大纲
1.Netty的两大性能优化工具
2.FastThreadLocal的实现之构造方法
3.FastThreadLocal的实现之get()方法
4.FastThreadLocal的实现之set()方法
5.FastThreadLocal的总结
6.Recycler的设计理念
7.Recycler的使用
8.Recycler的四个核心组件
9.Recycler的初始化
10.Recycler的对象获取
11.Recycler的对象回收
12.异线程收割对象
13.Recycler的总结
14.Netty设计模式之单例模式
15.Netty设计模式之策略模式
16.Netty设计模式之装饰器模式
17.Netty设计模式之观察者模式
18.Netty设计模式之迭代器模式
19.Netty设计模式之责任链模式
1.Netty的两大性能优化工具
(1)FastThreadLocal
(2)Recycler
(1)FastThreadLocal
FastThreadLocal的作用与ThreadLocal相当,但比ThreadLocal更快。ThreadLocal的作用是多线程访问同一变量时能够通过线程本地化的方式避免多线程竞争、实现线程隔离。
Netty的FastThreadLocal重新实现了JDK的ThreadLocal的功能,且访问速度更快,但前提是使用FastThreadLocalThread线程。
(2)Recycler
Recycler实现了一个轻量级的对象池机制。对象池的作用是一方面可以实现快速创建对象,另一方面可以避免反复创建对象、减少YGC压力。
Netty使用Recycler的方式来获取ByteBuf对象的原因是:ByteBuf对象的创建在Netty里是非常频繁的且又比较占空间。但是如果对象比较小,使用对象池也不是那么划算。
2.FastThreadLocal的实现之构造方法
Netty为FastThreadLocal量身打造了FastThreadLocalThread和InternalThreadLocalMap两个重要的类,FastThreadLocal的构造方法会设置一个由final修饰的int型变量index,该index变量的值会由InternalThreadLocalMap的静态方法通过原子类来进行获取。- //A special variant of ThreadLocal that yields higher access performance when accessed from a FastThreadLocalThread.
- //Internally, a FastThreadLocal uses a constant index in an array, instead of using hash code and hash table, to look for a variable.
- //Although seemingly very subtle, it yields slight performance advantage over using a hash table, and it is useful when accessed frequently.
- //To take advantage of this thread-local variable, your thread must be a FastThreadLocalThread or its subtype.
- //By default, all threads created by DefaultThreadFactory are FastThreadLocalThread due to this reason.
- //Note that the fast path is only possible on threads that extend FastThreadLocalThread,
- //because it requires a special field to store the necessary state.
- //An access by any other kind of thread falls back to a regular ThreadLocal.
- //@param <V> the type of the thread-local variable
- public class FastThreadLocal<V> {
- //每个FastThreadLocal都有一个唯一的身份标识ID
- private final int index;
- //类初始化时调用,所以默认为variablesToRemoveIndex = 0
- //第n个值存放在数组下标为n的位置,下标为0的位置存所有FastThreadLocal<V>
- private static final int variablesToRemoveIndex = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
- public FastThreadLocal() {
- index = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
- }
- ...
- }
- //The internal data structure that stores the thread-local variables for Netty and all FastThreadLocals.
- //Note that this class is for internal use only and is subject to change at any time.
- //Use FastThreadLocal unless you know what you are doing.
- public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {
- public static final Object UNSET = new Object();
- public static int nextVariableIndex() {
- int index = nextIndex.getAndIncrement();
- if (index < 0) {
- nextIndex.decrementAndGet();
- throw new IllegalStateException("too many thread-local indexed variables");
- }
- return index;
- }
- ...
- }
- //The internal data structure that stores the thread-local variables for Netty and all FastThreadLocals.
- //Note that this class is for internal use only and is subject to change at any time.
- //Use FastThreadLocal unless you know what you are doing.
- class UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {
- static final ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap = new ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>();
- static final AtomicInteger nextIndex = new AtomicInteger();
- //Used by FastThreadLocal
- Object[] indexedVariables;
- ...
- }
3.FastThreadLocal的实现之get()方法
(1)FastThreadLocalThread的关键属性
(2)Thread与ThreadLocalMap
(3)FastThreadLocal.get()方法的实现流程
(4)从InternalThreadLocalMap中获取值
(1)FastThreadLocalThread的关键属性
FastThreadLocal继承了Thread类,每个FastThreadLocalThread线程对应一个InternalThreadLocalMap实例。只有FastThreadLocal和FastThreadLocalThread线程组合在一起使用的时候才能发挥出FastThreadLocal的性能优势。- public class FastThreadLocalThread extends Thread {
- private InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap;
- public FastThreadLocalThread() { }
- public FastThreadLocalThread(Runnable target) {
- super(target);
- }
- public FastThreadLocalThread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target) {
- super(group, target);
- }
- public FastThreadLocalThread(String name) {
- super(name);
- }
- public FastThreadLocalThread(ThreadGroup group, String name) {
- super(group, name);
- }
- public FastThreadLocalThread(Runnable target, String name) {
- super(target, name);
- }
- public FastThreadLocalThread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name) {
- super(group, target, name);
- }
- public FastThreadLocalThread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) {
- super(group, target, name, stackSize);
- }
-
- //Returns the internal data structure that keeps the thread-local variables bound to this thread.
- //Note that this method is for internal use only, and thus is subject to change at any time.
- public final InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap() {
- return threadLocalMap;
- }
-
- //Sets the internal data structure that keeps the thread-local variables bound to this thread.
- //Note that this method is for internal use only, and thus is subject to change at any time.
- public final void setThreadLocalMap(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
- //这个方法会在调用InternalThreadLocalMap.get()方法时被调用
- //具体就是通过fastGet()方法设置FastThreadLocalThread一个新创建的InternalThreadLocalMap对象
- this.threadLocalMap = threadLocalMap;
- }
- }
注意:每个Thread线程对应一个ThreadLocalMap实例。ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap是采用线性探测法来解决哈希冲突的。- public class Thread implements Runnable {
- ...
- //ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained by the ThreadLocal class.
- ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
- ...
- }
- public class ThreadLocal<T> {
- ...
- //Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable.
- //If the variable has no value for the current thread,
- //it is first initialized to the value returned by an invocation of the #initialValue method.
- //@return the current thread's value of this thread-local
- public T get() {
- Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
- ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
- if (map != null) {
- ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
- if (e != null) {
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- T result = (T)e.value;
- return result;
- }
- }
- return setInitialValue();
- }
-
- //ThreadLocalMap is a customized hash map suitable only for maintaining thread local values.
