作者:SkyXZ
CSDN:SkyXZ~-CSDN博客
博客园:SkyXZ - 博客园
机械臂:LeRobot-SO101 数采机:MacBook-Pro Python3.10
开发机:Ubuntu 22.04, Cuda12.4,8 × NVIDIA A100-SXM4-40GB
开发板:RDK OS 4.0.2 Based on Ubuntu 22.04, Python 3.10.12, OpenExplore 3.2.0
相关资料:
- LeRobot Doc:https://huggingface.co/docs/lerobot/main/en/index
- RDT 170M&1B:https://github.com/thu-ml/RoboticsDiffusionTransformer
- RDT on RDKS100:RDT on Double RDK S100P 全流程文档
一、环境安装&机械臂配置
- 所有代码已上传至GitHub:GitHub - xiongqi123123/LeRobot-VLA: Classic VLA for LeRobot
环境安装
我们首先完成LeRobot环境的安装,我们默认使用conda作为环境管理,先运行以下命令创建一个Python3.10的虚拟环境- conda create -y -n lerobot python=3.10
- # step:0 安装编译依赖
- sudo apt-get install cmake build-essential python-dev pkg-config libavformat-dev libavcodec-dev libavdevice-dev libavutil-dev libswscale-dev libswresample-dev libavfilter-dev pkg-config
- # step:1 激活环境
- conda activate lerobot
- # step:2 安装ffmpeg
- conda install ffmpeg -c conda-forge
- # 以下两种方式任选其一:
- # step:3 从源码安装lerobot
- git clone https://github.com/xiongqi123123/LeRobot-VLA.git
- cd LeRobot-VLA/lerobot
- pip install -e .
- # step:3 从PyPI 安装
- pip install lerobot
- # 要安装附加功能,请使用以下之一
- pip install 'lerobot[all]' # All available features
- pip install 'lerobot[aloha,pusht]' # Specific features (Aloha & Pusht)
- pip install 'lerobot[feetech]' # Feetech motor support
- 官方安装教程:SO-101 - Hugging Face 机器学习平台
由于SO-ARM101机械臂默认不提供机械臂上的相机安装位置,因此我们在原始的机械臂夹爪部分自行设计添加了一个相机固定的位置(安装孔位与夹爪是对齐的),我们使用的相机是亚博智能的1080P高清免驱摄像头,打印文件已保存进仓库中:
拿到刚拆封的机械臂配件我们首先将Follower和Leader臂的物料进行区分,要注意的是Follower机械臂使用的是12个ST-3215-C001(7.4V)1:345齿轮比的电机,而Leader臂不同关机使用的电机型号有所不同,不同关节的电机型号区分如下图及上表:
接下来我们便可以按照官方提供的如下3D演示动画安装Follower和Leader了,下面是关节一到关节五以及夹爪的安装实例,除了夹爪之外,前面五个关节的安装方法均一致,仅需注意Leader臂的电机型号:
机械臂电机配置
在完成机械臂的安装后我们便可以开始对机械臂两个臂的电机进行配置设置其对应的ID了,新版的LeRobot提供了CLI命令可以直接运行对应的任务,我们首先将两个机械臂的串口钱全部接上电脑并运行如下命令,接着按照提示拔出其中一个串口线按下回车即可知道拔出的串口号是多少(实际就是记录插上的所有串口,然后再和拔出后的进行对比就可以知道哪个串口少了...),示例输出如下图:
由于LeRobot使用的是总线舵机,每个电机都通过总线上的唯一 ID 进行识别,而全新电机通常带有一个默认 ID 为 1,所以为了让电机和控制器之间正常通信,我们需要为每个电机设置一个唯一的、不同的 ID,在确定了自己的两个机械臂分别对应的串口后我们便可以一个臂一个臂一个电机一个电机的进行配置啦,在新版的LeRobot库不需要重复多次运行电机配置命令,我们只需要运行以下命令并依次将不同的舵机线插到控制板按回车即可,具体可以参考以下视频:- lerobot-setup-motors \
- --robot.type=so101_follower \
- --robot.port=/dev/tty.usbmodem585A0076841 # <- paste here the port found at previous step
- lerobot-calibrate \
- --robot.type=so101_follower \
- --robot.port=/dev/tty.usbmodem58760431551 \ # <- The port of your robot
- --robot.id=my_awesome_follower_arm # <- Give the robot a unique name
- lerobot-find-cameras opencv
训练环境配置
我们首先来安装RDT训练所需的环境,此我们进入RDT目录下依次安装如下包即可:- lerobot-teleoperate \
- --robot.type=so101_follower \
- --robot.port=/dev/tty.usbmodem5AB90671801 \
- --robot.id=my_awesome_follower_arm \
- --teleop.type=so101_leader \
- --teleop.port=/dev/tty.usbmodem5AB90671501 \
- --teleop.id=my_awesome_leader_arm \
- lerobot-teleoperate \
- --robot.type=so101_follower \
- --robot.port=/dev/tty.usbmodem5AB90671801 \
- --robot.id=my_awesome_follower_arm \
- --robot.cameras="{ arm: {type: opencv, index_or_path: 0, width: 1920, height: 1080, fps: 30}, front: {type: opencv, index_or_path: 2, width: 1920, height: 1080, fps: 30}}" \
- --teleop.type=so101_leader \
- --teleop.port=/dev/tty.usbmodem5AB90671501 \
- --teleop.id=my_awesome_leader_arm \
- --display_data=true
- lerobot-record \
- --robot.type=so101_follower \
- --robot.port=/dev/tty.usbmodem5AB90671801 \
- --robot.id=my_awesome_follower_arm \
- --robot.cameras="{ arm: {type: opencv, index_or_path: 0, width: 1920, height: 1080, fps: 30}, front: {type: opencv, index_or_path: 2, width: 1920, height: 1080, fps: 30}}" \
- --teleop.type=so101_leader \
- --teleop.port=/dev/tty.usbmodem5AB90671501 \
- --teleop.id=my_awesome_leader_arm \
- --display_data=true \
- --dataset.repo_id=skyxz/blackmarker_scence1 \
- --dataset.num_episodes=5 \
- --dataset.single_task="Grab the black marker and put it in the bin" \
- --dataset.push_to_hub=False \
- --dataset.episode_time_s=15 \
- --dataset.reset_time_s=5
- (RoboTwin) qi.xiong@A100-Test:~/Data_Qi/LeRobot/skyxz/blackmarker_scence1$ python3 -c "import h5py; f=h5py.File('/home/qi.xiong/Data_Qi/RDT/processed_data/place_dual_shoes-demo_clean-300/episode_3/episode_3.hdf5','r'); f.visit(print); f.close()"
- action
- observations
- observations/images
- observations/images/cam_high
- observations/images/cam_left_wrist
- observations/images/cam_right_wrist
- observations/left_arm_dim
- observations/qpos
- observations/right_arm_dim
RDT分为了1B版本(SigLip+DIT+Adaptor)以及单独的170M(DiT)两个版本,其中的区别仅在于最后的DiT的hidden_size和depth维度区别,170M相比于1B的版本直接减半了,如果需要在RDKS100上部署的话请参考接下来的RDT170M模型版本以保证可行的性能,在训练之前还需按照如下的步骤下载预训练模型及完成训练环境的安装;- #!/usr/bin/env python3
- """
- LeRobot到RDT数据转换脚本
- LeRobot机器人结构:
- - 5个关节 (shoulder_pan, shoulder_lift, elbow_flex, wrist_flex, wrist_roll)
- - 1个夹爪 (gripper)
- - 总计:6个自由度 (6DOF)
- 维度映射(匹配RDT训练代码):
- - left_arm_dim = 0 (单臂机器人,左臂不存在)
- - right_arm_dim = 6 (5关节 + 1夹爪,映射到RDT的right_arm部分)
- - 状态向量:6维 [joint1, joint2, joint3, joint4, joint5, gripper]
- - RDT索引映射:right_arm_joint_0_pos到right_arm_joint_5_pos (索引0-5)
- """
- import sys
- import os
- import h5py
- import numpy as np
- import cv2
- import argparse
- import yaml
- import json
- import subprocess
- from pathlib import Path
- import pandas as pd
- import torch
- current_dir = os.path.dirname(__file__)
- sys.path.append(os.path.join(current_dir, ".."))
