前言
对于Java开发来说,天天都在用SpringBoot,每次启动都执行了main方法,该方法应该是最容易让人忽视的地方之一,不过几行代码,为什么执行完后JVM不结束呢?
本文以内嵌tomcat为例进行说明,并分享一些debug和画图的技巧。
原因
先说结论,是因为main方法启动了一个线程,这个线程是非daemon的,并且run方法执行的任务是TomcatWebServer.this.tomcat.getServer().await();(死循环),即非daemon线程+任务不停止=程序不退出。
debug源码
技巧
在debug时,有的源码是抽象方法,我们可以用快捷键F7跳转到具体正在执行的实现类方法,另外Alt+F9可以强制到达光标的位置。
流程
下面将debug对应的源码,有兴趣的朋友可以跟着动手试试。
SpringBoot启动入口,调用静态run方法。- /** 一般demo
- * @date 2021/9/12 9:09
- * @author www.cnblogs.com/theRhyme
- */
- @SpringBootApplication
- public class CommonDemoApplication {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- SpringApplication.run(CommonDemoApplication.class, args);
- }
- }
- public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
- return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
- }
- public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
- return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
- }
- public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
- StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
- stopWatch.start();
- DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
- ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
- configureHeadlessProperty();
- SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
- listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
- try {
- ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
- ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
- configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
- Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
- context = createApplicationContext();
- context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
- prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
- refreshContext(context);
- ……
- protected void refresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
- applicationContext.refresh();
- }
- @Override
- public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
- synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
- StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
- // Prepare this context for refreshing.
- prepareRefresh();
- // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
- ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
- // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
- prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
- try {
- // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
- postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
- StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
- // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
- invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
- // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
- registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
- beanPostProcess.end();
- // Initialize message source for this context.
- initMessageSource();
- // Initialize event multicaster for this context.
- initApplicationEventMulticaster();
- // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
- onRefresh();
- ……
- @Override
- protected void onRefresh() {
- super.onRefresh();
- try {
- createWebServer();
- }
- catch (Throwable ex) {
- throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
- }
- }
- @Override
- public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
- if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
- Registry.disableRegistry();
- }
- Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
- File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
- tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
- Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
- connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
- tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
- customizeConnector(connector);
- tomcat.setConnector(connector);
- tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
- configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
- for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
- tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
- }
- prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
- return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
- }
- protected TomcatWebServer getTomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat) {
- return new TomcatWebServer(tomcat, getPort() >= 0, getShutdown());
- }
- public TomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat, boolean autoStart, Shutdown shutdown) {
- Assert.notNull(tomcat, "Tomcat Server must not be null");
- this.tomcat = tomcat;
- this.autoStart = autoStart;
- this.gracefulShutdown = (shutdown == Shutdown.GRACEFUL) ? new GracefulShutdown(tomcat) : null;
- initialize();
- }
- private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
- logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
- synchronized (this.monitor) {
- try {
- addInstanceIdToEngineName();
- Context context = findContext();
- context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> {
- if (context.equals(event.getSource()) && Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
- // Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't
- // happen when the service is started.
- removeServiceConnectors();
- }
- });
- // Start the server to trigger initialization listeners
- this.tomcat.start();
- // We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread
- rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
- try {
- ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), getClass().getClassLoader());
- }
- catch (NamingException ex) {
- // Naming is not enabled. Continue
- }
- // Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a
- // blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown
- startDaemonAwaitThread();
- }
- catch (Exception ex) {
- stopSilently();
- destroySilently();
- throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex);
- }
- }
- }
- private void startDaemonAwaitThread() {
- Thread awaitThread = new Thread("container-" + (containerCounter.get())) {
- @Override
- public void run() {
- TomcatWebServer.this.tomcat.getServer().await();
- }
- };
- awaitThread.setContextClassLoader(getClass().getClassLoader());
- awaitThread.setDaemon(false);
- awaitThread.start();
- }
https://www.cnblogs.com/theRhyme/p/-/springboot-not-stop-after-main
await方法
这里单独看一下TomcatWebServer.this.tomcat.getServer().await();。
该方法的Java doc:
- /**
- * Wait until a proper shutdown command is received, then return.
- * This keeps the main thread alive - the thread pool listening for http
- * connections is daemon threads.
- */
指的是通过等候关闭命令这个动作来保持main线程存活,而HTTP线程作为daemon线程会在main线程结束时终止。
任务一直运行的原因:源码如下,debug会进入getPortWithOffset()的值是-1的分支(注意这里不是server.port端口号),然后会不断循环Thread.sleep( 10000 )直到发出关机指令修改stopAwait的值为true。- @Override
- public void await() {
- // Negative values - don't wait on port - tomcat is embedded or we just don't like ports
- if (getPortWithOffset() == -2) {
- // undocumented yet - for embedding apps that are around, alive.