- //No operations are exported outside of the ThreadLocal class.
- //The class is package private to allow declaration of fields in class Thread.
- //To help deal with very large and long-lived usages, the hash table entries use WeakReferences for keys.
- //However, since reference queues are not used,
- //stale entries are guaranteed to be removed only when the table starts running out of space.
- static class ThreadLocalMap {
- //The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using its main ref field as the key (which is always a ThreadLocal object).
- //Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get() == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the entry can be expunged from table.
- //Such entries are referred to as "stale entries" in the code that follows.
- static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
- //The value associated with this ThreadLocal.
- Object value;
- Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
- super(k);
- value = v;
- }
- }
- //The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two.
- private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
-
- //The table, resized as necessary.
- //table.length MUST always be a power of two.
- private Entry[] table;
- //The number of entries in the table.
- private int size = 0;
- //The next size value at which to resize.
- private int threshold; // Default to 0
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
InternalThreadLocalMap.get()方法会分别通过fastGet()和slowGet()来获取一个InternalThreadLocalMap对象。
如果当前线程是普通线程则调用slowGet()方法,让每个线程通过JDK的ThreadLocal来拿到一个InternalThreadLocalMap对象,所以如果普通线程使用FastThreadLocal其实和普通线程使用ThreadLocal是一样的。
如果当前线程是FastThreadLocalThread线程则调用fastGet()方法,由于FastThreadLocalThread线程维护了一个InternalThreadLocalMap对象,所以fastGet()方法相当于直接从线程对象里把这个InternalThreadLocalMap拿出来。
注意:Reactor线程所创建的线程实体便是FastThreadLocalThread线程。- //A special variant of ThreadLocal that yields higher access performance when accessed from a FastThreadLocalThread.
- //Internally, a FastThreadLocal uses a constant index in an array, instead of using hash code and hash table, to look for a variable.
- //Although seemingly very subtle, it yields slight performance advantage over using a hash table, and it is useful when accessed frequently.
- //To take advantage of this thread-local variable, your thread must be a FastThreadLocalThread or its subtype.
- //By default, all threads created by DefaultThreadFactory are FastThreadLocalThread due to this reason.
- //Note that the fast path is only possible on threads that extend FastThreadLocalThread,
- //because it requires a special field to store the necessary state.
- //An access by any other kind of thread falls back to a regular ThreadLocal.
- //@param <V> the type of the thread-local variable
- public class FastThreadLocal<V> {
- //每个FastThreadLocal都有一个唯一的身份标识ID
- //每个FastThreadLocal对应的V值存储在当前FastThreadLocalThread线程维护的InternalThreadLocalMap的下标为index的位置
- private final int index;
-
- //类初始化时调用,所以默认为variablesToRemoveIndex = 0
- //第n个值存放在数组下标为n的位置,下标为0的位置会存储所有FastThreadLocal<V>
- private static final int variablesToRemoveIndex = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
- public FastThreadLocal() {
- //每new一个FastThreadLocal,index就会自增1,所以index是FastThreadLocal的唯一身份ID
- index = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
- }
-
- //Returns the current value for the current thread
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public final V get() {
- //首先获取由当前FastThreadLocalThread线程维护的InternalThreadLocalMap
- InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();
- //从数组中取出index位置的元素
- Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index);
- //如果获取到的元素不是一个UNSET即一个new Object(),则返回该元素
- if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
- return (V) v;
- }
- //如果获取到的数组元素是缺省对象,则对threadLocalMap在index位置的元素值执行初始化操作
- return initialize(threadLocalMap);
- }
-
- private V initialize(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
- V v = null;
- try {
- //通过initialValue()方法对threadLocalMap在index位置的元素值进行初始化
- //initialValue()方法可以被FastThreadLocal<V>的子类重写
- v = initialValue();
- } catch (Exception e) {
- PlatformDependent.throwException(e);
- }
- //设置threadLocalMap数组在下标index处的元素值
- threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(index, v);
- addToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);
- return v;
- }
-
- //Returns the initial value for this thread-local variable.
- protected V initialValue() throws Exception {
- return null;
- }
- private static void addToVariablesToRemove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, FastThreadLocal<?> variable) {
- //获取threadLocalMap数组下标为0的元素
- Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex);
- Set<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove;
-
- //将variable添加到数组下标为0位置的Set集合中,以便可以通过remove()方法统一删除
- if (v == InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET || v == null) {
- //创建FastThreadLocal类型的Set集合
- variablesToRemove = Collections.newSetFromMap(new IdentityHashMap<FastThreadLocal<?>, Boolean>());
- //将variablesToRemove这个Set集合设置到数组下标为0的位置
- threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex, variablesToRemove);
- } else {
- //强转获得Set集合
- variablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v;
- }
- variablesToRemove.add(variable);
- }
- ...
- }
对于当前线程维护的InternalThreadLocalMap对象里的数组indexedVariables,可以通过下标方式indexedVariables[index]获取一个Object。
初始化InternalThreadLocalMap对象时,会初始化一个32个元素的indexedVariables数组,每一个元素都是UNSET值。
4.FastThreadLocal的实现之set()方法
(1)FastThreadLocal.set()方法的实现流程
(2)向InternalThreadLocalMap设置值
(3)InternalThreadLocalMap的扩容原理
(1)FastThreadLocal.set()方法的实现流程
首先获取由当前FastThreadLocalThread线程维护的InternalThreadLocalMap。然后通过唯一标识当前FastThreadLocal对象的索引index,给InternalThreadLocalMap数组中对应的位置设置值。接着将当前FastThreadLocal对象保存到待清理的Set中,如果设置的值是一个缺省的Object对象,则通过remove()方法删除InternalThreadLocalMap数组中对应位置的元素。- //The internal data structure that stores the thread-local variables for Netty and all FastThreadLocals.
- //Note that this class is for internal use only and is subject to change at any time.
- //Use FastThreadLocal unless you know what you are doing.
- public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {
- public static final Object UNSET = new Object();
- private static final int INDEXED_VARIABLE_TABLE_INITIAL_SIZE = 32;
- ...