- from models.multimodal_encoder.t5_encoder import T5Embedder
- def extract_frames_from_video(video_path, output_dir, episode_idx):
- if not os.path.exists(video_path):
- print(f" No video file: {video_path}")
- return []
-
- temp_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, f"temp_frames_{episode_idx}")
- if not os.path.exists(temp_dir):
- os.makedirs(temp_dir)
-
- output_pattern = os.path.join(temp_dir, "frame_%04d.jpg")
-
- try:
- cmd = [
- 'ffmpeg', '-i', video_path,
- '-vf', 'fps=30',
- '-q:v', '2',
- output_pattern,
- '-y'
- ]
-
- result = subprocess.run(cmd, capture_output=True, text=True)
-
- if result.returncode != 0:
- print(f" Failed to extract frames with ffmpeg: {result.stderr}")
- return []
-
- frames = []
- frame_files = sorted([f for f in os.listdir(temp_dir) if f.endswith('.jpg')])
-
- for frame_file in frame_files:
- frame_path = os.path.join(temp_dir, frame_file)
- frame = cv2.imread(frame_path)
- if frame is not None:
- frame_resized = cv2.resize(frame, (640, 480))
- frames.append(frame_resized)
-
- print(f" Successfully extracted {len(frames)} frames")
-
- for frame_file in frame_files:
- os.remove(os.path.join(temp_dir, frame_file))
- os.rmdir(temp_dir)
-
- return frames
-
- except Exception as e:
- print(f" Error extracting frames: {e}")
- return []
- def load_lerobot_episode(data_dir, episode_idx, output_dir):
- """加载LeRobot的单个episode数据
-
- LeRobot数据结构:
- - action: 6维 [shoulder_pan, shoulder_lift, elbow_flex, wrist_flex, wrist_roll, gripper]
- - observation.state: 6维 [shoulder_pan, shoulder_lift, elbow_flex, wrist_flex, wrist_roll, gripper]
- - 图像: 高位相机 + 手臂相机
- """
- parquet_path = os.path.join(data_dir, "data/chunk-000", f"episode_{episode_idx:06d}.parquet")
- if not os.path.exists(parquet_path):
- print(f"Episode {episode_idx} parquet file does not exist: {parquet_path}")
- return None
-
- df = pd.read_parquet(parquet_path)
-
- actions = []
- qpos = []
-
- for i in range(len(df)):
- action = df['action'].iloc[i]
- state = df['observation.state'].iloc[i]
-
- if isinstance(action, np.ndarray):
- actions.append(action.astype(np.float32))
- else:
- actions.append(np.array(action, dtype=np.float32))
-
- if isinstance(state, np.ndarray):
- qpos.append(state.astype(np.float32))
- else:
- qpos.append(np.array(state, dtype=np.float32))
-
- high_cam_path = os.path.join(data_dir, "videos/chunk-000/observation.images.high", f"episode_{episode_idx:06d}.mp4")
- arm_cam_path = os.path.join(data_dir, "videos/chunk-000/observation.images.arm", f"episode_{episode_idx:06d}.mp4")
-
- print(f" Extracting high camera frames...")
- high_images = extract_frames_from_video(high_cam_path, output_dir, episode_idx)
-
- print(f" Extracting arm camera frames...")
- arm_images = extract_frames_from_video(arm_cam_path, output_dir, episode_idx)
-
- target_frames = len(df)
- if len(high_images) > target_frames:
- high_images = high_images[:target_frames]
- if len(arm_images) > target_frames:
- arm_images = arm_images[:target_frames]
-
- while len(high_images) < target_frames and high_images:
- high_images.append(high_images[-1])
- while len(arm_images) < target_frames and arm_images:
- arm_images.append(arm_images[-1])
-
- return {
- 'actions': np.array(actions),
- 'qpos': np.array(qpos),
- 'high_images': high_images,
- 'arm_images': arm_images,
- 'episode_length': len(df)
- }
- def images_encoding(imgs):
- if not imgs:
- return [], 0
-
- encode_data = []
- padded_data = []
- max_len = 0
-
- for i in range(len(imgs)):
- success, encoded_image = cv2.imencode(".jpg", imgs[i])
- if success:
- jpeg_data = encoded_image.tobytes()
- encode_data.append(jpeg_data)
- max_len = max(max_len, len(jpeg_data))
- else:
- print(f" Image encoding failed: {i}")
- empty_data = b""
- encode_data.append(empty_data)
-
- for i in range(len(imgs)):
- padded_data.append(encode_data[i].ljust(max_len, b"\0"))
-
- return encode_data, max_len
- def load_task_instructions(data_dir):
- tasks_file = os.path.join(data_dir, "meta/tasks.jsonl")
- if not os.path.exists(tasks_file):
- print(f"Warning: tasks file not found: {tasks_file}")
- return None
-
- instructions = []
- with open(tasks_file, 'r') as f:
- for line in f:
- if line.strip():
- task_data = json.loads(line.strip())
- instructions.append(task_data["task"])
-
- print(f" 加载了 {len(instructions)} 个任务指令")
- return instructions
- def encode_language_instruction(instruction_text, t5_embedder, device):
- try:
- text_embeds, attn_mask = t5_embedder.get_text_embeddings([instruction_text])
-
- valid_embeds = text_embeds[0][attn_mask[0]].float()
- return valid_embeds.cpu().numpy()
-
- except Exception as e:
- print(f" Language encoding failed: {e}")
- return np.zeros((1, 4096))
- def convert_lerobot_to_rdt(data_dir, output_dir, episode_num, gpu=0, no_language=False):
- if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
- os.makedirs(output_dir)
-
- print(f"Start converting LeRobot data to RDT format...")
- print(f"Data source: {data_dir}")
- print(f"Output directory: {output_dir}")
- print(f"Processing episode number: {episode_num}")
- print(f"GPU device: {gpu}")
-
- scene_name = os.path.basename(data_dir)
-
- instructions = None
- if not no_language:
- instructions = load_task_instructions(data_dir)
-
- t5_embedder = None
- if not no_language and instructions:
- try:
- print(f" Initializing T5 encoder...")
- t5_model_path = "/home/qi.xiong/Data_Qi/t5-v1_1-xxl"
- if not os.path.exists(t5_model_path):
- print(f" Warning: T5 model path does not exist: {t5_model_path}")
- print(f" Will skip language processing")
- no_language = True
- else:
- t5_embedder = T5Embedder(
- from_pretrained=t5_model_path,
- device=f"cuda:{gpu}" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu",
- model_max_length=120,
- use_offload_folder=None,
- )
- print(f" T5 encoder initialized successfully")
- except Exception as e:
- print(f" T5 encoder initialization failed: {e}")
- print(f" Will skip language processing")
- no_language = True
-
- for i in range(episode_num):
- print(f"Processing episode {i}...")
-
- episode_data = load_lerobot_episode(data_dir, i, output_dir)
- if episode_data is None:
- print(f"Skipping episode {i}")
- continue
-
- episode_output_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, f"episode_{i}")
- if not os.path.exists(episode_output_dir):
- os.makedirs(episode_output_dir)
-
- hdf5_path = os.path.join(episode_output_dir, f"episode_{i}.hdf5")
-
- with h5py.File(hdf5_path, "w") as f:
- f.create_dataset("action", data=episode_data['actions'])
-
- obs = f.create_group("observations")
- obs.create_dataset("qpos", data=episode_data['qpos'])
-
- image = obs.create_group("images")
-
- if episode_data['high_images']:
- print(f" Encoding high camera images...")
- high_enc, len_high = images_encoding(episode_data['high_images'])
- if high_enc and len_high > 0:
- image.create_dataset("cam_high", data=high_enc, dtype=f"S{len_high}")
- print(f" Saved high camera images: {len(episode_data['high_images'])} frames")
- else:
- print(f" Warning: High camera images encoding failed")
-
- if episode_data['arm_images']:
- print(f" Encoding arm camera images...")
- arm_enc, len_arm = images_encoding(episode_data['arm_images'])
- if arm_enc and len_arm > 0:
- image.create_dataset("cam_right_wrist", data=arm_enc, dtype=f"S{len_arm}")
- print(f" Saved arm camera images: {len(episode_data['arm_images'])} frames")
- else:
- print(f" Warning: Arm camera images encoding failed")
-
- # 添加机器人维度信息(LeRobot: 5个关节 + 1个夹爪)
- # 根据process_data.py的逻辑,每个时间步都需要记录维度信息
- # LeRobot是单臂机器人,只有右臂:5个关节 + 1个夹爪 = 6维
- # 左臂:0维(单臂机器人)
-
- # 为每个时间步记录维度信息
- left_arm_dim = [0] * len(episode_data['actions']) # 左臂0维(单臂机器人)
- right_arm_dim = [6] * len(episode_data['actions']) # 右臂6维(5关节+1夹爪)
-
- obs.create_dataset("left_arm_dim", data=np.array(left_arm_dim))
- obs.create_dataset("right_arm_dim", data=np.array(right_arm_dim))
-
- print(f" Episode {i} converted successfully: {hdf5_path}")
- print(f" Data length: {episode_data['episode_length']}")
- print(f" Action shape: {episode_data['actions'].shape}")
- print(f" Qpos shape: {episode_data['qpos'].shape}")
- print(f" High camera frames: {len(episode_data['high_images'])}")
- print(f" Arm camera frames: {len(episode_data['arm_images'])}")
-
- if not no_language and t5_embedder and instructions:
- print(f" Processing language instructions...")
