketFactory。
实际上,构造socketFactory没做啥事,只是new了一个sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketFactoryImpl,然后把context包装了下。
createSocket
- public Socket createSocket(String var1, int var2, InetAddress var3, int var4) throws IOException {
- return new SSLSocketImpl(this.context, var1, var2, var3, var4);
- }
这个init,也比较重要,就用到了我们前面的defaultClientSSLParams:
最终,就导致:sun.security.ssl.SSLContextImpl#defaultClientProtocolList也变成了仅包含tlsv1
然后呢,sun.security.ssl.SSLSocketImpl#enabledProtocols也就变成了tlsv1
接下来,开始三次握手(如下的:super.connect),
然后,在三次握手后,初始化ssl握手:- void doneConnect() throws IOException {
- if (this.self == this) {
- this.sockInput = super.getInputStream();
- this.sockOutput = super.getOutputStream();
- } else {
- this.sockInput = this.self.getInputStream();
- this.sockOutput = this.self.getOutputStream();
- }
- //
- this.initHandshaker();
- }
- private void initHandshaker() {
- switch(this.connectionState) {
- case 0:
- case 2:
- this.handshaker = new ClientHandshaker(this, this.sslContext, this.enabledProtocols, this.protocolVersion, this.connectionState == 1, this.secureRenegotiation, this.clientVerifyData, this.serverVerifyData);
-
- this.handshaker.setEnabledCipherSuites(this.enabledCipherSuites);
- this.handshaker.setEnableSessionCreation(this.enableSessionCreation);
- return;
此时,把版本继续传递给了handshaker:
至此,createSocket这个方法就完成了,但是,我们现在只是完成了三次握手,ssl中的clienthello消息还没开始发送呢。
httpclient.HttpMethod#execute
我们一路回到了org.apache.commons.httpclient,开始执行如下的execute:
接下来,看到sslSocketImpl在写消息的时候,要先进行ssl握手:
handshaker.activate
注意,如下这处,取了activeProtols中的最大的那个协议,而我们目前activeProtols这个list中,只有tlsv1,所以取到的自然就是tlsv1,然后赋值给了this.protocolVersion:
接下来,又使用了this.protocolVersion:
handshaker.kickstart
接下来,在构造消息时,还是使用了this.protocolVersion:
这里有点意思的是,红框处,是将this.protocolVersion赋值给了this.maxProtocolVersion,说明我们握手消息里的那个version,其实指的是客户端支持的最大版本:
基于这个,我在网上查找了一下,确实是这样:
tls1.0:
https://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2246.txt
tls1.1:
https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc4346
版本号验证
此时,我们基本也完成了关于版本号是怎么一步一步设置的过程的研究,最终,就会指定到如下图的位置:
不抓包如何查看使用的版本
- -Djavax.net.debug=ssl:handshake:verbose
- 或者
- System.setProperty("javax.net.debug","ssl:handshake:verbose");
- 然后标准输出中会打印很多握手消息,可以搜索: ClientHello ,就能看到用的啥。
可选方案
针对不同的http调用方式,方法不一样,如,对于原生的URL、httpUrlConnection等,用以下方法基本够了:- System.setProperty("https.protocols", "TLSv1.2");
- 或者
- 虚拟机参数设置 -Dhttps.protocols=TLSv1.2
如果你们也有老项目,使用我这里的commons httpclient的话:
可以先看下如下文章:https://blog.csdn.net/jilo88/article/details/123424442
这个方法的重点就在于:
我们前面提到过,以下代码,默认返回的是:sun.security.ssl.SSLContextImpl.DefaultSSLContext
而上述文章中,就是先自己手动指定了1.2:- SSLContext sc = SSLContext.getInstance("TLSv1.2");
这个方式,影响很深远,因为这个是一个静态变量,整个jdk也就这一个SSLContext类,也就这一个静态变量,所以是全局的影响。
我试过了,改这里,会导致使用原生的URL、httpUrlConnection的方式的代码也受到影响,大家可以自己试试。
apache httpclient,有没有影响,我有点忘了,大家自己测下。
我的方案
我是希望使用影响最小的方法,我如下的方法,只影响使用commons httpclient这种框架的,不使用这种框架的,不会受到影响。
commons httpclient支持对于https,注册自己的socketFactory:
我这边给https自定义了一个ProtocolSocketFactory,代码很简单,大家只要找个合适的时机(如发起http调用之前),调用一次如下的init方法,就可以了- import org.apache.commons.httpclient.protocol.Protocol;
- import org.apache.commons.httpclient.protocol.ProtocolSocketFactory;
- import org.slf4j.Logger;
- import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
- import java.security.KeyManagementException;
- import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
- public class HttpClientSupport {
- private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HttpClientSupport.class);
- public static void init(){
- Protocol protocol = Protocol.getProtocol("https");
- if (protocol != null) {
- ProtocolSocketFactory socketFactory = protocol.getSocketFactory();
- if (socketFactory instanceof CustomSSLProtocolSocketFactory){
- // logger.info("already registered");
- return;
- }
- logger.error("registered protocol for https is not CustomSSLProtocolSocketFactory type,will register");
- }
- // 注册自定义的 ProtocolSocketFactory 到 HTTPS 协议
- CustomSSLProtocolSocketFactory socketFactory = null;
- try {
- socketFactory = new CustomSSLProtocolSocketFactory();
- Protocol.registerProtocol("https", new Protocol("https", socketFactory, 443));
- logger.info("register tls1.2 socket factory success");
- } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException | KeyManagementException e) {