- private InternalThreadLocalMap() {
- //设置父类的成员变量indexedVariables的初始值
- super(newIndexedVariableTable());
- }
- private static Object[] newIndexedVariableTable() {
- //初始化一个32个元素的数组
- Object[] array = new Object[INDEXED_VARIABLE_TABLE_INITIAL_SIZE];
- //每个元素都是UNSET值
- Arrays.fill(array, UNSET);
- return array;
- }
-
- //index是当前访问的FastThreadLocal在JVM里的索引
- //indexedVariables数组是当前线程维护的InternalThreadLocalMap对象在初始化时创建的
- public Object indexedVariable(int index) {
- Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
- //直接通过索引来取出对象
- return index < lookup.length? lookup[index] : UNSET;
- }
-
- public static InternalThreadLocalMap get() {
- Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
- if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
- return fastGet((FastThreadLocalThread) thread);
- } else {
- return slowGet();
- }
- }
- private static InternalThreadLocalMap fastGet(FastThreadLocalThread thread) {
- InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = thread.threadLocalMap();
- if (threadLocalMap == null) {
- thread.setThreadLocalMap(threadLocalMap = new InternalThreadLocalMap());
- }
- return threadLocalMap;
- }
- private static InternalThreadLocalMap slowGet() {
- //如果普通线程使用FastThreadLocal其实和普通线程使用ThreadLocal是一样的
- //因为此时返回的是一个通过ThreadLocal维护的InternalThreadLocalMap对象
- ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap = UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap.slowThreadLocalMap;
- InternalThreadLocalMap ret = slowThreadLocalMap.get();
- if (ret == null) {
- ret = new InternalThreadLocalMap();
- slowThreadLocalMap.set(ret);
- }
- return ret;
- }
- ...
- }
- class UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {
- static final ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap = new ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>();
- static final AtomicInteger nextIndex = new AtomicInteger();
- //Used by FastThreadLocal
- Object[] indexedVariables;
- ...
- UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap(Object[] indexedVariables) {
- this.indexedVariables = indexedVariables;
- }
- ...
- }
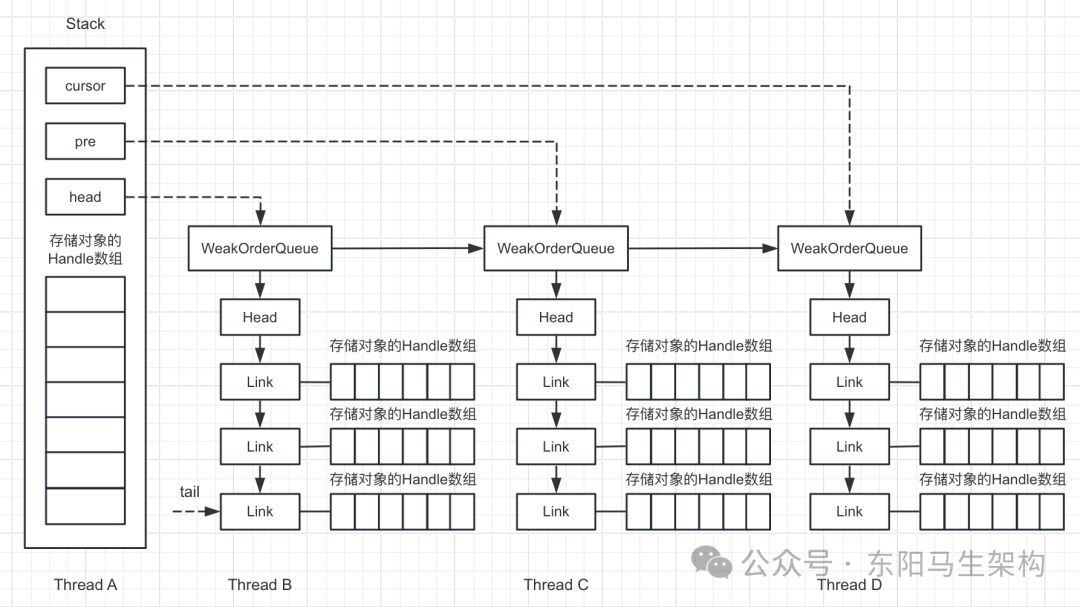
(3)第二个核心组件是WeakOrderQueue
WeakOrderQueue的作用是用于存储其他线程(异线程)回收由当前线程所分配的对象,并且在合适的时机,Stack会从异线程的WeakOrderQueue中收割对象。- public class FastThreadLocal<V> {
- //每个FastThreadLocal都有一个唯一的身份标识ID
- //每个FastThreadLocal对应的V值存储在当前FastThreadLocalThread线程维护的InternalThreadLocalMap的下标为index的位置
- private final int index;
-
- //类初始化时调用,所以默认为variablesToRemoveIndex = 0
- //第n个值存放在数组下标为n的位置,下标为0的位置会存储所有FastThreadLocal<V>
- private static final int variablesToRemoveIndex = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
- ...
-
- //Set the value for the current thread.
- public final void set(V value) {
- if (value != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
- InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();
- setKnownNotUnset(threadLocalMap, value);
- } else {
- remove();
- }
- }
-
- private void setKnownNotUnset(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, V value) {
- //将当前FastThreadLocal对象对应的数据添加到当前线程维护的InternalThreadLocalMap中
- if (threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(index, value)) {
- //将当前FastThreadLocal对象保存到待清理的Set中
- addToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);
- }
- }
-
- private static void addToVariablesToRemove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, FastThreadLocal<?> variable) {
- //获取threadLocalMap数组下标为0的元素
- Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex);
- Set<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove;
-
- //将variable添加到数组下标为0位置的Set集合中,以便可以通过remove()方法统一删除
- if (v == InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET || v == null) {
- //创建FastThreadLocal类型的Set集合
- variablesToRemove = Collections.newSetFromMap(new IdentityHashMap<FastThreadLocal<?>, Boolean>());
- //将variablesToRemove这个Set集合设置到数组下标为0的位置
- threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex, variablesToRemove);
- } else {
- //强转获得Set集合
- variablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v;
- }
- variablesToRemove.add(variable);
- }
-
- //Sets the value to uninitialized;
- //a proceeding call to get() will trigger a call to initialValue().
- public final void remove() {
- remove(InternalThreadLocalMap.getIfSet());
- }
- //Sets the value to uninitialized for the specified thread local map;
- //a proceeding call to get() will trigger a call to initialValue().
- //The specified thread local map must be for the current thread.