- try:
- instruction = instructions[0]
-
- language_features = encode_language_instruction(instruction, t5_embedder, f"cuda:{gpu}")
-
- instructions_dir = os.path.join(episode_output_dir, "instructions")
- if not os.path.exists(instructions_dir):
- os.makedirs(instructions_dir)
-
- lang_embed_path = os.path.join(instructions_dir, "lang_embed_0.pt")
- torch.save(torch.from_numpy(language_features), lang_embed_path)
-
- print(f" Language instruction encoded successfully: {instruction}")
- print(f" Language features saved to: {lang_embed_path}")
- print(f" Language features shape: {language_features.shape}, data type: {language_features.dtype}")
-
- except Exception as e:
- print(f" Language instruction processing failed: {e}")
-
- print(f"\nConversion completed! Processed {episode_num} episodes")
- print(f"Output directory: {output_dir}")
- def main():
- parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Convert LeRobot data to RDT format")
- parser.add_argument("--data_dir", type=str, required=True,
- help="LeRobot data directory path")
- parser.add_argument("--output_dir", type=str, required=True,
- help="Output directory path")
- parser.add_argument("--episode_num", type=int, default=10,
- help="Number of episodes to process")
- parser.add_argument("--gpu", type=int, default=0,
- help="GPU device ID")
- parser.add_argument("--no_language", action="store_true",
- help="Skip language processing")
-
- args = parser.parse_args()
-
- if not os.path.exists(args.data_dir):
- print(f"Error: Data directory does not exist: {args.data_dir}")
- return
-
- meta_file = os.path.join(args.data_dir, "meta/info.json")
- if not os.path.exists(meta_file):
- print(f"Error: Meta information file not found: {meta_file}")
- return
-
- try:
- subprocess.run(['ffmpeg', '-version'], capture_output=True, check=True)
- print("ffmpeg is available, will use ffmpeg to extract video frames")
- except (subprocess.CalledProcessError, FileNotFoundError):
- print("Warning: ffmpeg is not available, image data may not be extracted correctly")
- print("Please install ffmpeg: conda install -c conda-forge ffmpeg=6.1")
- return
-
- with open(meta_file, 'r') as f:
- meta_info = yaml.safe_load(f)
-
- total_episodes = meta_info.get('total_episodes', 10)
- if args.episode_num > total_episodes:
- print(f"Warning: Requested episode number ({args.episode_num}) exceeds available number ({total_episodes})")
- args.episode_num = total_episodes
-
- convert_lerobot_to_rdt(
- args.data_dir,
- args.output_dir,
- args.episode_num,
- args.gpu,
- args.no_language
- )
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- main()
要训练1B的版本我们需要修改RDT/configs/base.yaml文件中model类下的rdt参数- # 法一 bash process_data_rdt.sh data_dir=${1} output_dir=${2} episode_num=${3} gpu_id=${4}
- bash process_data_rdt.sh /home/qi.xiong/Data_Qi/LeRobot/skyxz/redmarker_scence4 /home/qi.xiong/DualArm/RoboTwin/policy/RDT-LeRobot/processed_data/redmarker_scence4 5 0
- # 法二 python scripts/process_data_lerobot.py --data_dir --output_dir --episode_num --gpu
- python3 scripts/process_data_lerobot.py --data_dir /home/qi.xiong/Data_Qi/LeRobot/skyxz/redmarker_scence4 --output_dir /home/qi.xiong/DualArm/RoboTwin/policy/RDT-LeRobot/processed_data/redmarker_scence4
- import os
- import fnmatch
- import json
- import h5py
- import yaml
- import cv2
- import numpy as np
- from configs.state_vec import STATE_VEC_IDX_MAPPING
- class HDF5VLADataset:
- """
- This class is used to sample episodes from the embododiment dataset
- stored in HDF5.
- """
- def __init__(self, model_config_path) -> None:
- # [Modify] The path to the HDF5 dataset directory
- # Each HDF5 file contains one episode
- with open(model_config_path, "r") as f:
- model_config = yaml.safe_load(f)
- HDF5_DIR = model_config["data_path"]
- self.DATASET_NAME = "agilex"
- self.file_paths = []
- for root, _, files in os.walk(HDF5_DIR):
- for filename in fnmatch.filter(files, "*.hdf5"):
- file_path = os.path.join(root, filename)
- self.file_paths.append(file_path)
- # Load the config
- with open("configs/base.yaml", "r") as file:
- config = yaml.safe_load(file)
- self.CHUNK_SIZE = config["common"]["action_chunk_size"]
- self.IMG_HISORY_SIZE = config["common"]["img_history_size"]
- self.STATE_DIM = config["common"]["state_dim"]
- # Get each episode's len (use original length, not standardized length)
- episode_lens = []
- for file_path in self.file_paths:
- try:
- with h5py.File(file_path, "r") as f:
- qpos = f["observations"]["qpos"][:]
- num_steps = qpos.shape[0]
- episode_lens.append(num_steps)
- except Exception as e:
- print(f"Warning: Could not read {file_path}: {e}")
- episode_lens.append(0)
- self.episode_sample_weights = np.array(episode_lens) / np.sum(episode_lens)
- def __len__(self):
- return len(self.file_paths)
- def get_dataset_name(self):
- return self.DATASET_NAME
- def get_item(self, index: int = None, state_only=False):
- """Get a training sample at a random timestep.
- Args:
- index (int, optional): the index of the episode.
- If not provided, a random episode will be selected.
- state_only (bool, optional): Whether to return only the state.
- In this way, the sample will contain a complete trajectory rather
- than a single timestep. Defaults to False.
- Returns:
- sample (dict): a dictionary containing the training sample.
- """
- while True:
- if index is None:
- file_path = np.random.choice(self.file_paths, p=self.episode_sample_weights)
- else:
- file_path = self.file_paths[index]
- valid, sample = (self.parse_hdf5_file(file_path)
- if not state_only else self.parse_hdf5_file_state_only(file_path))
- if valid:
- return sample
- else:
- index = np.random.randint(0, len(self.file_paths))
- def parse_hdf5_file(self, file_path):
- """[Modify] Parse a hdf5 file to generate a training sample at
- a random timestep.
- Args:
- file_path (str): the path to the hdf5 file
- Returns:
- valid (bool): whether the episode is valid, which is useful for filtering.
- If False, this episode will be dropped.
- dict: a dictionary containing the training sample,
- {
- "meta": {
- "dataset_name": str, # the name of your dataset.
- "#steps": int, # the number of steps in the episode,
- # also the total timesteps.
- "instruction": str # the language instruction for this episode.
- },
- "step_id": int, # the index of the sampled step,
- # also the timestep t.
- "state": ndarray, # state[t], (1, STATE_DIM).
- "state_std": ndarray, # std(state[:]), (STATE_DIM,).
- "state_mean": ndarray, # mean(state[:]), (STATE_DIM,).
- "state_norm": ndarray, # norm(state[:]), (STATE_DIM,).
- "actions": ndarray, # action[t:t+CHUNK_SIZE], (CHUNK_SIZE, STATE_DIM).
- "state_indicator", ndarray, # indicates the validness of each dim, (STATE_DIM,).
- "cam_high": ndarray, # external camera image, (IMG_HISORY_SIZE, H, W, 3)
- # or (IMG_HISORY_SIZE, 0, 0, 0) if unavailable.
- "cam_high_mask": ndarray, # indicates the validness of each timestep, (IMG_HISORY_SIZE,) boolean array.
- # For the first IMAGE_HISTORY_SIZE-1 timesteps, the mask should be False.
- "cam_left_wrist": ndarray, # left wrist camera image, (IMG_HISORY_SIZE, H, W, 3).
- # or (IMG_HISORY_SIZE, 0, 0, 0) if unavailable.
- "cam_left_wrist_mask": ndarray,
- "cam_right_wrist": ndarray, # right wrist camera image, (IMG_HISORY_SIZE, H, W, 3).
- # or (IMG_HISORY_SIZE, 0, 0, 0) if unavailable.
- # If only one wrist, make it right wrist, plz.
- "cam_right_wrist_mask": ndarray
- } or None if the episode is invalid.
- """
- with h5py.File(file_path, "r") as f:
- qpos = f["observations"]["qpos"][:]
- left_arm_dim = f["observations"]["left_arm_dim"][:]
- right_arm_dim = f["observations"]["right_arm_dim"][:]
- num_steps = qpos.shape[0]
- action_dim = qpos
- # [Optional] We drop too-short episode
- # if num_steps < 128:
- # return False, None
- # [Optional] We skip the first few still steps
- EPS = 1e-2
- # Get the idx of the first qpos whose delta exceeds the threshold
- qpos_delta = np.abs(qpos - qpos[0:1])
- indices = np.where(np.any(qpos_delta > EPS, axis=1))[0]
- if len(indices) > 0:
- first_idx = indices[0]
- else:
- raise ValueError("Found no qpos that exceeds the threshold.")
- # We randomly sample a timestep
- step_id = np.random.randint(first_idx - 1, num_steps)
- # Load the instruction
- dir_path = os.path.dirname(file_path)
- # with open(os.path.join(dir_path, 'instruction.json'), 'r') as f_instr:
- # instruction_dict = json.load(f_instr)
- # # We have 1/3 prob to use original instruction,
- # # 1/3 to use simplified instruction,
- # # and 1/3 to use expanded instruction.
- # instruction_type = np.random.choice([
- # 'instruction', 'expanded_instruction'])
- # instruction = instruction_dict[instruction_type]
- # if isinstance(instruction, list):
- # instruction = np.random.choice(instruction)
- # You can also use precomputed language embeddings (recommended)
- # instruction = "path/to/lang_embed.pt"
- instructions_path = os.path.join(dir_path, "instructions")
- instructions_names = []
- for filename in os.listdir(instructions_path):
- # 检查文件名是否以.pt结尾
- if filename.endswith(".pt"):
- instructions_names.append(os.path.join(instructions_path, filename))
- instruction = np.random.choice(instructions_names)
- # print(f"choose {instruction} file as instruction.")