- return;
- }
- if (getPortWithOffset() == -1) {
- try {
- awaitThread = Thread.currentThread();
- while(!stopAwait) {
- try {
- Thread.sleep( 10000 );
- } catch( InterruptedException ex ) {
- // continue and check the flag
- }
- }
- } finally {
- awaitThread = null;
- }
- return;
- }
- ……
- public void stopAwait() {
- stopAwait=true;
- Thread t = awaitThread;
- if (t != null) {
- ServerSocket s = awaitSocket;
- if (s != null) {
- awaitSocket = null;
- try {
- s.close();
- } catch (IOException e) {
- // Ignored
- }
- }
- t.interrupt();
- try {
- t.join(1000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- // Ignored
- }
- }
- }
非daemon线程的意义
setDaemon介绍
上面将线程设置为非daemon线程:awaitThread.setDaemon(false)。
java.lang.Thread#setDaemon源码如下:- /**
- * Marks this thread as either a {@linkplain #isDaemon daemon} thread
- * or a user thread. The Java Virtual Machine exits when the only
- * threads running are all daemon threads.
- *
- * <p> This method must be invoked before the thread is started.
- *
- * @param on
- * if {@code true}, marks this thread as a daemon thread
- *
- * @throws IllegalThreadStateException
- * if this thread is {@linkplain #isAlive alive}
- *
- * @throws SecurityException
- * if {@link #checkAccess} determines that the current
- * thread cannot modify this thread
- */
- public final void setDaemon(boolean on) {
- checkAccess();
- if (isAlive()) {
- throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
- }
- daemon = on;
- }
所以非daemon线程存活,JVM是不会退出的。
例子
如下代码,我们在main方法中启动了一个非daemon线程,并且调用了阻塞方法java.io.InputStream#read()。- // https://www.cnblogs.com/theRhyme/p/-/springboot-not-stop-after-main
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": start");
- Thread awaitThread =
- new Thread("non-daemon") {
- @Override
- public void run() {
- try {
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": start");
- System.in.read();
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": end");
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- };
- awaitThread.setDaemon(false);
- awaitThread.start();
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": end");
- }
- main: start
- main: end
- non-daemon: start
-1的原因
上面留了个问题,为什么getPortWithOffset()的返回值是-1。
如下getPort()的值为-1,此时相当于直接调用了getPort()方法。- https://www.cnblogs.com/theRhyme/p/-/springboot-not-stop-after-main
- @Override
- public int getPortWithOffset() {
- // Non-positive port values have special meanings and the offset should
- // not apply.
- int port = getPort();
- if (port > 0) {
- return port + getPortOffset();
- } else {
- return port;
- }
- }
- @Override
- public int getPort() {
- return this.port;
- }
- /**
- * The port number on which we wait for shutdown commands.
- */
- private int port = 8005;
port属性提供的修改方式是setPort(),而使用Alt+F7找到在getServer中被修改为-1。
在server.setPort( -1 );打一个断点,重新debug,可以知道具体修改的时机。
之前我们debug过方法createWebServer,是具体创建webServer的步骤,但是我们这里要进入getWebServer。- private void createWebServer() {
- WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
- ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
- if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
- StartupStep createWebServer = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.boot.webserver.create");
- ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
- createWebServer.tag("factory", factory.getClass().toString());
- this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
- ……
- public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
- if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
- Registry.disableRegistry();
- }
- Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
- File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
- tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
- Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
- connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
- tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
- customizeConnector(connector);
- tomcat.setConnector(connector);
- tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
- configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
- for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
- tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
- }
- prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
- return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
- }
- public Service getService() {
- return getServer().findServices()[0];
- }
- public Server getServer() {
- if (server != null) {
- return server;
- }
- System.setProperty("catalina.useNaming", "false");
- server = new StandardServer();
- initBaseDir();
- // Set configuration source
- ConfigFileLoader.setSource(new CatalinaBaseConfigurationSource(new File(basedir), null));
- // https://www.cnblogs.com/theRhyme/p/-/springboot-not-stop-after-main
- server.setPort( -1 );
- Service service = new StandardService();
- service.setName("Tomcat");
- server.addService(service);
- return server;
- }
技巧
如果我们想画一个方法本次被调用(线程内部)的流程图,那么我们可以debug进入该方法,Alt+F8执行如下代码,打印出方法调用栈对应的mermaid js 内容,然后使用文本绘图工具进行渲染。- // https://www.cnblogs.com/theRhyme
- StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace();
- List<String> methodChain = Arrays.stream(stackTrace)
- .filter(e -> !e.getClassName().startsWith("java.") && !e.getClassName().startsWith("jdk.") && !e.getMethodName().contains("<"))
- .map(e -> e.getClassName() + "." + e.getMethodName())
- .collect(Collectors.toList());
- StringBuilder mermaidCode = new StringBuilder("graph TD\n");
- for (int i = methodChain.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {
- mermaidCode.append(String.format(" %s --> %s\n",
- methodChain.get(i),
- methodChain.get(i-1)));
- }
- System.out.println(mermaidCode);
具体内容
如图,debug到org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer#startDaemonAwaitThread内部,执行上面的代码。
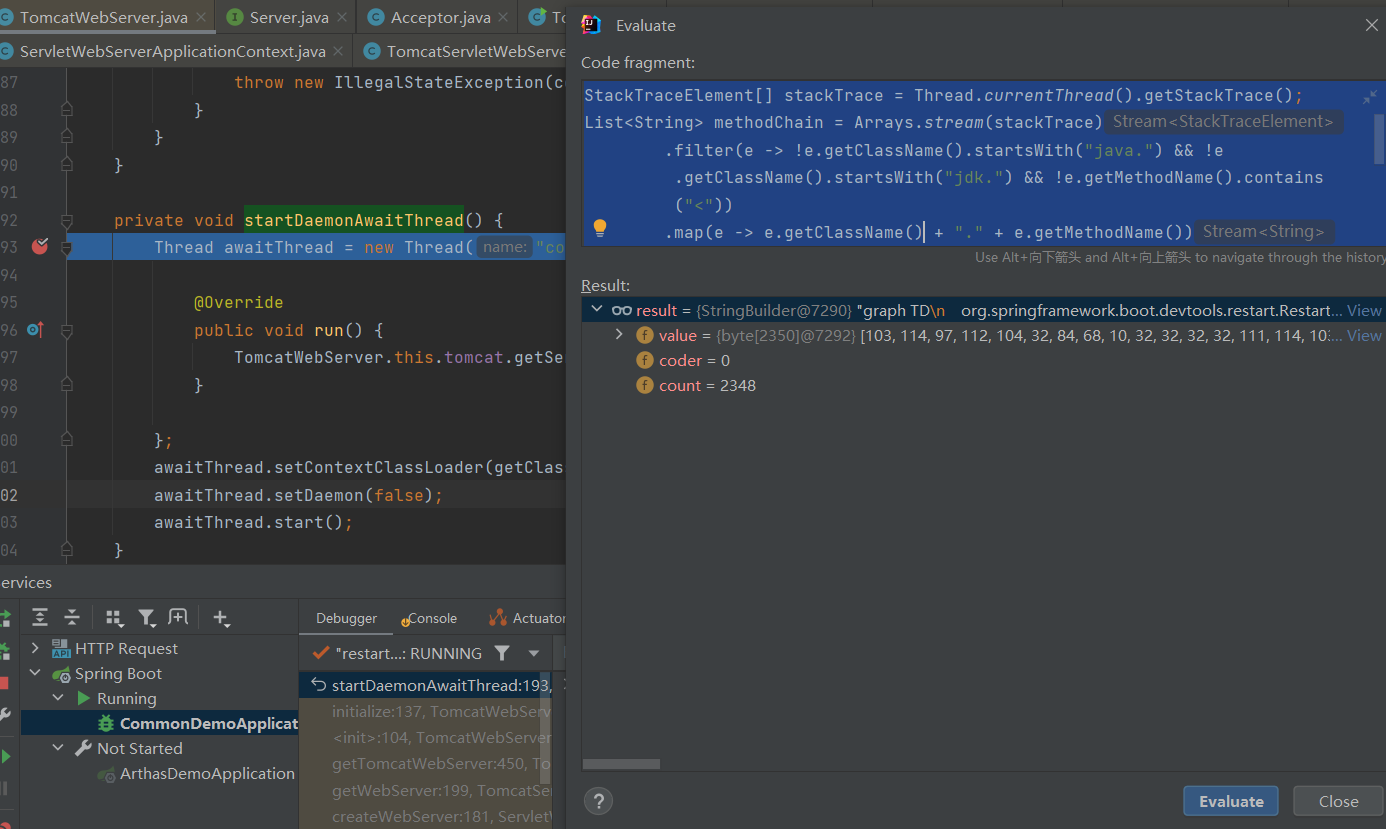
输出内容:- graph TD
- org.springframework.boot.devtools.restart.RestartLauncher.run --> cnblogscomtheRhyme.infrastructure.demos.common.CommonDemoApplication.main
- cnblogscomtheRhyme.infrastructure.demos.common.CommonDemoApplication.main --> org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run
- org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run --> org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run
- org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run --> org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run
- org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run --> org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refreshContext
- org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refreshContext --> org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh
- org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh --> org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh
- org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh --> org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.refresh
- org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.refresh --> org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh
- org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh --> org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.onRefresh
- org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.onRefresh --> org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.createWebServer
- org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerApplicationContext.createWebServer --> org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory.getWebServer
- org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory.getWebServer --> org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory.getTomcatWebServer
- org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory.getTomcatWebServer --> org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer.initialize
- org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer.initialize --> org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer.startDaemonAwaitThread
- org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer.startDaemonAwaitThread --> idea.debugger.rt.GeneratedEvaluationClass.invoke

出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/theRhyme/

来源:程序园用户自行投稿发布,如果侵权,请联系站长删除
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作! |