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public final void remove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
- if (threadLocalMap == null) {
- return;
- }
-
- //删除数组下标index位置对应的value
- Object v = threadLocalMap.removeIndexedVariable(index);
-
- //从数组下标0的位置取出Set集合,删除当前FastThreadLocal对象
- removeFromVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);
- if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
- try {
- //和initValue()方法一样,可以被FastThreadLocal的子类重写
- onRemoval((V) v);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- PlatformDependent.throwException(e);
- }
- }
- }
-
- //Returns the initial value for this thread-local variable.
- protected V initialValue() throws Exception {
- return null;
- }
- //Invoked when this thread local variable is removed by #remove().
- //Be aware that #remove() is not guaranteed to be called when the `Thread` completes which means
- //you can not depend on this for cleanup of the resources in the case of `Thread` completion.
- protected void onRemoval(@SuppressWarnings("UnusedParameters") V value) throws Exception {
-
- }
- ...
- }
每个WeakOrderQueue中都包含一个Link链表。回收对象都会被存放在Link链表的结点上,每个Link结点默认存储16个对象。当每个Link结点存储满了,会创建新的Link结点并放入链表尾部。
(5)第四个核心组件是DefaultHandle
一个对象在发起回收时需要调用DefaultHandle的recycle()方法进行具体的回收处理,这个要被回收的对象会保存在DefaultHandle中。
Stack和WeakOrderQueue都使用DefaultHandle来存储被回收的对象。在Stack和Link中都有一个elements数组,该数组保存的就是一个个的DefaultHandle实例。- //The internal data structure that stores the thread-local variables for Netty and all FastThreadLocals.
- //Note that this class is for internal use only and is subject to change at any time.
- //Use FastThreadLocal unless you know what you are doing.
- public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap {
- public static final Object UNSET = new Object();
- ...
- //index是当前访问的FastThreadLocal在JVM里的索引
- //indexedVariables数组是当前线程维护的InternalThreadLocalMap对象在初始化时创建的
- public Object indexedVariable(int index) {
- Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
- //直接通过索引来取出对象
- return index < lookup.length? lookup[index] : UNSET;
- }
-
- //如果设置的是新值,则返回true;如果设置的是旧值,则返回false;
- public boolean setIndexedVariable(int index, Object value) {
- Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
- if (index < lookup.length) {
- Object oldValue = lookup[index];
- //直接将数组index位置的元素设置为value,时间复杂度为O(1)
- lookup[index] = value;
- return oldValue == UNSET;
- } else {
- //扩容数组
- expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(index, value);
- return true;
- }
- }
-
- //通过无符号右移和位或运算实现2^n * 2,这与HashMap的扩容原理是一样的
- private void expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(int index, Object value) {
- Object[] oldArray = indexedVariables;
- final int oldCapacity = oldArray.length;
- int newCapacity = index;//假设index = 16,也就是1000
- newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 1;//变为1100
- newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 2;//变为1111
- newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 4;//还是1111
- newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 8;//还是1111
- newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 16;//还是1111
- newCapacity ++;//变为10000
- Object[] newArray = Arrays.copyOf(oldArray, newCapacity);
- Arrays.fill(newArray, oldCapacity, newArray.length, UNSET);
- newArray[index] = value;
- indexedVariables = newArray;
- }
-
- //根据不同的Thread返回InternalThreadLocalMap
- public static InternalThreadLocalMap getIfSet() {
- Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
- if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
- return ((FastThreadLocalThread) thread).threadLocalMap();
- }
- return slowThreadLocalMap.get();
- }
- ...
- }
创建Recycler的方法是直接new一个Recycler。每个Recycler里都有一个threadLocal变量,即FastThreadLocal。所以每个Recycler里对于每个线程都会有一个Stack对象。调用Recycler的get()方法获取T类对象时,便会初始化一个Stack对象。- public class RecycleTest {
- private static final Recycler<User> RECYCLER = new Recycler<User>() {
- protected User newObject(Handle<User> handle) {
- return new User(handle);
- }
- };
-
- private static class User {
- //创建Recycler.Handle<User>对象与User对象进行绑定
- private final Recycler.Handle<User> handle;
- public User(Recycler.Handle<User> handle) {
- this.handle = handle;
- }
- public void recycle() {
- handle.recycle(this);
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //1.从对象池中获取User对象
- User user1 = RECYCLER.get();
- //2.回收对象到对象池
- user1.recycle();
- //3.从对象池中获取对象
- User user2 = RECYCLER.get();
- System.out.println(user1 == user2);
- }
- }
在当前线程创建对象,也在当前线程进行回收。
Stack的pushNow()方法的主要逻辑是:回收每8个对象中的一个,以及将回收的对象存放到Stack.elements数组时可能需要的扩容处理。
(3)异线程回收对象
在当前线程创建对象,但在其他线程进行回收。
说明一:
Stack.pushLater()方法中的DELAYED_RECYCLED是一个FastThreadLocal类型的对象,可以通过这个FastThreadLocal对象获取一个Map。
所以每个线程都会有一个Map,这个Map的key是Stack,这个Map的value是WeakOrderQueue。每个线程的Map表示的是对这个线程来说,不同的Stack对应着其他线程绑定的Stack,而由其他线程创建的对象会存放在其他线程绑定的Stack的WeakOrderQueue里。
使用Map结构是为了防止DELAYED_RECYCLED内存膨胀,使用Map结构也可以在当前线程中帮忙快速定位其他线程应该对应于当前线程Stack的哪个WeakOrderQueue。从"delayedRecycled.size() >= maxDelayedQueues"可以看出每个线程最多帮助2倍CPU核数的线程回收对象。
说明二:
在pushLater(item, currentThread)中,假设currentThread是线程2,里面的this是线程1的Stack。
那么"queue = delayedRecycled.get(this)"会去拿线程1对应的WeakOrderQueue。拿到后若"queue == null",那么就说明线程2从来没有回收过线程1的对象。