- # Assemble the meta
- meta = {
- "dataset_name": self.DATASET_NAME,
- "#steps": num_steps,
- "step_id": step_id,
- "instruction": instruction,
- }
- # Rescale gripper to [0, 1]
- # qpos = qpos / np.array([[1 for i in range(left_arm_dim[0] + 1 + right_arm_dim[0] + 1)]])
- # target_qpos = f["action"][step_id:step_id + self.CHUNK_SIZE] / np.array(
- # [[1 for i in range(left_arm_dim[0] + 1 + right_arm_dim[0] + 1)]])
- qpos = qpos / np.array(
- # [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4.7908, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4.7888]]
- [[180, 180, 180, 180, 180, 180]]
- )
- target_qpos = f['action'][step_id:step_id + self.CHUNK_SIZE] / np.array(
- # [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 11.8997, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 13.9231]]
- [[180, 180, 180, 180, 180, 180]]
- )
- # Parse the state and action
- state = qpos[step_id:step_id + 1]
- state_std = np.std(qpos, axis=0)
- state_mean = np.mean(qpos, axis=0)
- state_norm = np.sqrt(np.mean(qpos**2, axis=0))
- actions = target_qpos
- if actions.shape[0] < self.CHUNK_SIZE:
- # Pad the actions using the last action
- actions = np.concatenate(
- [
- actions,
- np.tile(actions[-1:], (self.CHUNK_SIZE - actions.shape[0], 1)),
- ],
- axis=0,
- )
- # Fill the state/action into the unified vector
- def fill_in_state(values):
- # Target indices corresponding to your state space
- # In this example: 6 joints + 1 gripper for each arm
- UNI_STATE_INDICES = [
- STATE_VEC_IDX_MAPPING[f"right_arm_joint_{i}_pos"] for i in range(6)
- # ] + [
- # STATE_VEC_IDX_MAPPING["right_gripper_open"]
- ]
- uni_vec = np.zeros(values.shape[:-1] + (self.STATE_DIM, ))
- uni_vec[..., UNI_STATE_INDICES] = values
- return uni_vec
- state = fill_in_state(state)
- state_indicator = fill_in_state(np.ones_like(state_std))
- state_std = fill_in_state(state_std)
- state_mean = fill_in_state(state_mean)
- state_norm = fill_in_state(state_norm)
- # If action's format is different from state's,
- # you may implement fill_in_action()
- actions = fill_in_state(actions)
- # Parse the images
- def parse_img(key):
- imgs = []
- for i in range(max(step_id - self.IMG_HISORY_SIZE + 1, 0), step_id + 1):
- img_bits = f["observations"]["images"][key][i]
- img = cv2.imdecode(np.frombuffer(img_bits, np.uint8), cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
- imgs.append(img)
- imgs = np.stack(imgs)
- if imgs.shape[0] < self.IMG_HISORY_SIZE:
- # Pad the images using the first image
- imgs = np.concatenate(
- [
- np.tile(
- imgs[:1],
- (self.IMG_HISORY_SIZE - imgs.shape[0], 1, 1, 1),
- ),
- imgs,
- ],
- axis=0,
- )
- return imgs
- # `cam_high` is the external camera image
- cam_high = parse_img("cam_high")
- # For step_id = first_idx - 1, the valid_len should be one
- valid_len = min(step_id - (first_idx - 1) + 1, self.IMG_HISORY_SIZE)
- cam_high_mask = np.array([False] * (self.IMG_HISORY_SIZE - valid_len) + [True] * valid_len)
- # cam_left_wrist = parse_img("cam_left_wrist")
- # cam_left_wrist_mask = cam_high_mask.copy()
- cam_left_wrist = np.zeros((self.IMG_HISORY_SIZE, 0, 0, 0))#parse_img('cam_right_wrist')
- cam_left_wrist_mask = np.array([False] * self.IMG_HISORY_SIZE)#cam_high_mask.copy()
- cam_right_wrist = parse_img("cam_right_wrist")
- cam_right_wrist_mask = cam_high_mask.copy() # 使用相同的掩码逻辑
- # Return the resulting sample
- # For unavailable images, return zero-shape arrays, i.e., (IMG_HISORY_SIZE, 0, 0, 0)
- # E.g., return np.zeros((self.IMG_HISORY_SIZE, 0, 0, 0)) for the key "cam_left_wrist",
- # if the left-wrist camera is unavailable on your robot
- return True, {
- "meta": meta,
- "state": state,
- "state_std": state_std,
- "state_mean": state_mean,
- "state_norm": state_norm,
- "actions": actions,
- "state_indicator": state_indicator,
- "cam_high": cam_high,
- "cam_high_mask": cam_high_mask,
- "cam_left_wrist": cam_left_wrist,
- "cam_left_wrist_mask": cam_left_wrist_mask,
- "cam_right_wrist": cam_right_wrist,
- "cam_right_wrist_mask": cam_right_wrist_mask,
- }
- def parse_hdf5_file_state_only(self, file_path):
- """[Modify] Parse a hdf5 file to generate a state trajectory.
- Args:
- file_path (str): the path to the hdf5 file
- Returns:
- valid (bool): whether the episode is valid, which is useful for filtering.
- If False, this episode will be dropped.
- dict: a dictionary containing the training sample,
- {
- "state": ndarray, # state[:], (T, STATE_DIM).
- "action": ndarray, # action[:], (T, STATE_DIM).
- } or None if the episode is invalid.
- """
- with h5py.File(file_path, "r") as f:
- qpos = f["observations"]["qpos"][:]
- left_arm_dim = f["observations"]["left_arm_dim"][:]
- right_arm_dim = f["observations"]["right_arm_dim"][:]
- num_steps = qpos.shape[0]
- # [Optional] We drop too-short episode
- # if num_steps < 128:
- # return False, None
- # [Optional] We skip the first few still steps
- EPS = 1e-2
- # Get the idx of the first qpos whose delta exceeds the threshold
- qpos_delta = np.abs(qpos - qpos[0:1])
- indices = np.where(np.any(qpos_delta > EPS, axis=1))[0]
- if len(indices) > 0:
- first_idx = indices[0]
- else:
- raise ValueError("Found no qpos that exceeds the threshold.")
- # Rescale gripper to [0, 1]
- # qpos = qpos / np.array([[1 for i in range(left_arm_dim[0] + right_arm_dim[0] + 2)]])
- # target_qpos = f["action"][:] / np.array([[1 for i in range(left_arm_dim[0] + right_arm_dim[0] + 2)]])
-
- qpos = qpos / np.array(
- # [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4.7908, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4.7888]]
- [[180, 180, 180, 180, 180, 180]]
- )
- target_qpos = f['action'][first_idx - 1:] / np.array(
- # [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 11.8997, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 13.9231]]
- [[180, 180, 180, 180, 180, 180]]
- )
- # Parse the state and action
- state = qpos[first_idx - 1:]
- action = target_qpos[first_idx - 1:]
-
- # Standardize trajectory length to avoid batch size mismatch
- # Use a fixed length (e.g., 128) or pad/truncate to match
- target_length = 128 # You can adjust this value
- if state.shape[0] > target_length:
- # Truncate to target length
- state = state[:target_length]
- action = action[:target_length]
- elif state.shape[0] < target_length:
- # Pad with the last state/action
- pad_length = target_length - state.shape[0]
- state = np.concatenate([state, np.tile(state[-1:], (pad_length, 1))], axis=0)
- action = np.concatenate([action, np.tile(action[-1:], (pad_length, 1))], axis=0)
- # Fill the state/action into the unified vector
- def fill_in_state(values):
- # Target indices corresponding to your state space
- # In this example: 6 joints + 1 gripper for each arm
- UNI_STATE_INDICES = [
- STATE_VEC_IDX_MAPPING[f"right_arm_joint_{i}_pos"] for i in range(6)
- # ] + [
- # STATE_VEC_IDX_MAPPING["right_gripper_open"]
- ]
- uni_vec = np.zeros(values.shape[:-1] + (self.STATE_DIM, ))
- uni_vec[..., UNI_STATE_INDICES] = values
- return uni_vec
- state = fill_in_state(state)
- action = fill_in_state(action)
- # Return the resulting sample
- return True, {"state": state, "action": action}
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- ds = HDF5VLADataset()
- for i in range(len(ds)):
- print(f"Processing episode {i}/{len(ds)}...")
