一、基础介绍:
具体可分为2个角色:
Prototype(原型类):声明一个Clone自身的接口;
ConcretePrototype(具体原型类):,实现一个Clone自身的操作。
在原型模式中,Prototype通常提供一个包含Clone方法的接口,具体的原型ConcretePrototype使用Clone方法完成对象的创建。
本质:通过拷贝这些原型对象创建新的对象。
根据其本质可以理解,原型本身就是通过一个自身的Clone方法来进行自我复制,从而产生新的对象。
比如,孙猴子吹猴毛变化多个克隆体时,就是用了原型模式,通过对自身的自我复制从而生产出N个分身。
所以从本质出发,想要实现这个功能,可以引出两个概念:其一就是浅层复制,再则就是深层复制。
浅层复制:通过this.MemberWiseClone(),对实例的值类型进行拷贝(包含string类型),对引用类型只拷贝了引用。浅拷贝只对值类型成员进行复制,对于引用类型,只是复制了其引用,并不复制其对象。
深层复制:需要通过反射和序列化来实现。
二、应用场景:
对象在创建(new)时,消耗资源过多或繁琐耗时。
本质就是在对象的构造函数中有耗时长或者占用系统资源多的情况,
使用原型模式进行复制对象时,可以省去这些耗时耗力的操作,直接获得对象的具体实例。
最常见的使用场景之一就是对象历史节点的保存,比如在对对象进行操作一次后,进行一次复制保存当前状态(恢复到某一历史状态),可实现撤销操作。
三、创建方式:
- 原型类----用来规范具体原型
- 1 /// <summary>
- 2 /// 原型类
- 3 /// </summary>
- 4 public abstract class Prototype
- 5 {
- 6 /// <summary>
- 7 /// 值类型
- 8 /// </summary>
- 9 public int Id { get; set; }
- 10
- 11 /// <summary>
- 12 /// 字符串
- 13 /// </summary>
- 14 public string strMessage { get; set; }
- 15
- 16 /// <summary>
- 17 /// 引用类型
- 18 /// </summary>
- 19 public Dictionary<int, string> keyValuePairs = new Dictionary<int, string>() { };
- 20
- 21 /// <summary>
- 22 /// 构造函数
- 23 /// </summary>
- 24 /// <param name="id"></param>
- 25 public Prototype(int id)
- 26 {
- 27 this.Id = id;
- 28 }
- 29
- 30 /// <summary>
- 31 /// 复制函数
- 32 /// </summary>
- 33 /// <returns></returns>
- 34 public abstract Prototype Clone();
- 35 }
- 具体原型类
- 1 /// <summary>
- 2 /// 创建具体原型
- 3 /// </summary>
- 4 public class ConcretePrototype : Prototype
- 5 {
- 6 public ConcretePrototype(int id)
- 7 : base(id)
- 8 { }
- 9
- 10 /// <summary>
- 11 /// 浅拷贝
- 12 /// </summary>
- 13 /// <returns></returns>
- 14 public override Prototype Clone()
- 15 {
- 16 // 调用MemberwiseClone方法实现的是浅拷贝,另外还有深拷贝
- 17 return (Prototype)this.MemberwiseClone();
- 18 }
- 19 }
- 客户端调用
- 1 class Program
- 2 {
- 3 static void Main(string[] args)
- 4 {
- 5 ConcretePrototype concretePrototype = new ConcretePrototype(1);
- 6 concretePrototype.strMessage = "AAAAAAAAA";
- 7 concretePrototype.keyValuePairs.Add(1, "A");
- 8 concretePrototype.keyValuePairs.Add(2, "B");
- 9 Console.WriteLine("id:{0}", concretePrototype.Id);
- 10 Console.WriteLine("strMessage:{0}", concretePrototype.strMessage);
- 11 Console.WriteLine("keyValuePairs:");
- 12 foreach (KeyValuePair<int,string> item in concretePrototype.keyValuePairs)
- 13 {
- 14 Console.WriteLine("KEY:{0} Value:{1}", item.Key, item.Value);