"queue = newWeakOrderQueue(thread)"会创建一个WeakOrderQueue,也就是去为线程2(thread)去分配一个线程1的Stack对应的WeakOrderQueue,然后通过delayedRecycled.put(this, queue)绑定线程1。
说明三:
WeakOrderQueue中有一个Link链表。一个Link的大小是16,每个元素都是一个DefaultHandle。为什么一个Link对应16个DefaultHandle,而不是一个Link对应一个DefaultHandle。
如果一个Link对应一个DefaultHandle,那么每次同线程去回收异线程都要创建一个Link对象。比如线程2去回收线程1创建的对象,每次都需要创建一个Link对象然后添加到Link链表中,并且每次都需要判断当前线程1是否还允许继续分配一个Link。
把多个DefaultHandle放在一个Link中的好处是不必每次都要判断当前线程2能否回收线程1的对象,只需要判断当前Link是否满了即可,这也体现了Netty进行优化处理的一个思路,也就是通过批量的方式减少某些操作的频繁执行。
说明四:
创建WeakOrderQueue对象时,也就是执行代码"new WeakOrderQueue(stack, thread)",使用的是头插法往当前线程的Stack添加WeakOrderQueue对象。
说明五:
WeakOrderQueue的add()方法添加对象到WeakOrderQueue时,首先会将tail结点的Link填满,然后再新创建一个Link插入到tail结点。其中LINK_CAPACITY表示Link的DefaultHandle数组的最大长度,默认是16。
12.异线程收割对象
说明一:
线程的Stack里有3指针:head、pre、cursor。往Stack中插入一个WeakOrderQueue都是往头部插入的(头插法)。head指向第一个WeakOrderQueue,cursor指向当前回收对象的WeakOrderQueue。
说明二:
scavenge()方法会从其他线程回收的对象中尝试转移对象。如果成功则返回,否则设置cursor为head,以便下次从头开始获取。
说明三:
scavengeSome()方法会首先判断cursor是否为null。如果cursor为null,则设置cursor为head结点。接着执行do while循环不断尝试从其他线程的WeakOrderQueue中,转移一些对象到当前线程的Stack的一个DefaultHandle数组中。
说明四:
cursor.transfer()方法会把WeakOrderQueue里的对象传输到当前线程的Stack的elements数组里。如果传输成功就结束do while循环,如果传输失败就获取cursor的下一个结点cursor.next继续处理。
说明五:
cursor.transfer()方法每次都只取WeakOrderQueue里的一个Link,然后传输Link里的elements数组元素到目标Stack的elements数组中。如果cursor = null或success = true,则do while循环结束。所有的WeakOrderQueue默认时最多总共可以有:2K / 16 = 128个Link。- public abstract class Recycler<T> {
- ...
- private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_MAX_CAPACITY_PER_THREAD = 4 * 1024;//Use 4k instances as default.
- private static final int DEFAULT_MAX_CAPACITY_PER_THREAD;
- private static final int MAX_SHARED_CAPACITY_FACTOR;
- private static final int MAX_DELAYED_QUEUES_PER_THREAD;
- private static final int LINK_CAPACITY;
- private static final int RATIO;
-
- static {
- int maxCapacityPerThread = SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.recycler.maxCapacityPerThread",
- SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.recycler.maxCapacity", DEFAULT_INITIAL_MAX_CAPACITY_PER_THREAD));
- if (maxCapacityPerThread < 0) {
- maxCapacityPerThread = DEFAULT_INITIAL_MAX_CAPACITY_PER_THREAD;
- }
- DEFAULT_MAX_CAPACITY_PER_THREAD = maxCapacityPerThread;
- MAX_SHARED_CAPACITY_FACTOR = max(2, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.recycler.maxSharedCapacityFactor", 2));
- MAX_DELAYED_QUEUES_PER_THREAD = max(0, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.recycler.maxDelayedQueuesPerThread", NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2));
- LINK_CAPACITY = safeFindNextPositivePowerOfTwo(max(SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.recycler.linkCapacity", 16), 16));
- RATIO = safeFindNextPositivePowerOfTwo(SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.recycler.ratio", 8));
- ...
- }
-
- private static final FastThreadLocal<Map<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue>> DELAYED_RECYCLED = new FastThreadLocal<Map<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue>>() {
- @Override
- protected Map<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue> initialValue() {
- return new WeakHashMap<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue>();
- }
- };
-
- private final int maxCapacityPerThread;
- private final int maxSharedCapacityFactor;
- private final int interval;
- private final int maxDelayedQueuesPerThread;
- private final FastThreadLocal<Stack<T>> threadLocal = new FastThreadLocal<Stack<T>>() {
- @Override
- protected Stack<T> initialValue() {
- return new Stack<T>(Recycler.this, Thread.currentThread(), maxCapacityPerThread, maxSharedCapacityFactor, interval, maxDelayedQueuesPerThread);
- }
- @Override
- protected void onRemoval(Stack<T> value) {
- //Let us remove the WeakOrderQueue from the WeakHashMap directly if its safe to remove some overhead
- if (value.threadRef.get() == Thread.currentThread()) {
- if (DELAYED_RECYCLED.isSet()) {
- DELAYED_RECYCLED.get().remove(value);
- }
- }
- }
- };
- protected Recycler() {
- this(DEFAULT_MAX_CAPACITY_PER_THREAD);
- }
- protected Recycler(int maxCapacityPerThread) {
- this(maxCapacityPerThread, MAX_SHARED_CAPACITY_FACTOR);
- }
- protected Recycler(int maxCapacityPerThread, int maxSharedCapacityFactor) {
- this(maxCapacityPerThread, maxSharedCapacityFactor, RATIO, MAX_DELAYED_QUEUES_PER_THREAD);
- }
- protected Recycler(int maxCapacityPerThread, int maxSharedCapacityFactor, int ratio, int maxDelayedQueuesPerThread) {
- interval = safeFindNextPositivePowerOfTwo(ratio);
- if (maxCapacityPerThread <= 0) {
- this.maxCapacityPerThread = 0;
- this.maxSharedCapacityFactor = 1;
- this.maxDelayedQueuesPerThread = 0;
- } else {
- this.maxCapacityPerThread = maxCapacityPerThread;
- this.maxSharedCapacityFactor = max(1, maxSharedCapacityFactor);
- this.maxDelayedQueuesPerThread = max(0, maxDelayedQueuesPerThread);
- }
- }
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public final T get() {
- if (maxCapacityPerThread == 0) {
- return newObject((Handle<T>) NOOP_HANDLE);
- }
- Stack<T> stack = threadLocal.get();
- DefaultHandle<T> handle = stack.pop();
- if (handle == null) {
- //创建一个DefaultHandle
- handle = stack.newHandle();
- //创建一个对象,并绑定这个DefaultHandle
- handle.value = newObject(handle);
- }
- return (T) handle.value;
- }
- ...