- ds.get_item(i)
- # step1:安装torch、torchvision
- pip install torch==2.1.0 torchvision==0.16.0 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121
- # step2:安装packaging
- pip install packaging==24.0
- # step3:安装其他依赖
- pip install -r requirements.txt
要训练170M的版本我们需要修改RDT/configs/base.yaml文件中model类下的rdt参数- $ python3 -c "import torch ; print(torch.__config__.show())"
- PyTorch built with:
- - GCC 9.3
- - C++ Version: 201703
- - Intel(R) oneAPI Math Kernel Library Version 2022.2-Product Build 20220804 for Intel(R) 64 architecture applications
- - Intel(R) MKL-DNN v3.4.2 (Git Hash 1137e04ec0b5251ca2b4400a4fd3c667ce843d67)
- - OpenMP 201511 (a.k.a. OpenMP 4.5)
- - LAPACK is enabled (usually provided by MKL)
- - NNPACK is enabled
- - CPU capability usage: AVX2
- - CUDA Runtime 12.1
- - NVCC architecture flags: -gencode;arch=compute_50,code=sm_50;-gencode;arch=compute_60,code=sm_60;-gencode;arch=compute_70,code=sm_70;-gencode;arch=compute_75,code=sm_75;-gencode;arch=compute_80,code=sm_80;-gencode;arch=compute_86,code=sm_86;-gencode;arch=compute_90,code=sm_90
- - CuDNN 90.1 (built against CUDA 12.4)
- - Magma 2.6.1
- - Build settings: BLAS_INFO=mkl, BUILD_TYPE=Release, CUDA_VERSION=12.1, CUDNN_VERSION=9.1.0, CXX_COMPILER=/opt/rh/devtoolset-9/root/usr/bin/c++, CXX_FLAGS= -D_GLIBCXX_USE_CXX11_ABI=0 -fabi-version=11 -fvisibility-inlines-hidden -DUSE_PTHREADPOOL -DNDEBUG -DUSE_KINETO -DLIBKINETO_NOROCTRACER -DUSE_FBGEMM -DUSE_PYTORCH_QNNPACK -DUSE_XNNPACK -DSYMBOLICATE_MOBILE_DEBUG_HANDLE -O2 -fPIC -Wall -Wextra -Werror=return-type -Werror=non-virtual-dtor -Werror=bool-operation -Wnarrowing -Wno-missing-field-initializers -Wno-type-limits -Wno-array-bounds -Wno-unknown-pragmas -Wno-unused-parameter -Wno-unused-function -Wno-unused-result -Wno-strict-overflow -Wno-strict-aliasing -Wno-stringop-overflow -Wsuggest-override -Wno-psabi -Wno-error=pedantic -Wno-error=old-style-cast -Wno-missing-braces -fdiagnostics-color=always -faligned-new -Wno-unused-but-set-variable -Wno-maybe-uninitialized -fno-math-errno -fno-trapping-math -Werror=format -Wno-stringop-overflow, LAPACK_INFO=mkl, PERF_WITH_AVX=1, PERF_WITH_AVX2=1, PERF_WITH_AVX512=1, TORCH_VERSION=2.4.1, USE_CUDA=ON, USE_CUDNN=ON, USE_CUSPARSELT=1, USE_EXCEPTION_PTR=1, USE_GFLAGS=OFF, USE_GLOG=OFF, USE_GLOO=ON, USE_MKL=ON, USE_MKLDNN=ON, USE_MPI=OFF, USE_NCCL=1, USE_NNPACK=ON, USE_OPENMP=ON, USE_ROCM=OFF, USE_ROCM_KERNEL_ASSERT=OFF,
- pip3 install flash_attn-2.7.2.post1+cu12torch2.1cxx11abiFALSE-cp310-cp310-linux_x86_64.whl
四、实际评测
在训练完成之后我们便可以开始实机评测啦,由于我们目前需要在Mac上连接LeRobot机械臂进行控制,因此我们在实际使用A100或者是RDKS100部署推理的时候还需要完成两端之间的通信代码,我们在这里就用最简单的Socket来实现ServerClient,还有其他更优的ZMQ等方式就不在这里呈现了,具体实现的代码如下,这份代码需要同时放到本地及推理服务器端进行调用- # 法一: 直接运行我仓库中写好的脚本
- cd weights/RDT
- bash _download.sh
- # 法二: 手动下载
- export HF_ENDPOINT=https://hf-mirror.com # 国内镜像,加速下载
- huggingface-cli download google/t5-v1_1-xxl --local-dir t5-v1_1-xxl
- huggingface-cli download google/siglip-so400m-patch14-384 --local-dir siglip-so400m-patch14-384
- huggingface-cli download robotics-diffusion-transformer/rdt-1b --local-dir rdt-1b
- huggingface-cli download robotics-diffusion-transformer/rdt-170m --local-dir rdt-170m
接着我们便可以完成我们服务器上的推理代码了,我们参考RDT中的RDT/scripts/agilex_model.py来完成我们的lerobot_rdt_server,我们在这个代码中完成对RoboticDiffusionTransformerModel类的修改同时使用类中的step执行推理,并集成我们的ServerClient来接收本地电脑发来的机械臂observation数据,具体的代码实现如下:- rdt:
- # 1B: num_head 32 hidden_size 2048 depth: 28
- # 170M: num_head 32 hidden_size 1024 depth: 14
- hidden_size: 2048
- depth: 28
- num_heads: 32
- cond_pos_embed_type: multimodal
- bash generate.sh RDT1B_LeRobot
- # Generated on 2025-08-28 17:14:20
- model: RDT1B_LeRobot
- data_path: training_data/RDT1B_LeRobot
- checkpoint_path: checkpoints/RDT1B_LeRobot
- pretrained_model_name_or_path: ../weights/RDT/rdt-1b
- cuda_visible_device: '0,1,2,3'
- train_batch_size: 16
- sample_batch_size: 32
- max_train_steps: 10000
- checkpointing_period: 2500
- sample_period: 100
- checkpoints_total_limit: 40
- learning_rate: 0.0001
- dataloader_num_workers: 8
- state_noise_snr: 40
- gradient_accumulation_steps: 1
- bash finetune.sh RDT1B_LeRobot
目前RDKS100上仅支持RDT170M的部署,接下来我们参考文档:RDT on Double RDK S100P 全流程文档,一步步的完成LeRobot的RDT的上板流程,我们首先使用仓库中RDT目录下的脚本RDT/export_all.py来完成RDT中所有ONNX模型的导出,这段脚本有如下的参数可以进行配置,大家仅需按照自己的实际情况配置即可- rdt:
- # 1B: num_head 32 hidden_size 2048 depth: 28
- # 170M: num_head 32 hidden_size 1024 depth: 14
- hidden_size: 1024
- depth: 14
- num_heads: 32
- cond_pos_embed_type: multimodal
- bash generate.sh RDT170M_LeRobot
- # Generated on 2025-08-28 17:14:20
- model: RDT170M_LeRobot
- data_path: training_data/RDT170M_LeRobot
- checkpoint_path: checkpoints/RDT170M_LeRobot
- pretrained_model_name_or_path: ../weights/RDT/rdt-170m
- cuda_visible_device: '0,1'
- train_batch_size: 16
- sample_batch_size: 32
- max_train_steps: 10000
- checkpointing_period: 2500
- sample_period: 100
- checkpoints_total_limit: 40
- learning_rate: 0.0001
- dataloader_num_workers: 8
- state_noise_snr: 40
- gradient_accumulation_steps: 1
- bash finetune.sh RDT170M_LeRobot
以下是DiT、img_adaptor、lang_adaptor以及state_adaptor模型量化过程中的部分指标参考:- import socket
- import numpy as np
- import zlib
- import json
- import base64
- import time
- from typing import Any
- import torch
- class NumpyEncoder(json.JSONEncoder):
- """Enhanced json encoder for numpy types and PyTorch tensors with array reconstruction info"""
- def default(self, obj):
- if isinstance(obj, np.ndarray):
- return {
- '__numpy_array__': True,
- 'data': base64.b64encode(obj.tobytes()).decode('ascii'),
- 'dtype': str(obj.dtype),
- 'shape': obj.shape
- }
- elif torch is not None and isinstance(obj, torch.Tensor):
- # 将 PyTorch Tensor 转换为 numpy 数组
- numpy_array = obj.cpu().detach().numpy()
- return {
- '__numpy_array__': True,
- 'data': base64.b64encode(numpy_array.tobytes()).decode('ascii'),
- 'dtype': str(numpy_array.dtype),
- 'shape': numpy_array.shape
- }
- elif isinstance(obj, (np.integer, np.floating, np.bool_)):
- return obj.item()
- return super().default(obj)
- def numpy_to_json(data: Any) -> str:
- return json.dumps(data, cls=NumpyEncoder)
- def json_to_numpy(json_str: str) -> Any:
- def hook(dct):
- if '__numpy_array__' in dct:
- data = base64.b64decode(dct['data'])
- return np.frombuffer(data, dtype=dct['dtype']).reshape(dct['shape'])
- return dct
- return json.loads(json_str, object_hook=hook)
- class CommonUtils:
- @staticmethod
- def serialize(data: Any) -> bytes:
- return zlib.compress(numpy_to_json(data).encode('utf-8'))
- @staticmethod
- def deserialize(data: bytes) -> Any:
- return json_to_numpy(zlib.decompress(data).decode('utf-8'))
- def send_all(sock, payload):
- sock.sendall(len(payload).to_bytes(8, 'big') + payload)
- def recv_all(sock) :
- length_bytes = sock.recv(8)
- if not length_bytes:
- return None
- length = int.from_bytes(length_bytes, 'big')
- buf = b''
- while len(buf) < length:
- chunk = sock.recv(length - len(buf))
- if not chunk:
- return None
- buf += chunk
- return buf
- class ServerClient:
- def __init__(self, host='localhost', port=5000, is_server=True):
- self.host, self.port, self.is_server = host, port, is_server
- self.utils = CommonUtils()
- self._connect()
- def _connect(self):
- if self.is_server:
- self.sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
- self.sock.bind((self.host, self.port))
- self.sock.listen(1)
- print(f"[ServerClient] Listening on {self.host}:{self.port}")
- self.conn, addr = self.sock.accept()
- print(f"[ServerClient] Connected by {addr}")
- else:
- while True:
- try:
- self.sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
- self.sock.connect((self.host, self.port))
- self.conn = self.sock
- print(f"[ServerClient] Connected to {self.host}:{self.port}")
- break
- except (ConnectionRefusedError, OSError):
- print("[ServerClient] Waiting for server...")
- time.sleep(2)
- def send(self, data):
- payload = self.utils.serialize(data)
- try:
- send_all(self.conn, payload)
- except (BrokenPipeError, ConnectionResetError, OSError):
- print("[ServerClient] Connection lost. Reconnecting...")