- logger.error("err",e);
- }
- }
- }
- import org.apache.commons.httpclient.ConnectTimeoutException;
- import org.apache.commons.httpclient.params.HttpConnectionParams;
- import org.apache.commons.httpclient.protocol.SecureProtocolSocketFactory;
- import org.slf4j.Logger;
- import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
- import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;
- import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
- import javax.net.ssl.TrustManager;
- import javax.net.ssl.X509TrustManager;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.net.InetAddress;
- import java.net.Socket;
- import java.net.UnknownHostException;
- import java.security.KeyManagementException;
- import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
- import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
- /**
- * oa侧升级tls协议为tls1.2及以上,我方进行适配
- */
- public class CustomSSLProtocolSocketFactory implements SecureProtocolSocketFactory {
- private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CustomSSLProtocolSocketFactory.class);
- private final SSLContext sslContext;
- public CustomSSLProtocolSocketFactory() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, KeyManagementException {
- sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLSv1.2");
- // 初始化 SSLContext(使用默认的 TrustManager)
- sslContext.init(null, new TrustManager[]{new X509TrustManager() {
- @Override
- public void checkClientTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain, String authType) {
- // 信任所有客户端证书
- }
- @Override
- public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain, String authType) {
- // 信任所有服务器证书
- }
- @Override
- public X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() {
- return new X509Certificate[0];
- }
- }}, null);
- }
- /**
- * @see SecureProtocolSocketFactory#createSocket(java.lang.String,int,java.net.InetAddress,int)
- */
- public Socket createSocket(
- String host,
- int port,
- InetAddress clientHost,
- int clientPort)
- throws IOException, UnknownHostException {
- SSLSocketFactory socketFactory = sslContext.getSocketFactory();
- // logger.info("socketFactory:" + socketFactory);
- return socketFactory.createSocket(
- host,
- port,
- clientHost,
- clientPort
- );
- }
- public Socket createSocket(
- final String host,
- final int port,
- final InetAddress localAddress,
- final int localPort,
- final HttpConnectionParams params
- ) throws IOException, UnknownHostException, ConnectTimeoutException {
- if (params == null) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parameters may not be null");
- }
- int timeout = params.getConnectionTimeout();
- if (timeout == 0) {
- return createSocket(host, port, localAddress, localPort);
- } else {
- logger.error("not support connection timeout param");
- return createSocket(host, port, localAddress, localPort);
- }
- }
- /**
- * @see SecureProtocolSocketFactory#createSocket(java.lang.String,int)
- */
- public Socket createSocket(String host, int port)
- throws IOException, UnknownHostException {
- SSLSocketFactory socketFactory = sslContext.getSocketFactory();
- return socketFactory.createSocket(
- host,
- port
- );
- }
- /**
- * @see SecureProtocolSocketFactory#createSocket(java.net.Socket,java.lang.String,int,boolean)
- */
- public Socket createSocket(
- Socket socket,
- String host,
- int port,
- boolean autoClose)
- throws IOException, UnknownHostException {
- SSLSocketFactory socketFactory = sslContext.getSocketFactory();
- return socketFactory.createSocket(
- socket,
- host,
- port,
- autoClose
- );
- }
- /**
- * All instances of CustomSSLProtocolSocketFactory are the same.
- */
- public boolean equals(Object obj) {
- return ((obj != null) && obj.getClass().equals(CustomSSLProtocolSocketFactory.class));
- }
- /**
- * All instances of CustomSSLProtocolSocketFactory have the same hash code.
- */
- public int hashCode() {
- return CustomSSLProtocolSocketFactory.class.hashCode();
- }
-
- }
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/security/jsse/ReadDebug.html
总结
这个问题能解决,说白了,还是因为jdk1.7本来就支持tls1.2,只是因为默认用了tls.10,这里只是强制指定下。
希望能解决大家的问题就行了,维护老项目,处处小心点即可。今年估计要开始学python了,有领导安排的其他任务,量化什么的,python更适合点,所以以后学废了的话,可能也会更新一些java语言之外的。
来源:程序园用户自行投稿发布,如果侵权,请联系站长删除
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作! |