- }
13.Recycler的总结
(1)获取对象和回收对象的思路总结
(2)获取对象的具体步骤总结
(3)对象池的设计核心
(1)获取对象和回收对象的思路总结
对象池有两个重要的组成部分:Stack和WeakOrderQueue。
从Recycler获取对象时,优先从Stack中查找可用对象。如果Stack中没有可用对象,会尝试从WeakOrderQueue迁移一些对象到Stack中。
Recycler回收对象时,分为同线程对象回收和异线程对象回收这两种情况。同线程回收直接向Stack添加对象,异线程回收会向WeakOrderQueue中的最后一个Link添加对象。
同线程回收和异线程回收都会控制回收速率,默认每8个对象会回收一个,其他的全部丢弃。
(2)获取对象的具体步骤总结
如何从一个对象池里获取对象:
步骤一:首先通过FastThreadLocal方式拿到当前线程的Stack。
步骤二:如果这个Stack里的elements数组有对象,则直接弹出。如果这个Stack里的elements数组没有对象,则从当前Stack关联的其他线程的WeakOrderQueue里的Link结点的elements数组中转移对象,到当前Stack里的elements数组里。
步骤三:如果转移成功,那么当前Stack里的elements数组就有对象了,这时就可以直接弹出。如果转移失败,那么接下来就直接创建一个对象然后和当前Stack进行关联。
步骤四:关联之后,后续如果是当前线程自己进行对象回收,则将该对象直接存放到当前线程的Stack里。如果是其他线程进行对象回收,则将该对象存放到其他线程与当前线程的Stack关联的WeakOrderQueue里。
(3)对象池的设计核心
为什么要分同线程和异线程进行处理,并设计一套比较复杂的数据结构?因为对象池的使用场景一般是高并发的环境,希望通过对象池来减少对象的频繁创建带来的性能损耗。所以在高并发的环境下,从对象池中获取对象和回收对象就只能通过以空间来换时间的思路进行处理,而ThreadLocal恰好是通过以空间换时间的思路来实现的,因此引入了FastThreadLocal来管理对象池里的对象。但是如果仅仅使用FastThreadLocal管理同线程创建和回收的对象,那么并不能充分体现对象池的作用。所以通过FastThreadLocal获取的Stack对象,应该不仅可以管理同线程的对象,也可以管理异线程的对象。为此,Recycler便分同线程和异线程进行处理并设计了一套比较复杂的数据结构。
14.Netty设计模式之单例模式
(1)单例模式的特点
(2)单例模式的例子
(3)Netty中的单例模式
(1)单例模式的特点
一.一个类全局只有一个对象
二.延迟创建
三.避免线程安全问题
(2)单例模式的例子- public abstract class Recycler<T> {
- ...
- private static final class Stack<T> {
- //所属的Recycler
- final Recycler<T> parent;
- //所属线程的弱引用
- final WeakReference<Thread> threadRef;
- //异线程回收对象时,其他线程能保存的被回收对象的最大个数
- final AtomicInteger availableSharedCapacity;
- //WeakOrderQueue最大个数
- private final int maxDelayedQueues;
- //对象池的最大大小,默认最大为4K
- private final int maxCapacity;
- //存储缓存数据的数组
- DefaultHandle<?>[] elements;
- //缓存的DefaultHandle对象个数
- int size;
- //WeakOrderQueue链表的三个重要结点
- private WeakOrderQueue cursor, prev;
- private volatile WeakOrderQueue head;
- Stack(Recycler<T> parent, Thread thread, int maxCapacity, int maxSharedCapacityFactor, int interval, int maxDelayedQueues) {
- this.parent = parent;
- threadRef = new WeakReference<Thread>(thread);
- this.maxCapacity = maxCapacity;
- availableSharedCapacity = new AtomicInteger(max(maxCapacity / maxSharedCapacityFactor, LINK_CAPACITY));
- elements = new DefaultHandle[min(INITIAL_CAPACITY, maxCapacity)];
- this.interval = interval;
- handleRecycleCount = interval;//Start at interval so the first one will be recycled.
- this.maxDelayedQueues = maxDelayedQueues;
- }
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
Netty中的单例模式大都使用饿汉模式,比如ReadTimeoutException、MqttEncoder。- public abstract class Recycler<T> {
- private static final int LINK_CAPACITY;
- static {
- ...
- LINK_CAPACITY = safeFindNextPositivePowerOfTwo(max(SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.recycler.linkCapacity", 16), 16));
- ...
- }
- ...
- //a queue that makes only moderate guarantees about visibility: items are seen in the correct order,
- //but we aren't absolutely guaranteed to ever see anything at all, thereby keeping the queue cheap to maintain
- private static final class WeakOrderQueue extends WeakReference<Thread> {
- ...
- static final class Link extends AtomicInteger {
- final DefaultHandle<?>[] elements = new DefaultHandle[LINK_CAPACITY];
- int readIndex;
- Link next;
- }
- private static final class Head {
- private final AtomicInteger availableSharedCapacity;
- Link link;
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
15.Netty设计模式之策略模式
(1)策略模式的特点
(2)策略模式的例子
(3)Netty中的策略模式
(1)策略模式的特点
一.封装一系列可相互替换的算法家族
二.动态选择某一个策略
(2)策略模式的例子- public abstract class Recycler<T> {
- ...
- private static final class DefaultHandle<T> implements Handle<T> {
- int lastRecycledId;
- int recycleId;
- boolean hasBeenRecycled;
- Stack<?> stack;
- Object value;
- DefaultHandle(Stack<?> stack) {
- this.stack = stack;
- }
- @Override
- public void recycle(Object object) {
- if (object != value) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("object does not belong to handle");
- }
- Stack<?> stack = this.stack;
- if (lastRecycledId != recycleId || stack == null) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("recycled already");
- }
- stack.push(this);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
Netty的DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory中的newChooser()方法就可以动态选择某具体策略;EventExecutorChooser接口中的next()方法就有两种实现算法:PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser.next()和GenericEventExecutorChooser.next()。- public abstract class Recycler<T> {
- ...