- self._connect()
- send_all(self.conn, payload)
- def receive(self):
- try:
- buf = recv_all(self.conn)
- return self.utils.deserialize(buf) if buf else None
- except (BrokenPipeError, ConnectionResetError, OSError):
- print("[ServerClient] Connection lost. Reconnecting...")
- self._connect()
- return None
- def close(self):
- self.conn.close()
- self.sock.close()
- class Client:
- def __init__(self, host='127.0.0.1', port=5000):
- self.host, self.port = host, port
- self.utils = CommonUtils()
- self.connect()
- def connect(self):
- while True:
- try:
- self.sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
- self.sock.connect((self.host, self.port))
- print(f"[Client] Connected to {self.host}:{self.port}")
- break
- except (ConnectionRefusedError, OSError):
- print("[Client] Waiting for server...")
- time.sleep(2)
- def send(self, data):
- payload = self.utils.serialize(data)
- try:
- send_all(self.sock, payload)
- except (BrokenPipeError, ConnectionResetError, OSError):
- print("[Client] Connection lost. Reconnecting...")
- self.connect()
- send_all(self.sock, payload)
- def receive(self):
- try:
- buf = recv_all(self.sock)
- return self.utils.deserialize(buf) if buf else None
- except (BrokenPipeError, ConnectionResetError, OSError):
- print("[Client] Connection lost. Reconnecting...")
- self.connect()
- return None
- def close(self):
- self.sock.close()
- print("[Client] Closed.")
- class Server:
- def __init__(self, host='0.0.0.0', port=5000):
- self.host, self.port = host, port
- self.utils = CommonUtils()
- self.sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
- self.sock.bind((self.host, self.port))
- self.sock.listen(1)
- print(f"[Server] Listening on {self.host}:{self.port}")
- self._wait_client()
- def _wait_client(self):
- print("[Server] Waiting for client...")
- self.conn, addr = self.sock.accept()
- print(f"[Server] Connected by {addr}")
- def send(self, data: Any):
- payload = self.utils.serialize(data)
- try:
- send_all(self.conn, payload)
- except (BrokenPipeError, ConnectionResetError, OSError):
- print("[Server] Client disconnected. Waiting new client...")
- self._wait_client()
- send_all(self.conn, payload)
- def receive(self):
- try:
- buf = recv_all(self.conn)
- return self.utils.deserialize(buf) if buf else None
- except (BrokenPipeError, ConnectionResetError, OSError):
- print("[Server] Client disconnected. Waiting new client...")
- self._wait_client()
- return None
- def close(self):
- self.conn.close()
- self.sock.close()
- print("[Server] Closed.")
- import os, sys
- import numpy as np
- import torch
- from PIL import Image
- from torchvision import transforms
- import yaml
- from pathlib import Path
- # get current workspace
- current_file = Path(__file__)
- sys.path.append(os.path.join(current_file.parent.parent, "models"))
- sys.path.append(os.path.join(current_file.parent.parent, "models"))
- sys.path.append(os.path.join(current_file.parent.parent))
- from configs.state_vec import STATE_VEC_IDX_MAPPING
- from multimodal_encoder.siglip_encoder import SiglipVisionTower
- from multimodal_encoder.t5_encoder import T5Embedder
- from rdt_runner import RDTRunner
- from server_client import ServerClient
- # The indices that the raw vector should be mapped to in the unified action vector
- AGILEX_STATE_INDICES = [
- STATE_VEC_IDX_MAPPING[f"right_arm_joint_{i}_pos"] for i in range(6)
- ]
- # Create the RDT model
- def create_model(args, **kwargs):
- model = RoboticDiffusionTransformerModel(args, **kwargs)
- pretrained = kwargs.get("pretrained", None)
- if pretrained is not None and os.path.isfile(pretrained):
- model.load_pretrained_weights(pretrained)
- return model
- class RoboticDiffusionTransformerModel(object):
- """A wrapper for the RDT model, which handles
- 1. Model initialization
- 2. Encodings of instructions
- 3. Model inference
- """
- def __init__(
- self,
- args,
- device="cuda",
- dtype=torch.bfloat16,
- image_size=None,
- control_frequency=25,
- pretrained=None,
- pretrained_vision_encoder_name_or_path=None,
- ):
- self.args = args
- self.dtype = dtype
- self.image_size = image_size
- self.device = device
- self.control_frequency = control_frequency
- # We do not use the text encoder due to limited GPU memory
- # self.text_tokenizer, self.text_model = self.get_text_encoder(pretrained_text_encoder_name_or_path)
- self.image_processor, self.vision_model = self.get_vision_encoder(pretrained_vision_encoder_name_or_path)
- self.policy = self.get_policy(pretrained)
- self.reset()
- def get_policy(self, pretrained):
- """Initialize the model."""
- # Initialize model with arguments
- if pretrained is None or os.path.isfile(pretrained):
- img_cond_len = (self.args["common"]["img_history_size"] * self.args["common"]["num_cameras"] *
- self.vision_model.num_patches)
- _model = RDTRunner(
- action_dim=self.args["common"]["state_dim"],
- pred_horizon=self.args["common"]["action_chunk_size"],
- config=self.args["model"],
- lang_token_dim=self.args["model"]["lang_token_dim"],
- img_token_dim=self.args["model"]["img_token_dim"],
- state_token_dim=self.args["model"]["state_token_dim"],
- max_lang_cond_len=self.args["dataset"]["tokenizer_max_length"],
- img_cond_len=img_cond_len,
- img_pos_embed_config=[
- # No initial pos embed in the last grid size
- # since we've already done in ViT
- (
- "image",
- (
- self.args["common"]["img_history_size"],
- self.args["common"]["num_cameras"],
- -self.vision_model.num_patches,
- ),
- ),
- ],
- lang_pos_embed_config=[
- # Similarly, no initial pos embed for language
- ("lang", -self.args["dataset"]["tokenizer_max_length"]),
- ],
- dtype=self.dtype,
- )
- else:
- _model = RDTRunner.from_pretrained(pretrained)
- return _model
- def get_text_encoder(self, pretrained_text_encoder_name_or_path):
- text_embedder = T5Embedder(
- from_pretrained=pretrained_text_encoder_name_or_path,
- model_max_length=self.args["dataset"]["tokenizer_max_length"],
- device=self.device,
- )
- tokenizer, text_encoder = text_embedder.tokenizer, text_embedder.model
- return tokenizer, text_encoder
- def get_vision_encoder(self, pretrained_vision_encoder_name_or_path):
- vision_encoder = SiglipVisionTower(vision_tower=pretrained_vision_encoder_name_or_path, args=None)
- image_processor = vision_encoder.image_processor
- return image_processor, vision_encoder
- def reset(self):
- """Set model to evaluation mode."""
- device = self.device
- weight_dtype = self.dtype
- self.policy.eval()
- # self.text_model.eval()
- self.vision_model.eval()
- self.policy = self.policy.to(device, dtype=weight_dtype)
- # self.text_model = self.text_model.to(device, dtype=weight_dtype)
- self.vision_model = self.vision_model.to(device, dtype=weight_dtype)
- def load_pretrained_weights(self, pretrained=None):
- if pretrained is None:
- return
- print(f"Loading weights from {pretrained}")
- filename = os.path.basename(pretrained)
- if filename.endswith(".pt"):
- checkpoint = torch.load(pretrained)
- self.policy.load_state_dict(checkpoint["module"])
- elif filename.endswith(".safetensors"):
- from safetensors.torch import load_model
- load_model(self.policy, pretrained)
- else:
- raise NotImplementedError(f"Unknown checkpoint format: {pretrained}")
- def encode_instruction(self, instruction, device="cuda"):
- """Encode string instruction to latent embeddings.
- Args:
- instruction: a string of instruction
- device: a string of device
- Returns:
- pred: a tensor of latent embeddings of shape (text_max_length, 512)
- """
- tokens = self.text_tokenizer(instruction, return_tensors="pt", padding="longest",
- truncation=True)["input_ids"].to(device)
- tokens = tokens.view(1, -1)
- with torch.no_grad():
- pred = self.text_model(tokens).last_hidden_state.detach()
- return pred
- def _format_joint_to_state(self, joints):
- """
- Format the joint proprioception into the unified action vector.
- Args:
- joints (torch.Tensor): The joint proprioception to be formatted.
- qpos ([B, N, 14]).
- Returns:
- state (torch.Tensor): The formatted vector for RDT ([B, N, 128]).
- """
- # Rescale the gripper to the range of [0, 1]
- joints = joints / torch.tensor(
- [[[180, 180, 180, 180, 180, 180]]],
- device=joints.device,
- dtype=joints.dtype,
- )
- B, N, _ = joints.shape
- state = torch.zeros(
- (B, N, self.args["model"]["state_token_dim"]),
- device=joints.device,
- dtype=joints.dtype,
- )
- # Fill into the unified state vector
- state[:, :, AGILEX_STATE_INDICES] = joints
- # Assemble the mask indicating each dimension's availability
- state_elem_mask = torch.zeros(
- (B, self.args["model"]["state_token_dim"]),
- device=joints.device,
- dtype=joints.dtype,
- )
- state_elem_mask[:, AGILEX_STATE_INDICES] = 1
- return state, state_elem_mask
- def _unformat_action_to_joint(self, action):
- """
- Unformat the unified action vector into the joint action to be executed.