- 15 }
- 16
- 17 Console.WriteLine("\r\n");
- 18
- 19 ConcretePrototype concretePrototype2 = (ConcretePrototype)concretePrototype.Clone();
- 20 concretePrototype2.strMessage = "BBBBBBBBB";
- 21 concretePrototype2.keyValuePairs[1] = "A1";
- 22 Console.WriteLine("id:{0}", concretePrototype2.Id);
- 23 Console.WriteLine("strMessage:{0}", concretePrototype2.strMessage);
- 24 Console.WriteLine("keyValuePairs:");
- 25 foreach (KeyValuePair<int, string> item in concretePrototype2.keyValuePairs)
- 26 {
- 27 Console.WriteLine("KEY:{0} Value:{1}", item.Key, item.Value);
- 28 }
- 29
- 30 Console.WriteLine("\r\n");
- 31
- 32 Console.WriteLine("id:{0}", concretePrototype.Id);
- 33 Console.WriteLine("strMessage:{0}", concretePrototype.strMessage);
- 34 Console.WriteLine("keyValuePairs:");
- 35 foreach (KeyValuePair<int, string> item in concretePrototype.keyValuePairs)
- 36 {
- 37 Console.WriteLine("KEY:{0} Value:{1}", item.Key, item.Value);
- 38 }
- 39 Console.ReadKey();
- 40 }
- 41 }
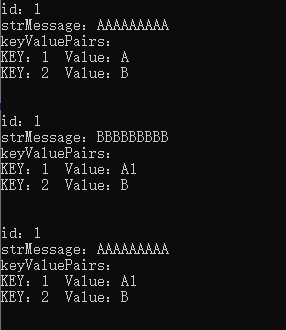
上述代码中,首先创建了一个concretePrototype原型对象,然后给字符串类型的strMessage赋值“AAAAAAAAA”。 然后给引用类型的keyValuePairs字典添加key=1和key=2,值分别是A和B。
通过Clone()方法进行原型对象的复制操作,生成新对象concretePrototype2。
修改新对象中的strMessage属性和keyValuePairs字典中key=1的值为“A1”。
通过打印出的内容可以看出新对象中的strMessage值修改并不会影响原型对象中的内容,而引用类型keyValuePairs则发生了改变。
通过这个实例可以看出浅复制,对值类型进行全盘拷贝,对引用类型只拷贝了引用地址。
- 修改上述实例,将浅复制改为深复制
- 1 /// <summary>
- 2 /// 原型类
- 3 /// </summary>
- 4 [Serializable]
- 5 public abstract class Prototype
- 6 {
- 7 ......
- 8 }
- 9
- 10 /// <summary>
- 11 /// 创建具体原型
- 12 /// 如果是要通过序列化来进行深拷贝的话,要打上Serializable标签
- 13 /// </summary>
- 14 [Serializable]
- 15 public class ConcretePrototype : Prototype
- 16 {
- 17 public ConcretePrototype(int id)
- 18 : base(id)
- 19 { }
- 20
- 21 /// <summary>
- 22 /// 深拷贝
- 23 /// </summary>
- 24 /// <returns>返回一个全新的Person对象</returns>
- 25 public override Prototype Clone()
- 26 {
- 27 //创建一个内存流
- 28 MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream();
- 29 //创建一个二进制序列化对象
- 30 BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();
- 31 //将当前对象序列化写入ms内存流中
- 32 bf.Serialize(ms, this);
- 33 //设置流读取的位置
- 34 ms.Position = 0;
- 35 //将流反序列化为Object对象
- 36 return bf.Deserialize(ms) as Prototype;
- 37 }
- 38 }
运行后可以看出,深复制后引用类型也会生成一个新的地址。
四、总结:
原型模式就是对对象进行复制操作,而避免重复进行初始化操作,生产多个克隆对象。
来源:程序园用户自行投稿发布,如果侵权,请联系站长删除
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作! |