- private final FastThreadLocal<Stack<T>> threadLocal = new FastThreadLocal<Stack<T>>() {
- //在Recycler中调用threadLocal.get()时,便会触发调用这个initialValue()方法
- @Override
- protected Stack<T> initialValue() {
- return new Stack<T>(Recycler.this, Thread.currentThread(), maxCapacityPerThread, maxSharedCapacityFactor, interval, maxDelayedQueuesPerThread);
- }
- @Override
- protected void onRemoval(Stack<T> value) {
- //Let us remove the WeakOrderQueue from the WeakHashMap directly if its safe to remove some overhead
- if (value.threadRef.get() == Thread.currentThread()) {
- if (DELAYED_RECYCLED.isSet()) {
- DELAYED_RECYCLED.get().remove(value);
- }
- }
- }
- };
-
- private final int interval;
- private final int maxCapacityPerThread;
- private final int maxSharedCapacityFactor;
- private final int maxDelayedQueuesPerThread;
-
- protected Recycler(int maxCapacityPerThread, int maxSharedCapacityFactor, int ratio, int maxDelayedQueuesPerThread) {
- //默认是8,用于控制对象的回收比率
- interval = safeFindNextPositivePowerOfTwo(ratio);
- if (maxCapacityPerThread <= 0) {
- this.maxCapacityPerThread = 0;
- this.maxSharedCapacityFactor = 1;
- this.maxDelayedQueuesPerThread = 0;
- } else {
- //对象池的最大大小,能存多少元素,默认4K
- this.maxCapacityPerThread = maxCapacityPerThread;
- //默认是2
- this.maxSharedCapacityFactor = max(1, maxSharedCapacityFactor);
- //默认2倍CPU核数
- this.maxDelayedQueuesPerThread = max(0, maxDelayedQueuesPerThread);
- }
- }
-
- private static final class Stack<T> {
- ...
- //异线程回收对象时,其他线程能保存的被回收对象的最大个数
- final AtomicInteger availableSharedCapacity;
-
- Stack(Recycler<T> parent, Thread thread, int maxCapacity, int maxSharedCapacityFactor, int interval, int maxDelayedQueues) {
- ...
- availableSharedCapacity = new AtomicInteger(max(maxCapacity / maxSharedCapacityFactor, LINK_CAPACITY));
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
16.Netty设计模式之装饰器模式
(1)装饰器模式的特点
(2)装饰器模式的例子
(3)Netty中的装饰器模式
(1)装饰器模式的特点
一.装饰者和被装饰者继承自同一个接口
二.装饰者给被装饰者动态修改行为(丰富类的功能)
(2)装饰器模式的例子- public abstract class Recycler<T> {
- ...
- public final T get() {
- ...
- //获取当前线程缓存的Stack
- Stack<T> stack = threadLocal.get();
- //从Stack中弹出一个DefaultHandle对象
- DefaultHandle<T> handle = stack.pop();
- if (handle == null) {
- //创建一个DefaultHandle
- handle = stack.newHandle();
- //创建一个对象并保存到DefaultHandle
- handle.value = newObject(handle);
- }
- return (T) handle.value;
- }
-
- //由Recycler的子类来实现创建对象
- protected abstract T newObject(Handle<T> handle);
-
- private static final class Stack<T> {
- ...
- DefaultHandle<T> pop() {
- int size = this.size;
- if (size == 0) {
- //尝试从其他线程回收的对象中转移一些到Stack的DefaultHandle数组中
- if (!scavenge()) {
- return null;
- }
- size = this.size;
- if (size <= 0) {
- return null;
- }
- }
- size --;
- //将对象实例从DefaultHandle数组(elements)的栈顶弹出
- DefaultHandle ret = elements[size];
- elements[size] = null;
- //As we already set the element[size] to null we also need to store the updated size before we do any validation.
- //Otherwise we may see a null value when later try to pop again without a new element added before.
- this.size = size;
-
- if (ret.lastRecycledId != ret.recycleId) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("recycled multiple times");
- }
- ret.recycleId = 0;
- ret.lastRecycledId = 0;
- return ret;
- }
-
- DefaultHandle<T> newHandle() {
- return new DefaultHandle<T>(this);
- }
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
Netty中的SimpleLeakAwareByteBuf、UnreleasableByteBuf、WrappedByteBuf便用到了装饰器模式。每次调用WrappedByteBuf的方法,都会委托到被装饰的ByteBuf。这个WrappedByteBuf其实是Netty里装饰ByteBuf的一个基类,它基本是直接使用了ByteBuf的方法。
WrappedByteBuf有两个子类:SimpleLeakAwareByteBuf和UnreleasableByteBuf。这两个子类都是装饰者,被装饰者都是ByteBuf,在它们的构造函数中传入。- public abstract class Recycler<T> {
- ...
- public final T get() {
- ...
- //获取当前线程缓存的Stack
- Stack<T> stack = threadLocal.get();
- //从Stack中弹出一个DefaultHandle对象
- DefaultHandle<T> handle = stack.pop();
- if (handle == null) {
- //创建一个DefaultHandle
- handle = stack.newHandle();
- //创建一个对象并保存到DefaultHandle
- handle.value = newObject(handle);
- }
- return (T) handle.value;
- }
-
- //从Recycler的get()方法可知:
- //一个对象在创建时就会和一个新创建的DefaultHandle绑定
- //而该DefaultHandle又会和创建该对象的线程绑定,因为DefaultHandle会和Stack绑定,而Stack又会绑定创建该对象的线程
- private static final class DefaultHandle<T> implements Handle<T> {
- ...
- Stack<?> stack;
- Object value;
- DefaultHandle(Stack<?> stack) {
- this.stack = stack;
- }
- @Override
- public void recycle(Object object) {
- ...
- Stack<?> stack = this.stack;
- stack.push(this);
- }
- }
-
- private static final class Stack<T> {
- //一个线程调用Recycler.get()方法创建一个对象时,会先获取和该线程绑定的Stack
- //然后由该Stack创建一个DefaultHandle,接着再创建一个对象并将对象保存到这个DefaultHandle中
- final WeakReference<Thread> threadRef;
- ...
- //当一个对象调用它绑定的DefaultHandle进行回收时,可以通过threadRef取到创建它的线程
- void push(DefaultHandle<?> item) {
- Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
- if (threadRef.get() == currentThread) {
- //The current Thread is the thread that belongs to the Stack, we can try to push the object now.
- pushNow(item);
- } else {
- //The current Thread is not the one that belongs to the Stack (or the Thread that belonged to the Stack was collected already),
- //we need to signal that the push happens later.
- pushLater(item, currentThread);
- }
- }
-
- private void pushNow(DefaultHandle<?> item) {
- //防止被多次回收
- if ((item.recycleId | item.lastRecycledId) != 0) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("recycled already");
- }
- item.recycleId = item.lastRecycledId = OWN_THREAD_ID;
-
- int size = this.size;
- //通过dropHandle(item)来实现:回收每8个对象中的一个
- if (size >= maxCapacity || dropHandle(item)) {
- //超出最大容量或被回收速率控制则不回收
- return;
- }
- if (size == elements.length) {
- //扩容
- elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, min(size << 1, maxCapacity));
- }
- elements[size] = item;
- this.size = size + 1;
- }
-
- //回收每8个对象中的一个
- boolean dropHandle(DefaultHandle<?> handle) {
- if (!handle.hasBeenRecycled) {
- //interval默认是8
- if (handleRecycleCount < interval) {
- handleRecycleCount++;
- //Drop the object.