- Args:
- action (torch.Tensor): The unified action vector to be unformatted.
- ([B, N, 128])
- Returns:
- joints (torch.Tensor): The unformatted robot joint action.
- qpos ([B, N, 14]).
- """
- action_indices = AGILEX_STATE_INDICES
- joints = action[:, :, action_indices]
- # Rescale the gripper back to the action range
- # Note that the action range and proprioception range are different
- # for Mobile ALOHA robot
- joints = joints * torch.tensor(
- [[[180, 180, 180, 180, 180, 180]]],
- device=joints.device,
- dtype=joints.dtype,
- )
- return joints
- @torch.no_grad()
- def step(self, proprio, images, text_embeds):
- """
- Predict the next action chunk given the
- proprioceptive states, images, and instruction embeddings.
- Args:
- proprio: proprioceptive states
- images: RGB images, the order should be
- [ext_{t-1}, right_wrist_{t-1}, left_wrist_{t-1},
- ext_{t}, right_wrist_{t}, left_wrist_{t}]
- text_embeds: instruction embeddings
- Returns:
- action: predicted action
- """
- device = self.device
- dtype = self.dtype
- # The background image used for padding
- background_color = np.array([int(x * 255) for x in self.image_processor.image_mean],
- dtype=np.uint8).reshape(1, 1, 3)
- background_image = (np.ones(
- (
- self.image_processor.size["height"],
- self.image_processor.size["width"],
- 3,
- ),
- dtype=np.uint8,
- ) * background_color)
- # Preprocess the images by order and encode them
- image_tensor_list = []
- for image in images:
- if image is None:
- # Replace it with the background image
- image = Image.fromarray(background_image)
- else:
- # Convert numpy array to PIL Image if needed
- if isinstance(image, np.ndarray):
- image = Image.fromarray(image)
- if self.image_size is not None:
- image = transforms.Resize(self.image_size)(image)
- if self.args["dataset"].get("auto_adjust_image_brightness", False):
- pixel_values = list(image.getdata())
- average_brightness = sum(sum(pixel) for pixel in pixel_values) / (len(pixel_values) * 255.0 * 3)
- if average_brightness <= 0.15:
- image = transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=(1.75, 1.75))(image)
- if self.args["dataset"].get("image_aspect_ratio", "pad") == "pad":
- def expand2square(pil_img, background_color):
- width, height = pil_img.size
- if width == height:
- return pil_img
- elif width > height:
- result = Image.new(pil_img.mode, (width, width), background_color)
- result.paste(pil_img, (0, (width - height) // 2))
- return result
- else:
- result = Image.new(pil_img.mode, (height, height), background_color)
- result.paste(pil_img, ((height - width) // 2, 0))
- return result
- image = expand2square(image, tuple(int(x * 255) for x in self.image_processor.image_mean))
- image = self.image_processor.preprocess(image, return_tensors="pt")["pixel_values"][0]
- image_tensor_list.append(image)
- image_tensor = torch.stack(image_tensor_list, dim=0).to(device, dtype=dtype)
- image_embeds = self.vision_model(image_tensor).detach()
- image_embeds = image_embeds.reshape(-1, self.vision_model.hidden_size).unsqueeze(0)
- # Prepare the proprioception states and the control frequency
- # Convert numpy array to tensor if needed
- if isinstance(proprio, np.ndarray):
- # Copy the array to make it writable
- proprio = torch.from_numpy(proprio.copy())
-
- joints = proprio.to(device).unsqueeze(0) # (1, 1, 14)
- states, state_elem_mask = self._format_joint_to_state(joints) # (1, 1, 128), (1, 128)
- states, state_elem_mask = states.to(device, dtype=dtype), state_elem_mask.to(device, dtype=dtype)
- states = states[:, -1:, :] # (1, 1, 128)
- ctrl_freqs = torch.tensor([self.control_frequency]).to(device)
- text_embeds = text_embeds.to(device, dtype=dtype)
- # Predict the next action chunk given the inputs
- trajectory = self.policy.predict_action(
- lang_tokens=text_embeds,
- lang_attn_mask=torch.ones(text_embeds.shape[:2], dtype=torch.bool, device=text_embeds.device),
- img_tokens=image_embeds,
- state_tokens=states,
- action_mask=state_elem_mask.unsqueeze(1),
- ctrl_freqs=ctrl_freqs,
- )
- trajectory = self._unformat_action_to_joint(trajectory).to(torch.float32)
- return trajectory
- class LERobotRDTServer:
- def __init__(self, pretrained_vision_encoder_name_or_path, pretrained, args, lang_model):
- self.policy = create_model(
- args=args,
- dtype=torch.bfloat16,
- pretrained=pretrained,
- pretrained_vision_encoder_name_or_path=pretrained_vision_encoder_name_or_path,
- control_frequency=30,
- )
- self.server = ServerClient(host="0.0.0.0", port=5002, is_server=True)
-
- # Load and debug language embeddings
- self.lang_embeddings = torch.load(lang_model)
- print(f"Loaded language embeddings shape: {self.lang_embeddings.shape}")
- print(f"Model expects tokenizer_max_length: {self.policy.args['dataset']['tokenizer_max_length']}")
- print(f"Model lang_token_dim: {self.policy.args['model']['lang_token_dim']}")
-
- # Check if dimensions match
- expected_seq_len = self.policy.args["dataset"]["tokenizer_max_length"]
- expected_hidden_dim = self.policy.args["model"]["lang_token_dim"]
-
- # Handle different embedding formats
- if len(self.lang_embeddings.shape) == 2:
- # Format: [seq_len, hidden_dim]
- actual_seq_len, actual_hidden_dim = self.lang_embeddings.shape
- if actual_seq_len != expected_seq_len:
- print(f"WARNING: Sequence length mismatch! Expected {expected_seq_len}, got {actual_seq_len}")
- if actual_hidden_dim != expected_hidden_dim:
- print(f"WARNING: Hidden dimension mismatch! Expected {expected_hidden_dim}, got {actual_hidden_dim}")
- elif len(self.lang_embeddings.shape) == 3:
- # Format: [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_dim]
- actual_batch, actual_seq_len, actual_hidden_dim = self.lang_embeddings.shape
- if actual_seq_len != expected_seq_len:
- print(f"WARNING: Sequence length mismatch! Expected {expected_seq_len}, got {actual_seq_len}")
- if actual_hidden_dim != expected_hidden_dim:
- print(f"WARNING: Hidden dimension mismatch! Expected {expected_hidden_dim}, got {actual_hidden_dim}")
- else:
- print(f"WARNING: Unexpected embedding shape: {self.lang_embeddings.shape}")
-
- def run(self):
- print("LERobot RDT Server started, waiting for messages...")
- try:
- while True:
- print("Waiting for RDT data...")
- rdt_data = self.server.receive()
- print(f"Received RDT data, message_id: {rdt_data['message_id']}")
-
- # Perform inference
- # Ensure language embeddings have correct shape
- if len(self.lang_embeddings.shape) == 2:
- # [seq_len, hidden_dim] -> [1, seq_len, hidden_dim]
- text_embeds = self.lang_embeddings.unsqueeze(0)
- else:
- # Already [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_dim]
- text_embeds = self.lang_embeddings
-
- action = self.policy.step(
- proprio=rdt_data["proprio"],
- images=rdt_data["images"],
- text_embeds=text_embeds,
- )
-
- # Prepare response - use 'actions' key to match client expectation
- message_id = rdt_data["message_id"]
- action_data = {
- "message_id": message_id,
- "actions": action, # Changed from 'action' to 'actions'
- }
-
- # Send response
- print(f"send action data, action_data: {action_data}")
- self.server.send(action_data)
- print(f"Sent action data for message_id: {message_id}")
-
- except KeyboardInterrupt:
- print("\nServer stopped by user")
- self.server.close()
- except Exception as e:
- print(f"Error in server loop: {e}")
- self.server.close()
- raise
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- path_to_rdt_model_wights = "/home/qi.xiong/DualArm/RoboTwin/policy/RDT/checkpoints/RDT_LeRobot/checkpoint-7500/pytorch_model/mp_rank_00_model_states.pt"
- path_to_vision_encoder_model = "/home/qi.xiong/DualArm/RoboTwin/policy/weights/RDT/siglip-so400m-patch14-384"
- lang_model = "/home/qi.xiong/DualArm/RoboTwin/policy/RDT/scripts/lerobot_rdt_data/greenmarker_scene1/episode_4/instructions/lang_embed_0.pt"
- with open("/home/qi.xiong/DualArm/RoboTwin/policy/RDT/configs/base.yaml", "r") as fp:
- config = yaml.safe_load(fp)
- rdt_server = LERobotRDTServer(path_to_vision_encoder_model, path_to_rdt_model_wights, config, lang_model)
- rdt_server.run()
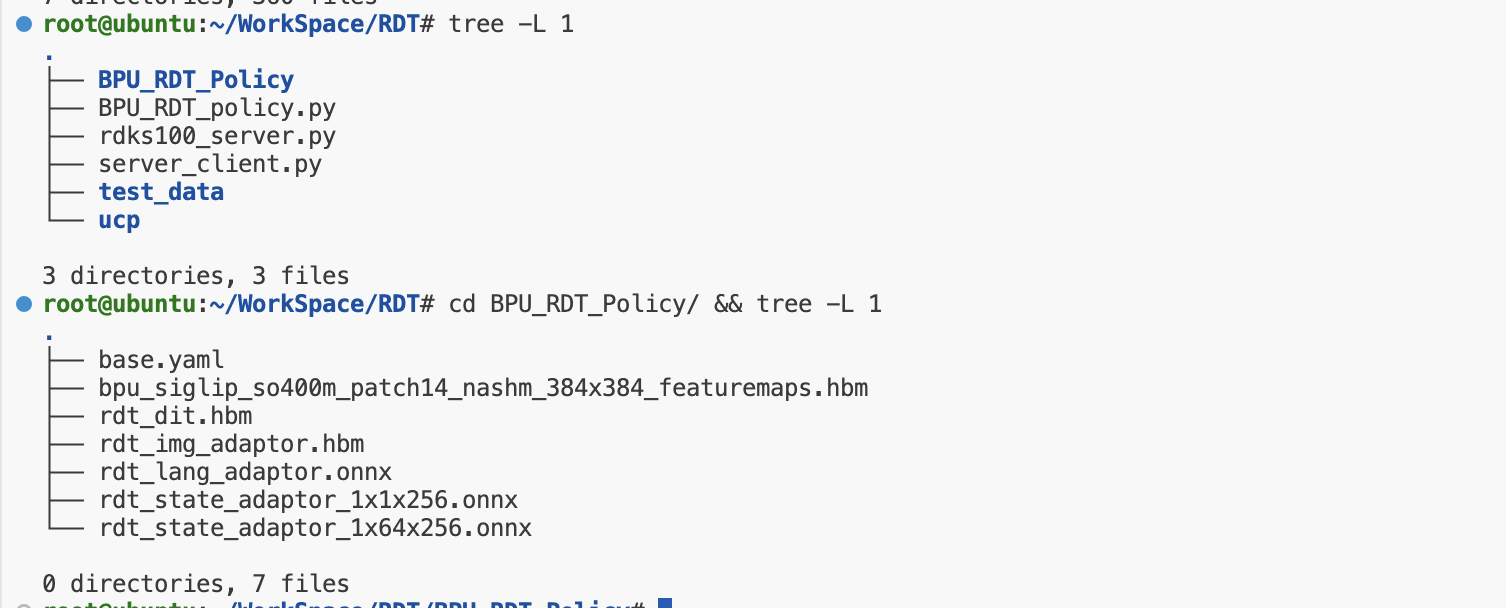
接着我们直接运行以下命令即可首先使用校准测试数据验证模型推理是否成功,若无报错即证明模型可正常推理无异常,若运行过程中缺少某个依赖,直接安装即可:- import logging
- import time
- from dataclasses import asdict, dataclass
- from pathlib import Path
- from pprint import pformat
- from collections import deque
- import torch
- from PIL import Image
- import numpy as np
- from lerobot.cameras import ( # noqa: F401
- CameraConfig, # noqa: F401
- )
- from lerobot.cameras.opencv.configuration_opencv import OpenCVCameraConfig # noqa: F401
- from lerobot.configs import parser
- from lerobot.configs.policies import PreTrainedConfig
- from lerobot.datasets.image_writer import safe_stop_image_writer
- from lerobot.datasets.lerobot_dataset import LeRobotDataset
- from lerobot.datasets.utils import build_dataset_frame, hw_to_dataset_features
- from lerobot.datasets.video_utils import VideoEncodingManager
- from lerobot.policies.factory import make_policy
- from lerobot.policies.pretrained import PreTrainedPolicy
- from lerobot.robots import ( # noqa: F401
- Robot,
- RobotConfig,
- bi_so100_follower,
- hope_jr,
- koch_follower,
- make_robot_from_config,
- so100_follower,
- so101_follower,
- )
- from lerobot.robots.so101_follower.so101_follower import SO101Follower
- from lerobot.robots.so101_follower.config_so101_follower import SO101FollowerConfig
- from lerobot.teleoperators import ( # noqa: F401
- Teleoperator,
- TeleoperatorConfig,
- bi_so100_leader,
- homunculus,
- koch_leader,
- make_teleoperator_from_config,
- so100_leader,
- so101_leader,
- )
- from lerobot.teleoperators.keyboard.teleop_keyboard import KeyboardTeleop
- from lerobot.utils.control_utils import (
- init_keyboard_listener,
- is_headless,
- predict_action,
- sanity_check_dataset_name,
- sanity_check_dataset_robot_compatibility,
- )
- from lerobot.utils.robot_utils import busy_wait
- from lerobot.utils.visualization_utils import _init_rerun, log_rerun_data
- from server_client import *
- debug_save_img = True
- _action_queue = deque([], maxlen=64)
- _message_id = 0
- _last_cam_high = None
- _last_cam_right_wrist = None
- @safe_stop_image_writer
- def record_loop(
- robot: Robot,
- client: Client,
- ):
- global _action_queue, _message_id, _last_cam_high, _last_cam_right_wrist
- observation = robot.get_observation()
- cam_high = observation['high']
- cam_right_wrist = observation['arm']
- image_arrs = [
- _last_cam_high,
- _last_cam_right_wrist,
- None,
- cam_high,
- cam_right_wrist,
- None
- ]
- images = [arr if arr is not None else None
- for arr in image_arrs]
- joint_positions = [observation[key] for key in observation.keys() if key.endswith('.pos')]
- proprio = torch.tensor(joint_positions, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0)
- ###################Debug图像########################
- if debug_save_img:
- imgs_to_show = [cam_high, cam_right_wrist, _last_cam_high, _last_cam_right_wrist]
- if all(img is not None for img in imgs_to_show):
- pil_imgs = []
- for img in imgs_to_show:
- if img.dtype != np.uint8:
- img = np.clip(img, 0, 1)
- img = (img * 255).astype(np.uint8)
- if img.ndim == 2:
- img = np.stack([img]*3, axis=-1)
- elif img.shape[-1] == 1:
- img = np.repeat(img, 3, axis=-1)
- pil_imgs.append(Image.fromarray(img))
- w, h = pil_imgs[0].size
- for i in range(4):
- if pil_imgs[i].size != (w, h):
- pil_imgs[i] = pil_imgs[i].resize((w, h))
- new_img = Image.new('RGB', (w*2, h*2))
- new_img.paste(pil_imgs[0], (0, 0)) # 左上:新high
- new_img.paste(pil_imgs[1], (w, 0)) # 右上:新wrist
- new_img.paste(pil_imgs[2], (0, h)) # 左下:老high
- new_img.paste(pil_imgs[3], (w, h)) # 右下:老wrist
- debug_save_path = "debug_2x2.png"
- new_img.save(debug_save_path)
- print(f"Have been saved at: {debug_save_path}")
- # new_img.show()
- ###################Debug图像########################
- rdt_data = {
- 'message_id': _message_id,
- 'proprio': proprio,
- 'images': images,
- 'text_embeds': ""
- }
- client.send(rdt_data)
- _message_id += 1
- print(f"send new rdt data done, message_id: {_message_id-1}")
- action_data = client.receive()
- if action_data is None:
- print("ERROR: Server returned None. Is the RDT server running?")
- print("Please start the RDT server first!")
- raise ConnectionError("Failed to receive response from RDT server")
- actions = action_data['actions']
- action_message_id = action_data["message_id"]
- print(f"receive actions done, message_id: {action_message_id}")
- # print(f"receive actions contents: {actions}")
- actions_array = np.array(actions)
- if len(actions_array.shape) == 3:
- action_sequence = actions_array[0, :, :] # 取第一个batch的所有时间步
- else:
- print(f"action shape should be 3 dim, but get {actions_array.shape} ")
-
- joint_names = ["shoulder_pan", "shoulder_lift", "elbow_flex", "wrist_flex", "wrist_roll", "gripper"]
- for step_idx in range(0, len(action_sequence), 4): # 64个动作隔4个执行一次动作
- action_values = action_sequence[step_idx]
- action_dict = {f"{joint}.pos": float(action_values[i]) for i, joint in enumerate(joint_names)}
- sent_action = robot.send_action(action_dict)
- time.sleep(0.1)
- _last_cam_high = cam_high
- _last_cam_right_wrist = cam_right_wrist
- def main():
- robot = SO101Follower(SO101FollowerConfig(
- port="/dev/tty.usbmodem5AB90671801",
- id="my_awesome_follower_arm",
- cameras={
- "arm": OpenCVCameraConfig(index_or_path=0, width=1920, height=1080, fps=30),
- "high": OpenCVCameraConfig(index_or_path=2, width=1920, height=1080, fps=30)
- }
- ))
-
- robot.connect()
- client = Client(host="localhost", port=5002)
- try:
- while True:
- record_loop(
- robot,
- client
- )
- time.sleep(0.1)
- except KeyboardInterrupt:
- pass
- robot.disconnect()
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- main()
- # 服务端
- python3 RDT/scripts/lerobot_rdt_server.py
- # 客户端
- python3 lerobot/src/lerobot/record_rdt.py
RDKS100可直接连接LeRobot控制机械臂,但由于写文档的时候手上没有多余的摄像头,头部的摄像头只能使用Apple的连续互通实现,若使用RDK直接连接LeRobot的话将无法当问头部摄像头,因此只能绕个弯用本地Mac来控制机械臂了...
来源:程序园用户自行投稿发布,如果侵权,请联系站长删除
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作! |