- return true;
- }
- handleRecycleCount = 0;
- handle.hasBeenRecycled = true;
- }
- return false;
- }
- private void pushLater(DefaultHandle<?> item, Thread thread) {
- ...
- //取出由当前线程帮助其他线程回收对象的缓存
- Map<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue> delayedRecycled = DELAYED_RECYCLED.get();
- //取出对象绑定的Stack对应的WeakOrderQueue
- WeakOrderQueue queue = delayedRecycled.get(this);
- if (queue == null) {
- //最多帮助2 * CPU核数的线程回收对象
- if (delayedRecycled.size() >= maxDelayedQueues) {
- //WeakOrderQueue.DUMMY就是new一个WeakOrderQueue,表示无法再帮该Stack回收对象
- delayedRecycled.put(this, WeakOrderQueue.DUMMY);
- return;
- }
- //新建WeakOrderQueue
- if ((queue = newWeakOrderQueue(thread)) == null) {
- //drop object
- return;
- }
- delayedRecycled.put(this, queue);
- } else if (queue == WeakOrderQueue.DUMMY) {
- //drop object
- return;
- }
- //添加对象到WeakOrderQueue的Link链表中
- queue.add(item);
- }
-
- //Allocate a new WeakOrderQueue or return null if not possible.
- private WeakOrderQueue newWeakOrderQueue(Thread thread) {
- return WeakOrderQueue.newQueue(this, thread);
- }
- ...
- }
-
- //每个线程都有一个Map<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue>,存放了其他线程及其对应WeakOrderQueue的映射
- private static final FastThreadLocal<Map<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue>> DELAYED_RECYCLED =
- new FastThreadLocal<Map<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue>>() {
- @Override
- protected Map<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue> initialValue() {
- return new WeakHashMap<Stack<?>, WeakOrderQueue>();
- }
- };
- ...
-
- private static final class WeakOrderQueue extends WeakReference<Thread> {
- ...
- static final class Link extends AtomicInteger {
- //一个大小为16的DefaultHandle数组
- final DefaultHandle<?>[] elements = new DefaultHandle[LINK_CAPACITY];
- int readIndex;
- Link next;
- }
-
- static WeakOrderQueue newQueue(Stack<?> stack, Thread thread) {
- //We allocated a Link so reserve the space
- if (!Head.reserveSpaceForLink(stack.availableSharedCapacity)) {
- return null;
- }
- final WeakOrderQueue queue = new WeakOrderQueue(stack, thread);
- stack.setHead(queue);
- return queue;
- }
-
- private WeakOrderQueue(Stack<?> stack, Thread thread) {
- super(thread);
- tail = new Link();
- head = new Head(stack.availableSharedCapacity);
- head.link = tail;
- interval = stack.interval;
- handleRecycleCount = interval;
- }
-
- void add(DefaultHandle<?> handle) {
- handle.lastRecycledId = id;
- if (handleRecycleCount < interval) {
- handleRecycleCount++;
- return;
- }
- handleRecycleCount = 0;
- Link tail = this.tail;
- int writeIndex;
- if ((writeIndex = tail.get()) == LINK_CAPACITY) {
- Link link = head.newLink();
- if (link == null) {
- return;
- }
- this.tail = tail = tail.next = link;
- writeIndex = tail.get();
- }
- tail.elements[writeIndex] = handle;
- handle.stack = null;
- tail.lazySet(writeIndex + 1);
- }
- ...
- }
- }
17.Netty设计模式之观察者模式
(1)观察者模式的特点
(2)观察者模式的例子
(3)Netty中的观察者模式
(1)观察者模式的特点
一.观察者和被观察者
二.观察者订阅消息,被观察者发布消息
三.订阅则能收到消息,取消订阅则不能收到消息
(2)观察者模式的例子
女神是被观察者,男孩、男人、老男人是观察者。第一步需要注册观察者到被观察者的一个列表中,第二步当被观察者触发某个动作后需遍历观察者列表执行观察者的方法。(3)Netty中的观察者模式
Netty的writeAndFlush()方法就是典型的观察者模式。Netty的Future或Promise模式实现了writeAndFlush()的异步化,并且每次写成功或者写失败都能收到回调。
我们在调用writeAndFlush()方法后,Netty会创建一个被观察者ChannelFuture。然后在调用channelFuture.addListener()方法时,其实就是往被观察者ChannelFuture中添加一系列的观察者。- public class Singleton {
- private volatile static Singleton singleton;
- private Singleton() {
-
- }
- public static Singleton getInstance() {
- if (singleton == null) {
- synchronized(Singleton.class) {
- if (singleton == null) {
- singleton = new Singleton();
- }
- }
- }
- return singleton;
- }
- }
- public final class ReadTimeoutException extends TimeoutException {
- public static final ReadTimeoutException INSTANCE =
- PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7 ? new ReadTimeoutException(true) : new ReadTimeoutException();
- ReadTimeoutException() {
- }
-
- private ReadTimeoutException(boolean shared) {
- super(shared);
- }
- }
- @ChannelHandler.Sharable
- public final class MqttEncoder extends MessageToMessageEncoder<MqttMessage> {
- public static final MqttEncoder INSTANCE = new MqttEncoder();
- private MqttEncoder() {
-
- }
- ...
- }
- public class Strategy {
- private Cache cacheMemory = new CacheMemoryImpl();
- private Cache cacheRedis = new CacheRedisImpl();
-
- public interface Cache {
- boolean add(String key, Object object);
- }
-
- public class CacheMemoryImpl implements Cache {
- public boolean add(String key, Object object) {
- //保存到Memory
- return false;
- }
- }
-
- public class CacheRedisImpl implements Cache {
- public boolean add(String key, Object object) {
- //保存到Redis
- return false;
- }
- }
-
- public Cache getCache(String key) {
- if (key.length() < 10) {
- return cacheRedis;
- } else {
- return cacheMemory;
- }
- }
- }
[code]public class DefaultPromise extends AbstractFuture implements Promise { private Object listeners; ... //添加观察者 @Override public Promise addListener(GenericFutureListener |